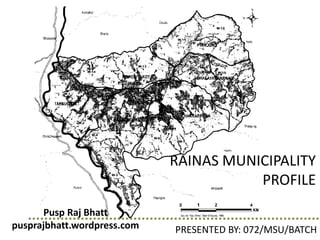
Rainas Municipality Profile Presented
- 1. RAINAS MUNICIPALITY PROFILE PRESENTED BY: 072/MSU/BATCH Pusp Raj Bhatt pusprajbhatt.wordpress.com
- 2. BACKGROUND • Nepal has gone through rapid urbanization in past decade • The GoN had declared 58 municipalities in 2053 B.S • In 2015, number increased to 217 Municipalities (in 3 phases) • Final phase: 26 new municipalities • Urban population increased from 17% to 42% • 3 Municipalities belonged to Lamjung : Karaputar Madhya Nepal Rainas
- 3. INDEX MAP
- 4. BACKGROUND • Rainas is among the youngest municipalities declared on 19 September 2015 • Vision: “Rainas Municipality: Agriculture, Tourism, Education and Environmentally friendly City” • Area: 73 sq. km. • Total population: 18,527 (CBS, 2011) • No. of Wards: 14 • Center of municipality: Former Tinpiple Bazaar
- 5. BACKGROUND Merging 6 VDCs: Tarkughat Dhamilikuwa Chakratirtha Bhalayakharka Pyarjung Mohoriyakot
- 6. POPULATION DENSITY Population Density: 254 person/sq. km. (CBS, 2011)
- 7. OBJECTIVES • Main objective: to prepare Municipal Profile of Rainas Municipality in order to use this profile for the formation of Local Area Plan in future as well • General objectives of the study of municipality profile is as follows: • To familiarize with the onsite current situation of the municipality • To prepare municipal profile which consists of whole spatial and non spatial data of the present day with analysis using statistical tools to give clear information for all stakeholders • To collect socio-economic, cultural and environmental data from the sample population through household survey • To gather relevant information about the study area through the study of secondary data and literature review
- 8. SCOPE & LIMITATIONS • Scope: • detail information • prioritized problems and opportunity related to physical, social, economic and environmental situation of Rainas • Limitation • Sample survey, 12% of total household due to limitation of time • data is collected by house to house data collection through primary survey • authenticity of the data depends very much on the facts provided by the public during the questionnaire • scope of the work is limited within the municipality only, will not incorporate the influences from the neighboring municipality
- 9. PARAMETERS OF SURVEY • General Information • Salient Feature of the Municipality • Demography • Municipality Office Information • Socio-Economic Indicators • Physical Infrastructures • Social and Cultural Institutions • Environmental Institutions • Health and Educational Institutions
- 10. METHODOLOGY
- 11. HISTORICAL BACKGROUND • In 15th Century: • YASHUBRAHMA SHAH King of LAMJUNG; • one of 22/24 States History: Play of TIME and POWER TWO PRINCES YASHUBRAHMA (King) + BASANTAWATI (Queen) Narahari Shah Drabya Shah Narahari Shah – Lamjung Drabya Shah – Gorkha after wining Ligligkot King Drabya Shah
