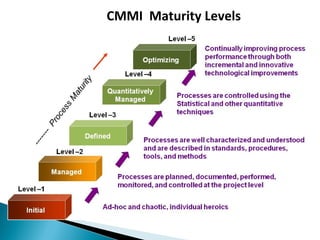
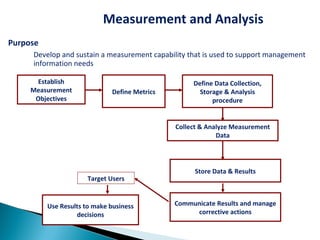
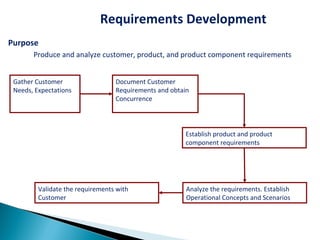
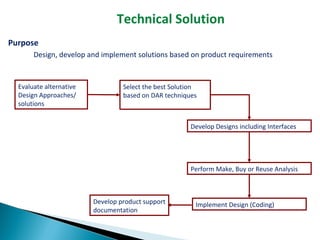
The CMMI framework helps organizations improve processes through process areas like requirements management, project planning, and project monitoring. It defines goals and practices for each process area. Implementing CMMI improves predictability, quality, productivity, and reduces costs and defects. It provides a common framework that organizations can use to assess their process maturity and identify improvement areas.