- Taxonomy is the science of describing, naming, and classifying organisms. It provides understanding of biodiversity which is important for conservation and sustainability.
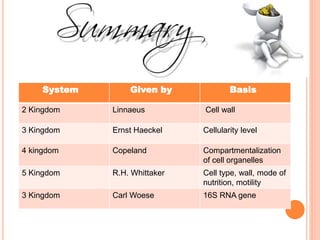
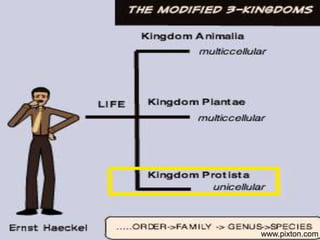
- Aristotle was the first to attempt classifying organisms by type and introduce binomial nomenclature. Later systems were proposed by Linnaeus, Whittaker, and Woese based on new understandings of cell structure, genetics, and evolution.
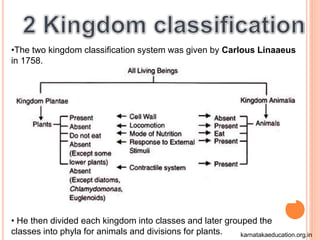
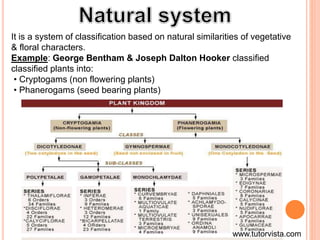
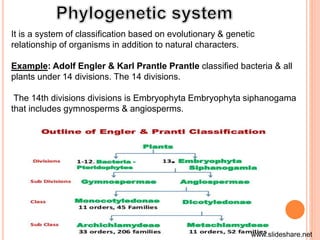
- Different classification systems include artificial, natural, phylogenetic, polyphasic, and numerical taxonomy which use varying characteristics and methodologies.








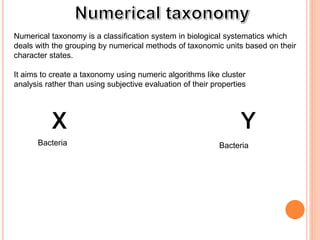
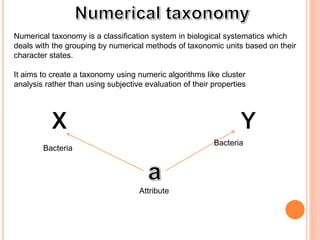
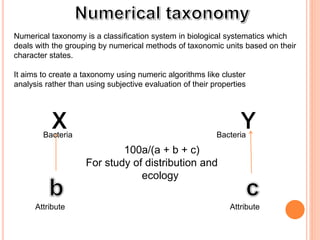
![Numerical taxonomy is a classification system in biological systematics which
deals with the grouping by numerical methods of taxonomic units based on their
character states.
It aims to create a taxonomy using numeric algorithms like cluster
analysis rather than using subjective evaluation of their properties
Attribute
Bacteria
Bacteria
100( a + d)]/( a + b + c + d)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sakshisaxenasbsp1-150410120855-conversion-gate01/85/Microbial-taxonomy-and-classification-system-23-320.jpg)