- 12. HISTORICAL BACKGROUND History: STORY of THE RULERS • Mother Basantawati called upon the Son Narahari and Dyabya and flowed down her milk to Chepe River (at Chakratirtha) : CONFORMATION OF PEACE AND CONFLICT RESOLUTION Chepe River Gorkha Lamjung
- 13. HISTORICAL BACKGROUND History: Bhakti Thapa • “Bhakti Thapa was sleeping on a big serpent coiled up on the boulder raising its wide hood high above casting shed that protected the young Bhakti Thapa against the scorching heat of the midday sun. The serpent slowly uncoiled without waking up the boy and descended from the boulder. It disappeared from the sight after slipping into the bushes nearby….” Bhakti Thapa
- 14. HISTORICAL BACKGROUND History: Siddakothan Temple • Siddanath Baba (Hostory of Around 400 years back) Blessed Drabya Shah to expand the Reign in the East – In Gorkha Siddakothan Historical Temple
- 15. HISTORICAL BACKGROUND History: Rainaaskot Kalika Temple at Rainaskot Fort
- 16. LOCATION Geographic Location • Latitudes : 28°03'21.49"N and 28°10'15.51"N • Longitudes : 84°26''04.71"E and 84°33''15"E • Elevation : 600m (Tinpiple) above sea level. Relative Location • East, South- East: Chepe River, Gorkha District • South: Marsyangdi River, Tanahu District (Purkot VDC) • West: Marsyangdi River, Sundar Bazaar Municipality • North: Bharte VDC, Gauda VDC, Kolki VDC
- 17. PHYSIOGRAPHY • Average Annual Rainfall Minimum 3mm (Jan, Feb, Nov) Maximum 129mm (July) (Data taken from 2000 to 2011, Lamjung) • Average Annual Temperature Minimum 0°C (Jan, Nov, Dec) Maximum 30°C (April, August) (Data taken from 2000 to 2011, Lamjung)
- 18. PHYSIOGRAPHY • Climate varies from tropical to sub-tropical • Main Rivers: Marsyangdi and Chepe
- 19. ACCESSIBILITY • Accessible from Gorkha and Bhoteodar • The Mid- hill highway running east west from the mid hill is under construction • 45 km of this highway lies in Lamjung district while almost 13 km of the overall length runs through Rainas municipality which is on the process of black topping • Nearest Black Topped Roads • Turture Bazar (Tanahu) to Borangkhola (Lamjung): 20 km • Nepal Danda (Tanahu) to Borangkhola (Lamjung): 17 km
- 20. ACCESSIBILITY • Internal roads: • Dumre to Turture Bazar: 10 km, Turture to Nepal Danda: 5+ km • Nepal Danda (Tanahu) to Tarkughat (Lamjung): 1 km • Turture to Chepeghat: 4km • Chepeghat (Lamjung) to Borangkhola (Lamjung): 16 km • Dumre to Besisahar: 42 km • Borangkhola to Besisahar: 42km (approx.) • Rainas Municipality is connected by 5 motorable bridges (Bhandarthok, Chepeghat, Baaisjangar, Tarkughat and Paundidhik)
- 22. INSTITUTIONAL SET UP AT RAINAS MUNICIPALITY • Newest Municipality of Nepal declared on 19th September 2015 ( 2nd Ashoj 2072) • Currently Municipality Office housed in the previous Tinpiple VDC Office. • Declared according to Local Self Governance Act 2055 (1999) LSGA, स्थानिय स्वायत्त शाशि ऐि • LSGA Cosiders VDC, Municipalities and DDCs as Local Bodies • Municipality is formed after merging the existing 6 VDC’s namely Pyarjung, Mohariyakot, Bhalayakharka, Chakratirth, Dhamilikuwa and Tarkughat and now the then 6 VDCs are converted in to 14 municipal wards.
