The document discusses various aspects of Distributed Configuration Management Systems (DCMS) and vulnerabilities associated with them, primarily focusing on Apache Zookeeper, HashiCorp Consul, and etcd. It outlines different types of DCMS, explains how remote code execution vulnerabilities can be exploited, and provides examples of attacks and countermeasures. Additionally, it touches on the importance of proper authentication and security measures in these systems, emphasizing the potential risks in misconfigured or unprotected DCMS.

















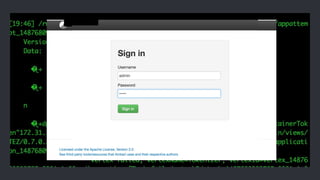
![Remote Code Execution - I
Final Payload
◦ consul exec -http-addr=remote_addr
[whoami/payload].
◦ If disable_remote_execution is enabled then we
are out of luck (which mostly never happens
though !!).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howwehackeddcms-170531082315/85/slide-19-320.jpg)

































![Inherent [In]security
◦ No Authentication by default.
◦ Authentication sucks if not implemented properly.
◦ HTTP Endpoints available at your disposal.
◦ RCE through un-authenticated instances when
exposed with a feature.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howwehackeddcms-170531082315/85/slide-53-320.jpg)