1) Cisco's supply chain collapsed in 2001 due to misaligned incentives that encouraged contractors to build excess inventory without concern for Cisco's real needs.
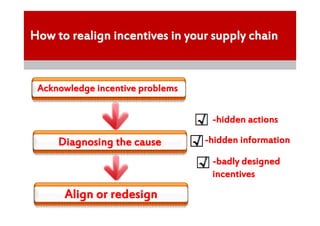
2) Most supply chains have misaligned incentives that cause problems like excess inventory, stock-outs, and poor customer service.
3) Well-designed incentives like 7-Eleven's that closely align partners' interests through penalties, profit sharing, and trust build efficient supply chains with low stock-outs.