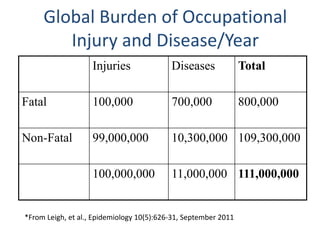
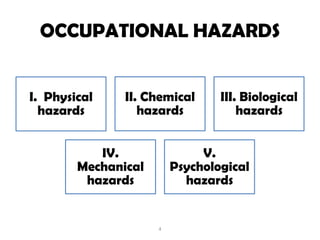
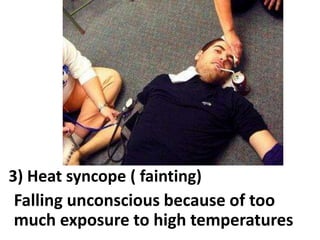
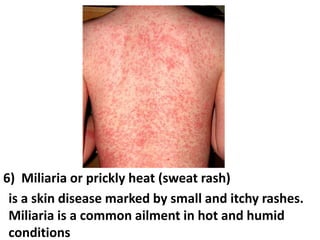
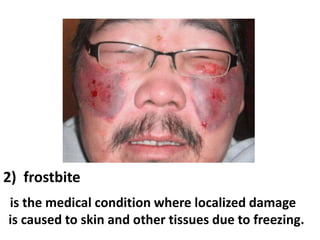
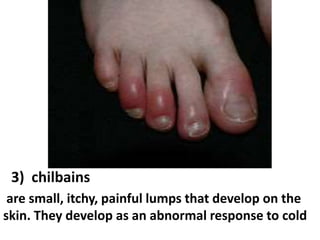
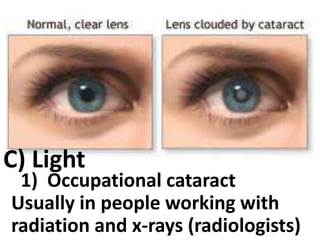
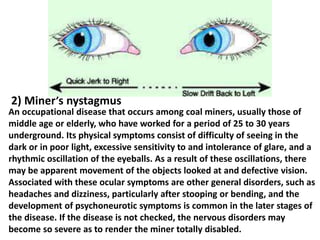
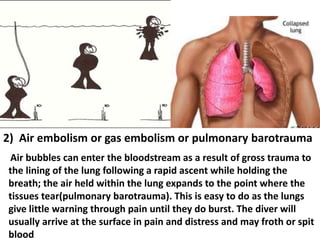
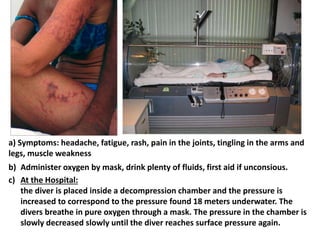
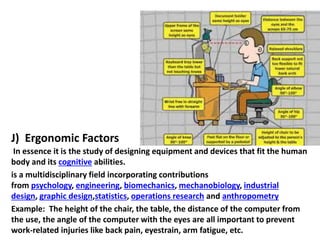
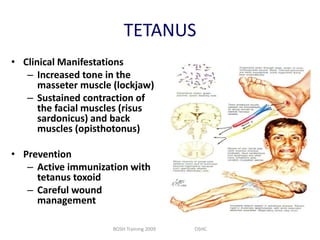
This document discusses occupational hazards and provides examples. It begins by explaining why occupational hazards need to be studied in order to make students aware of career dangers and risks. Statistics are then given on global work-related injuries and diseases each year. The document then outlines different types of physical, chemical, biological, mechanical, and psychological hazards. Specific occupational diseases and examples of workers at risk are given for each hazard type. Preventative measures are also described.