- 23. INSTITUTIONAL SET UP AT RAINAS MUNICIPALITY Previous VDC Ward Converted Municipality Ward Previous VDC Ward Converted Municipality Ward Tarkughat VDC 1,2,3,4,5 Rainaas-1 Chakratirtha VDC 1,2,3 Rainaas-8 Tarkughat VDC 6,7,8,9 Rainaas-2 Bhalayakharka VDC 1,2,5,6,7 Rainaas-9 Dhamilikuwa VDC 1,2,3 Rainaas-3 Bhalayakharka VDC 3,4,8,9 Rainaas-10 Dhamilikuwa VDC 4,5,6 Rainaas-4 Pyarjung VDC 4,5,6,7,8,9 Rainaas-11 Dhamilikuwa VDC 7,8,9 Rainaas-5 Pyarjung VDC 1,2,3 Rainaas-12 Chakratirtha VDC 7,8,9 Rainaas-6 Mohoriyakot VDC 6,7,8,9 Rainaas-13 Chakratirtha VDC 4,5,6 Rainaas-7 Mohoriyakot VDC 1,2,3,4,5 Rainaas-14
- 24. MUNICIPALITY STRUCTURE ACCORDING TO LSGA • Publically elected Chairman and Vice Chairman • Ward Chairman, Woman ward member and ward members of each ward committee • Six persons including one woman nominated by the Village Council from amongst those social workers, socially and economically backward tribes and ethnic communities, down trodden and indigenous people living within the village development area • VDC Secretary, any employee appointed by government to act as the Secretary of the Village Development Committee • supporting staff • One Ward Chairman, • One Woman Ward Member, and • Three Ward Members. TIER 1, Village Council TIER 2, Village Development Committee TIER 3, Ward Committees Elected Body and nominated locals Government Employee Elected Body
- 25. VDC STRUCTURE ACCORDING TO LSGA • Publically elected Mayor and Deputy Mayor • Ward Chairman, Woman ward member and ward members of each ward committee • No less than 6 persons and no more than 20 persons including woman nominated by the Municipal Council from amongst those social workers, socially and economically backward tribes and ethnic communities, down trodden and indigenous people living within the area of the Municipality • Executive Chairman, government employee appointed by the ministry • Administrative Staff • Account Staff • Technical Staff • Supporting staff • One Ward Chairman, • One Woman Ward Member, and • Three Ward Members. • Administrative and Technical Staff TIER 1, Municipal Council TIER 2, Municipality Office TIER 3, Ward Committees Elected Body and nominated locals Government Employee Elected Body
- 26. RAINAS MUNICIPALITY STRUCTURE • Representatives from the municipality level political parties, women and indigenous groups, socially and economically backward tribes, elderly people group and active social workers • Executive Chairman, government employee appointed by the ministry, Mr. Noor Raj Kadariya • 2 former VDC secretaries • 1 technical staff under LGCDP • 1 account officer from को ले नि का • 1 computer operator • Joint Ward Offices: • गा बि स सहायक ( VDC Level Assitants) • सामाजिक परिचालक ( Social Mobilizers) • peons TIER 1, Municipal Council TIER 2, Municipality Office TIER 3, Ward Committees Nominated locals Government Employee Government Employee Different NGOs and local organizations are also assisting the municipality
- 27. CASE STUDY OF BIDUR MUNICIPALITY ORGANIZATION
- 29. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS From CBS data a. Total Population According to census 2011, Total population= 18527 Average household size= 3.57 sex ratio = 77.67 Male population = 8099 Female population = 10428
- 30. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS • Expansive population show larger percentages of population of younger age group >> found in populations with large fertility rates and lower life expectancies 8 6 4 2 0 2 4 6 8 0_4 5_9 10_14 15_19 20_24 25_29 30_34 35_39 40_44 45_49 50_54 55_59 60_64 65_69 70_74 75+ Population Pyramid (CBS,2011) Male Female
- 31. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS b. Education Status • Although presence of schools up to secondary level, but no facility of higher education • Education >> one of major reasons for migration in Rainas Municipality 31.48% 68.52% Education status Literate (%) Illiterate (%) Population Literate (%) Illiterate (%) 18527 31.48 68.52
- 32. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS d. Major Ethnic Group Main ethnic groups >> Brahmin, Gurung and Chhetri with a population of 3475, 3221 and 2968 respectively 17.39 16.02 18.76 8.9 6.54 10.1 4.32 4.9 2.54 1.76 3.54 1.82 1.19 0.99 1.24 %
- 33. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS c. Ownership of Housing Unit Out of total 4751 households, 95.05% houses are owned by themselves, 3.75% are rented, and 0.29% are institutional and 0.91% others
- 34. e. Main Sources of Drinking Water Out of 4751 households, 83.41% use tap water while 8.74 % use spout water and 0.51% use other sources of water
- 35. f. Toilet Facilities and Types • Most of them use flush toilet (54.20%) • Still 20.25% of total population do not use toilets
- 36. Zone I Name of Place Mohoriyak ot Tarkughat Dhamilikuwa Total Ward no. 13 14 1 2 3 4 5 373 Surveye d HH 74 52 34 27 70 82 34 Zone II Name of Place Pyarjung Bhalayakha rkha Chakratirtha Ward no. 11 12 9 10 6 7 8 195 Surveye d HH 22 20 14 34 21 62 22 568 DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS a. Population Details of Sample Survey
- 37. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS 20 15 10 5 0 5 10 15 20 0-1 1-5 5-15 15-30 30-49 49-75 >75 Population Pyramid (Survey) Male Female
- 38. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS 53% 47% Gender composition Male Female • Slight difference in population distribution • Tentative equal distribution of male and female • In ward no. 13, more male (15.4%) than female (13.9%) b. Gender composition Ward- wise Gender Distribution 15.4% 13.9%
- 40. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS c. Age Group Composition • Population of age group 15 - 30 >> highest frequency >> 34% of total population • Lowest >> 1.9% lies below 1 year of age.
