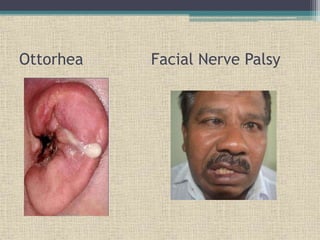
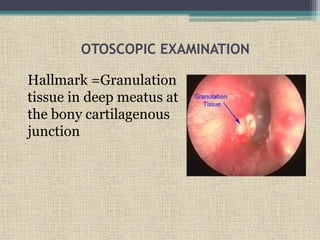
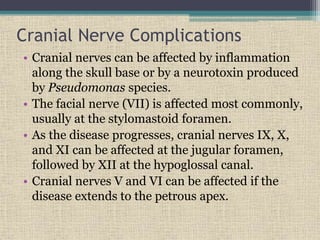
Malignant otitis externa is an aggressive infection of the external ear and skull base that predominantly affects older diabetics. It is caused most commonly by Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria. Clinical features include severe ear pain, discharge, hearing loss, and facial nerve palsy. Diagnosis involves culture of ear discharge, blood tests, imaging, and biopsy. Treatment requires long-term antibiotics, often fluoroquinolones, along with glucose control, ear cleaning, hyperbaric oxygen, and sometimes surgery. Cranial nerve palsies and intracranial complications can occur if the infection spreads.