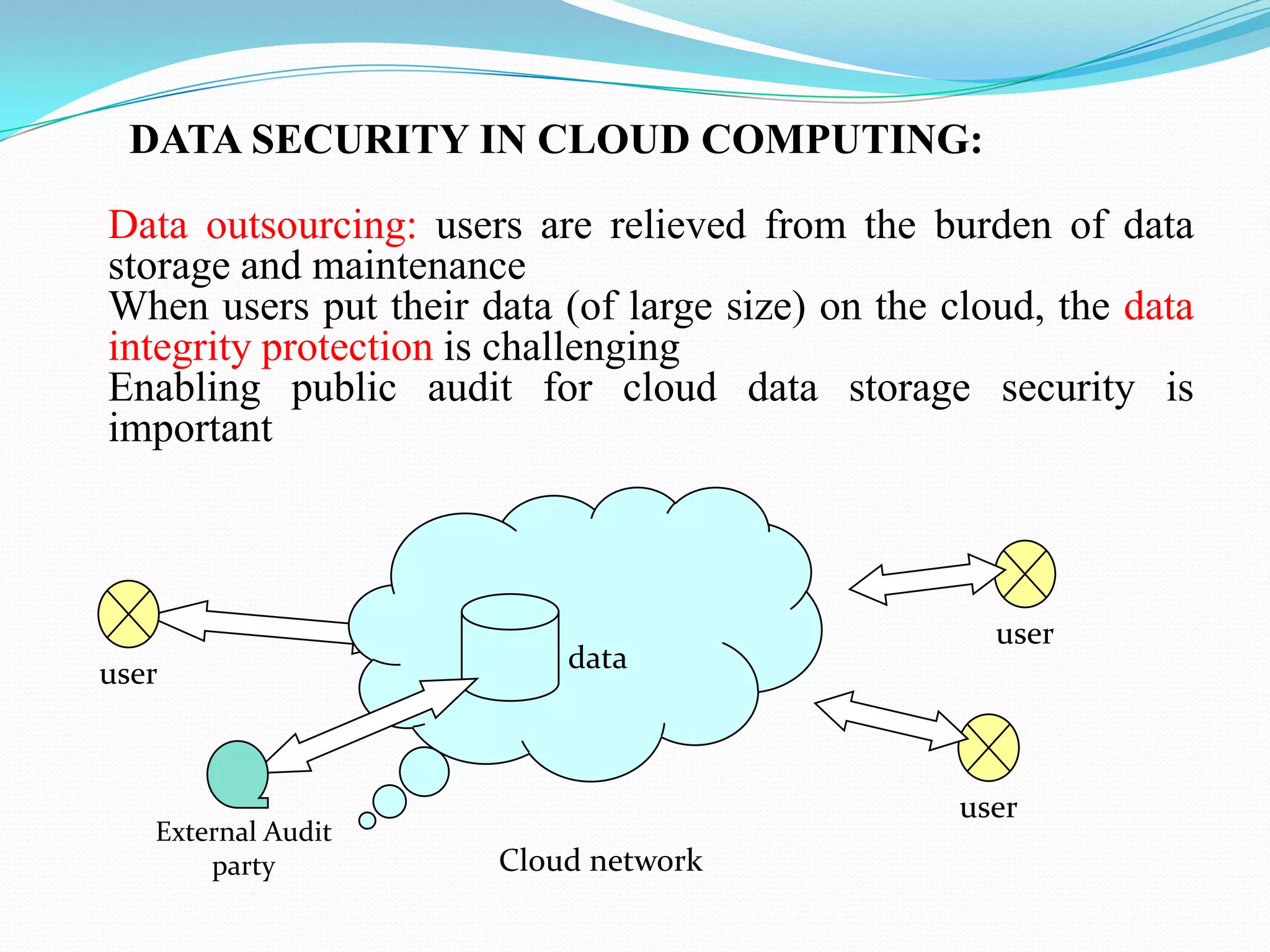
Cloud computing provides a way for organizations to share distributed resources over a network. However, data security is a major concern in cloud computing since data is stored remotely. The document discusses several techniques used for data security in cloud computing including authentication, encryption, data masking, and data traceability. The latest technologies discussed are a cloud information gateway that can control data transmission and secure logic migration that transfers applications to an internal sandbox for secure execution.