- 41. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS • Slight difference in population distribution between male and female in various age groups • In age group 5-15, female population is faintly higher as compare to that of male Age-Sex Composition
- 42. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS d. Caste Composition • Predominantly dominated by Brahmin community, which is about 32.7%.
- 44. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS Caste and Family Type • Family structure of society changing with time >> urbanization • Majority of Dalit >> nuclear family while Newars seem to have equal distribution of nuclear and joint family
- 45. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS Caste and Mother Tongue • Most of inhabitants speak their mother tongue • Newars do not speak Newari and prefer Nepali instead due to - - - scatter distribution, lack of practice in communication, cultural degradation
- 46. DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS e. Religious composition Religion Percentage Hinduism 78.7 Buddhism 18.8 Islam 0.7 Christianity 1.2 Others 0.5 • The municipality consists of predominant Hindu religion >> 78.7%, Buddhist religion occupies 18.8%, Christianity 1.2%, Islam 0.7% and other religions just 0.5%
- 47. RELIGION
- 48. LINGUISTIC COMPOSITION • 78% of total household speak Nepali. • 16.5% people speak Gurung followed by Tamang, Newari and other languages. 78% 16.5% 4% 0.7% 0.7% Mother Tongue Nepali Gurung Tamang Newari Others Mother Tongue Percentage(%) Nepali 78 Gurung 16.5 Tamang 4 Newari 0.7 Others 0.7
- 49. EDUCATION Literate population - 87.81% Illiterate population - 12.18%. 12.18% 87.81% Literacy status of Rainas Illiterate Literate Ward Number Literate % 1 5.85 2 4.00 3 10.37 4 12.25 5 4.95 6 2.74 7 8.95 8 3.42 9 2.15 10 5.88 11 3.91 12 3.05 13 12.74 14 7.57 Literacy status of different wards
- 50. EDUCATION STATUS Highest percentage of people with formal education is ward 13 and the lowest is in ward 9.
- 51. EDUCATION 12.18% 10.27% 14.58% 13.38% 27.6% 12.95% 7.53% 1.46% 0.03% 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Education level • 27.6% of total population completed secondary education level • 14.58% population completed primary level, followed by lower secondary, higher secondary level.
