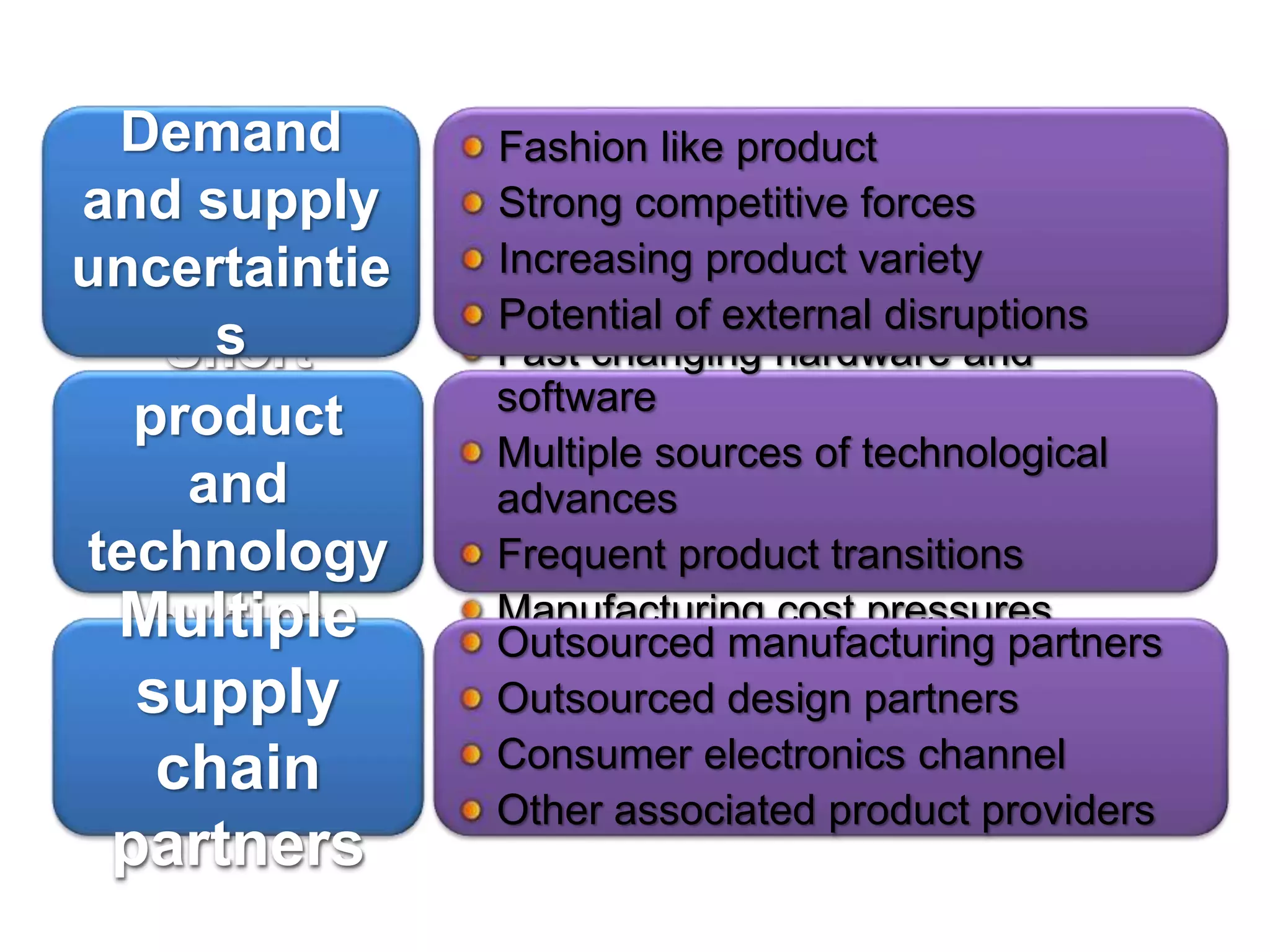
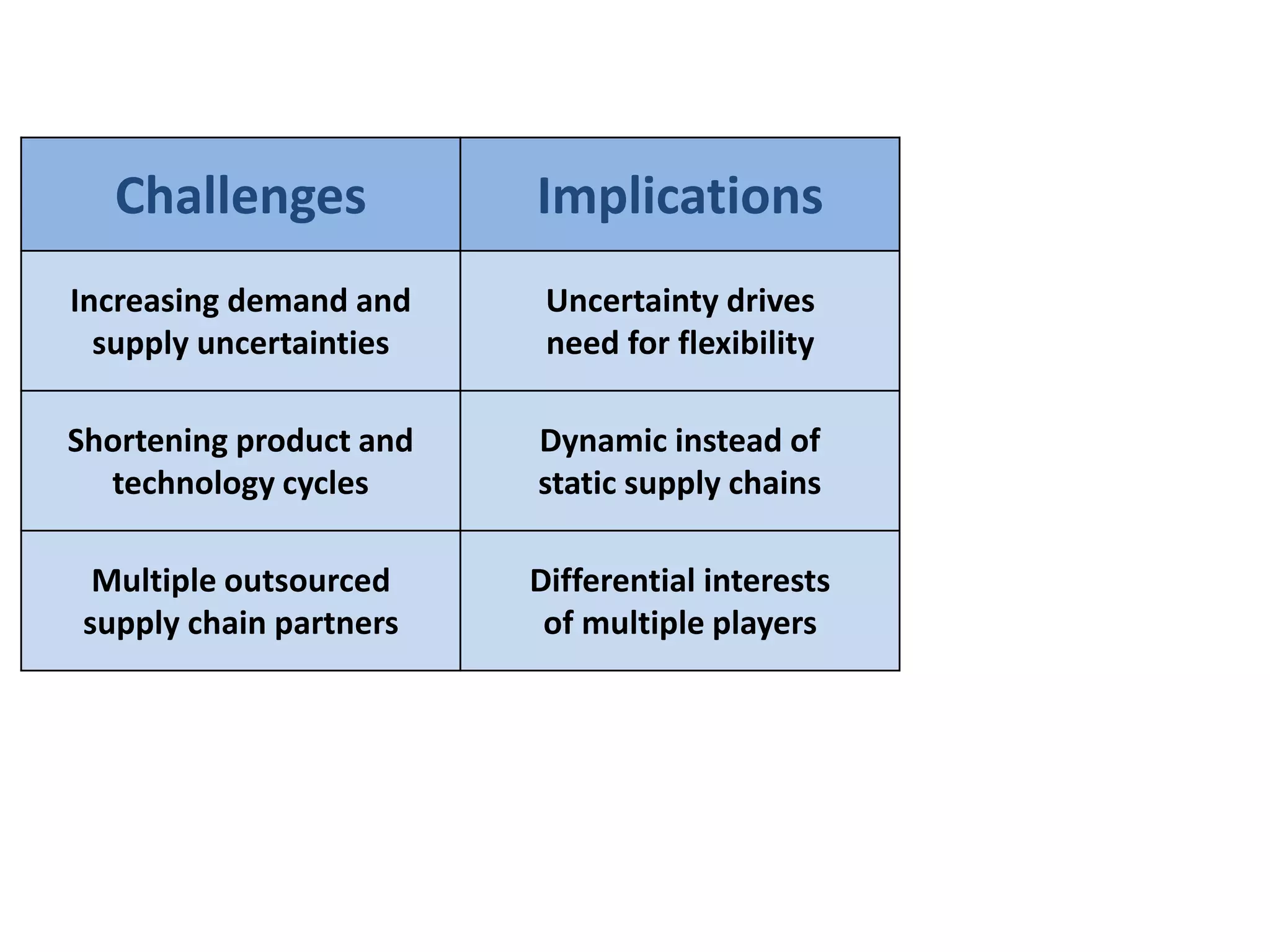
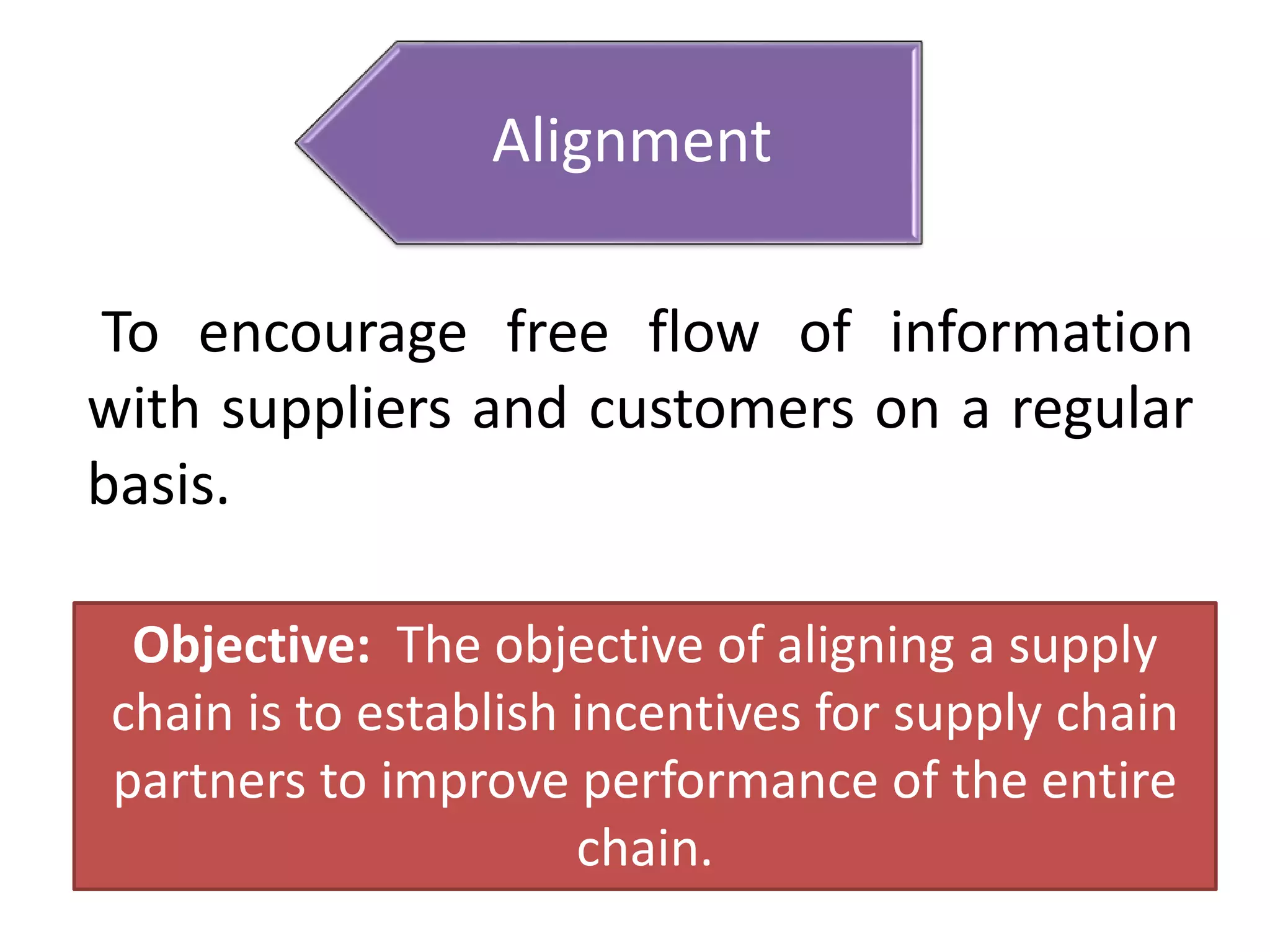
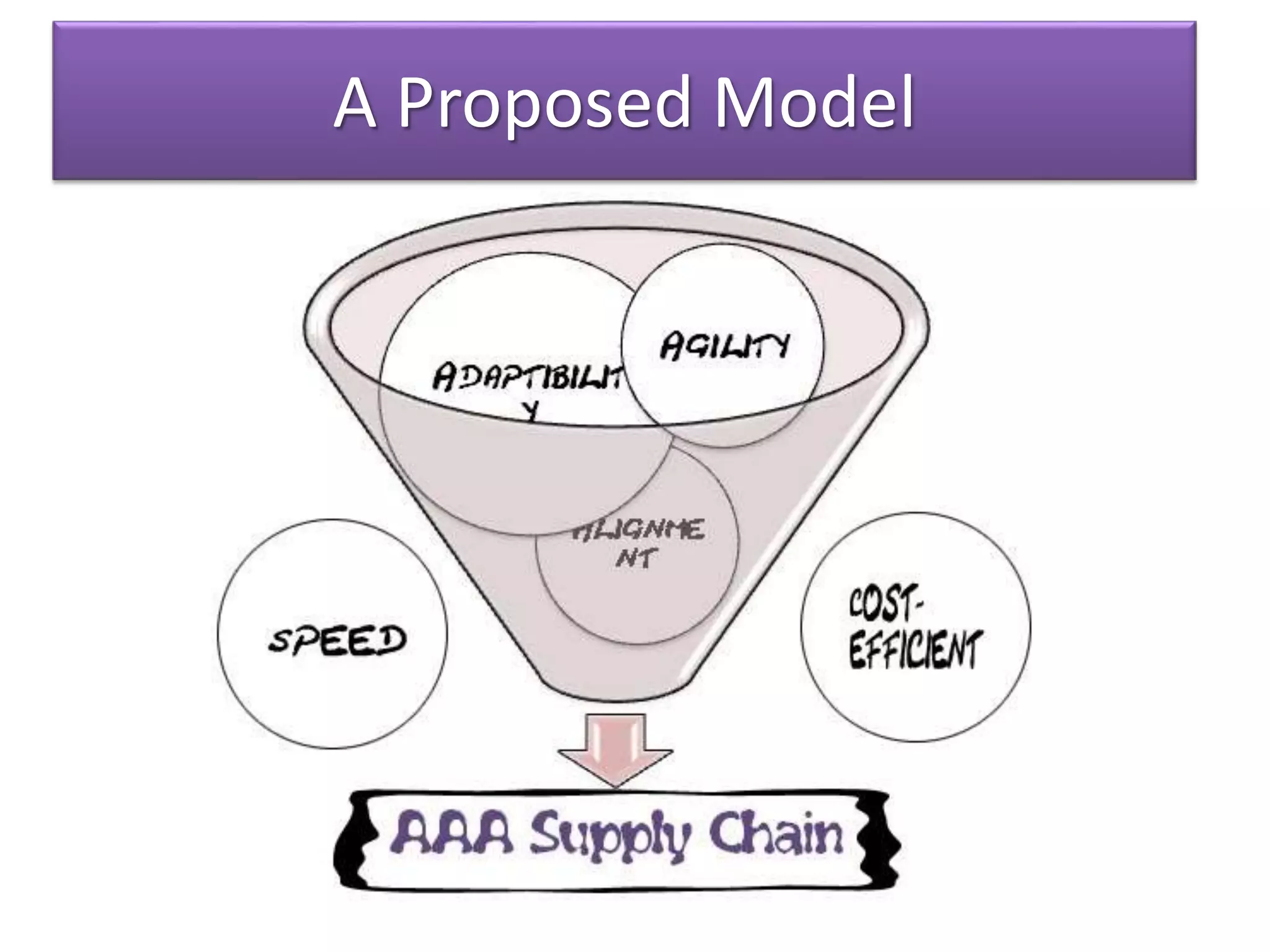
The document discusses the need for companies to develop agile, adaptable, and aligned ("Triple-A") supply chains. It defines each concept and provides examples. Agility allows companies to respond quickly to unexpected changes. Adaptability is the ability to adjust supply chain design over time as markets change. Alignment encourages information sharing between partners to improve overall chain performance. Developing a Triple-A supply chain requires new attitudes and cultures that prioritize responsiveness over efficiency and view responsibility as extending to the entire chain. Technology alone is not enough - managers must facilitate the necessary changes.