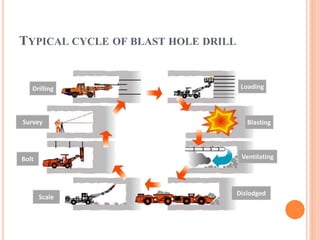
Blast hole drilling is a technique used in mining where holes are drilled into rock, packed with explosives, and detonated. The seminar discusses the blast hole drilling process, which involves drilling holes, loading explosives into the holes, detonating the explosives to blast the rock, ventilating smoke and fumes, removing blasted rock, and installing ground support. Different drill hole patterns, explosives, and the typical drilling and blasting cycle are also covered.