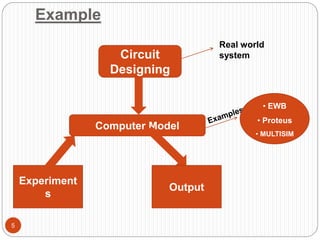
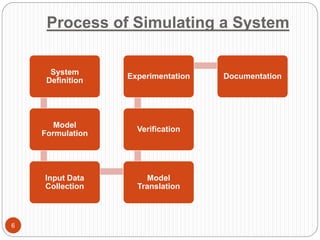
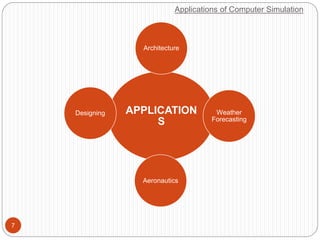
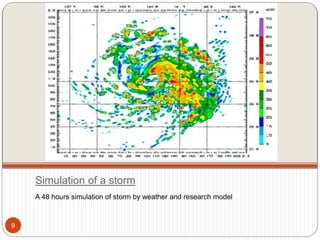
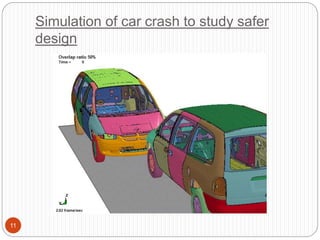
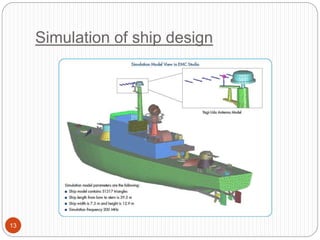
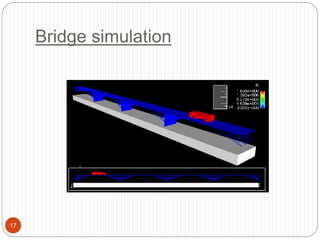
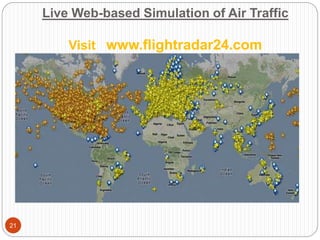
This document discusses computer simulation and modeling. It defines computer simulation as creating an imitation of a real-world system on a computer in order to experiment with and observe its behavior. The key steps in simulation are defining the system, formulating a model, collecting input data, translating the model, verifying results, and experimenting. Applications include weather forecasting, design of vehicles, architecture, and aeronautics. Computer simulation provides advantages like testing systems without building them physically and training for risky tasks virtually. Limitations are reliance on the model maker's skills and the time and costs involved.