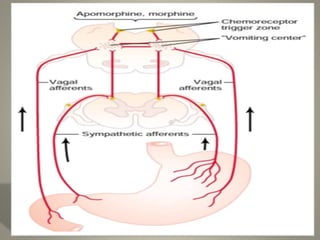
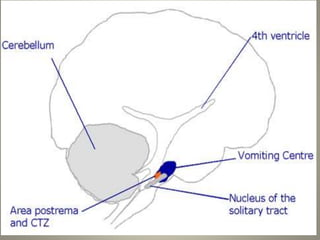
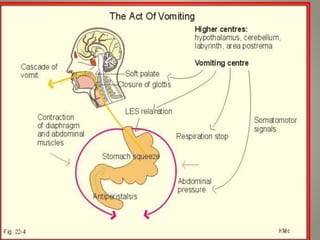
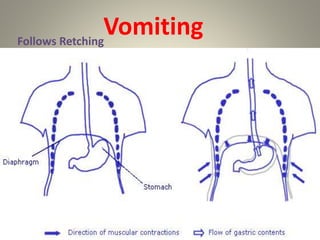
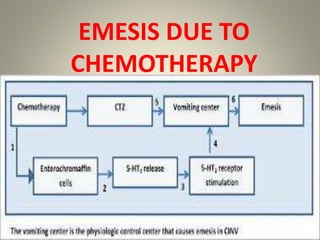
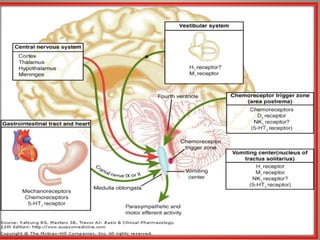
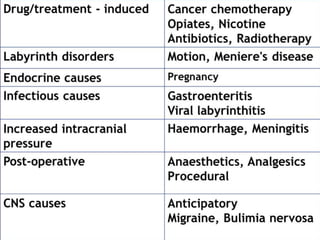
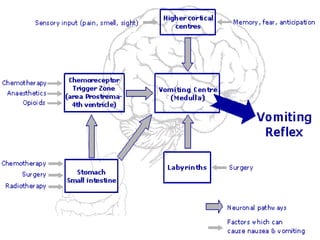
The vomiting reflex, or emetic reflex, involves three steps. First, nausea develops as a warning sensation. Then retching occurs through spasmodic contractions of the diaphragm and chest muscles combined with glottis closure. Finally, vomiting expels gastric contents through the mouth. The vomiting center located in the medulla receives input from the GI tract, chemoreceptor trigger zone, vestibular apparatus, and higher brain centers. It coordinates the motor responses through various cranial nerves that cause antiperistalsis and ejection of vomitus.