- 52. • Males given more priority to attend school than females. • Females either married at an early age or engaged in household activities. 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Education level by gender Male Female EDUCATION Significant gender disparity in literacy and educational attainment
- 53. FAMILY STRUCTURE Ward No. Nuclear Family (%) Joint Family (%) 1 6.3 5.6 2 4.5 5.1 3 12.9 11.5 4 12.9 16.7 5 6.6 5.1 6 4.5 2.6 7 14.1 6.4 8 4.5 3.0 9 2.4 2.6 10 6.6 5.1 11 4.2 3.4 12 4.5 2.1 13 6.9 21.8 14 9.3 9.0 • Greater percentage of nuclear family • People are adopting nuclear family due to change in lifestyle and education 58.80% 41.20% Family Structure Nuclear Joint
- 54. DEATH • Out of 568 household, death in 90 households in last five years • Male death - 61.11% • Female death - 38.89% • Majority of deaths occurred at the age group of 49-75, 75 and above age group 34% 3% 60% 3% Cause of Deaths Natural Accident Disease Others
- 55. Migration Trend: Within Rainas Municipality 74.8% 25.2% Indigeneous Migrated Place of Origin
- 56. 16.9% 16.8% 24.5% 0.0% 0.0%0.0% 5.0% 10.0% 15.0% 20.0% 25.0% 30.0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Wardwise Population Origin Ward No. Indigenous Migrated Migration Trend: Within Rainas Municipality Highest Migrated Ward with Indigenous Population
- 57. • 30.77% during the period of 2061-2070 • 2070- 2073: 11.54% migrants 0.00 5.00 10.00 15.00 20.00 25.00 30.00 35.00 Migration Year%age 0 2 4 6 8 10 1973 2012 2021 2024 2032 2037 2040 2044 2047 2050 2053 2056 2060 2063 2066 2069 2072 •Rapid pace of Migration • Upper hilly areas to lower flat urbanizing areas Migration Trend: Within Rainas Municipality
- 58. • Majority migrations for domestic (family) reasons: 35.66% • Employment, Education and Business • From villages in search of facilities: 8.39% 35.66 9.79 13.29 11.89 2.10 16.08 8.39 2.80 0.00 5.00 10.00 15.00 20.00 25.00 30.00 35.00 40.00 Domestic Education Employment Business Marriage Others Facilities Natural Calamities Percentage Reasons for Internal Migration Migration Trend: Within Rainas Municipality
- 59. • Majority of surveyed HH have family members outside the municipality • 25% of total surveyed population migrated MIGRATION OUTSIDE MUNICIPALITY 44.7% 55.3% No Yes Family member migrated outside municipality
- 60. • Of the 25% total migrated population • 62.53% migrants within Nepal • 37.41% outside Nepal MIGRATION OUTSIDE MUNICIPALITY Out migration 62.53% Emigration 37.47% Migrants Population
- 61. OUT-MIGRATION DESTINATIONS 4.5% 3.0% 5.5% 56.7% 19.1% 11.15% 0.0% 10.0% 20.0% 30.0% 40.0% 50.0% 60.0% • Kathmandu •42% for education •37% for employment
- 62. Out-Migration Reasons within Nepal 18.71% 40.64% 0.76% 2.84% 0.19% 36.86% Domestic Education Health Others Training Work 0.00 5.00 10.00 15.00 20.00 25.00 30.00 35.00 40.00 45.00 Reasons of Out-Migration within Nepal
- 63. Out-Migration based on Age Group 0.95% 5.10% 15.88% 53.88% 20.60% 3.59% 0.00 10.00 20.00 30.00 40.00 50.00 60.00 0-1 1-5 5-15 15-30 30-49 49-75 Out-Migration based on Age Group • Majority of students and working age group migrate • 53.88% of majority age group 15-30 years • About 41% of students age group migrate • 37% of working age group migrate
- 64. Out-Migration based on Gender 59.36% 40.64% Male Female Out-Migration based on Gender Distribution of population on various destinations
- 65. Out-Migration based on Caste 22.64% 32.45% 17.74% 11.70% 4.53% 5.66% 5.28% 0.00 5.00 10.00 15.00 20.00 25.00 30.00 35.00 Gurung Brahmin Chettri Dalit Tamang Newar Others Out-Migration based on Caste • 32.45% of Brahmins migrate for job opportunities • 22.64% Gurungs for government service (Nepal Army), followed by Chhetri
- 66. Out-Migration based on Family Structure 57.36% 42.64% Nuclear Joint Out-Migration based on Family Structure Distribution of migrated population on various destinations based on family structure
- 67. • 9.4% of total population surveyed • 37.47% of the total migrated population Migration Trend: International Out migration 62.53% Emigration 37.47% Migrants Population
- 68. International Destinations India Middle East Korea Japan Australia UK USA Hongkong Others 16.09% 58.36% 3.15% 1.58% 4.10% 1.26% 0.63% 0.63% 14.20%
- 69. International Migration Reasons 5.99% 0.63% 93.38% 0.00 20.00 40.00 60.00 80.00 100.00 Education Others Work Reasons for Emigration
- 70. Emigration based on Age Group 0.32% 0.95% 54.57% 40.69% 3.15% 0.32% 0.00 10.00 20.00 30.00 40.00 50.00 60.00 1-5 5-15 15-30 30-49 49-75 >75 Emigration based on Age group • Majority of working age group migrate • Job opportunities • Middle East and India
- 71. Emigration based on Gender 90.22% 9.78% Male Female Emigration based on Gender Distribution of population on various countries based on gender
- 72. Emigration based on Caste 19.87% 33.11% 16.56% 11.59% 6.95% 7.28% 4.64% 0.00 5.00 10.00 15.00 20.00 25.00 30.00 35.00 Gurung Brahmin Chettri Dalit Tamang Newar Others Emigartion based on Caste • 33.11% of Brahmins migrate for job opportunities
- 73. Emigration based on Family Structure 60.26% 39.74% Nuclear Joint Emigration based on Family Structure
- 74. Degree of Migration Problem Severe 6% Moderate 17% None 77% Degree of In-Migration
- 75. Degree of Migration Problem Severe 45.8% Moderate 25.5% None 28.7% Degree of Out-Migration
- 77. ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS MAJOR OCCUPATION • 20.7% engaged in agriculture, not commercialized. • Agricultural products not sufficient • Migrated population involved in services inside and outside Nepal. • Training programs for housewives
- 78. ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS MAJOR SOURCE OF INCOME • 32.34% have agriculture as main source of income • Remittance being other major source. • Animal husbandry can be encouraged.
- 79. ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS MAJOR SOURCE OF INCOME • Cow, goat and buffalo for dairy products. Graph showing types of Animal Rearing
- 80. ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS MAJOR SOURCE OF INCOME • The production of maize and Paddy is higher. Graph showing types of crops
- 81. ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS MONTHLY INCOME OF FAMILY • Almost 50% of population have monthly income of 10000- 25000 and >50% have expenses of the same amount. • The expenses are more on the education, festivals and health facilities. Graph showing monthly income of family Graph showing monthly expenditure of family
- 82. ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS BUILDING OWNERSHIP • Majority of people own their house i.e. 97.5% only 2.5% people rent their place • 35% of rented households are in Ward no. 7. Graph showing the building ownership Building Ownership Ward No. Percentage of Rented Households 1 7.14 % 2 0.00 3 0.00 4 7.14 % 5 0.00 6 14.29 % 7 35.71 % 8 7.14 % 9 0.00 10 14.29 % 11 7.14 % 12 7.14 % 13 0.00 14 0.00
- 83. ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS OWNERSHIP OF LAND Graph showing ownership of land within Rainas MunicipalityGraph showing ownership of land outside Rainas Municipality • 50.88% people have other land within Rainas Municipality and 85.009% of people own land outside the Municipality
- 84. Graph showing Vehicle Ownership Type ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS OWNERSHIP OF VEHICLE • 87.852% people do not own any vehicles
- 86. CULTURAL ASPECTS • Celebrate different festivals - Dashain, Tihar, Maghe Sankranti, Holi, Teej, Lhosar, Baisakh Purnima, Chaitya Dashain, Gai Jatra, Janai Purnima, Eid, Easter day, Christmas Special festivals Ekadasi mela • Celebrated on the day of Haribodhani Ekadashi in the month Kartik/Mangsir • Celebrated for a single day in Paudi Harrabot dovan in Tarkughat and in Bokseraha in the river bank of Chepe.
- 87. CULTURAL ASPECTS Shivaratri mela • Celebrated by people all over Mohoriyakot in Rainaskot • Lasts for three days on the month of Falgun (Shivaratri) Ghatu Nacch • Specially celebrated by Gurungs of Mohoriyakot • Lasts for two days during the month of Baisakh (Buddha Purnima) Maghesankranti Mela • Celebrated on 1st of Magh in Chepeghat in Marsyandi dovan
- 88. CULTURAL ASPECTS Ropai Jatra • Celebrated in Newar community mainly in Tarkughat area Teej Mela • Celebrated mainly by females on day of Teej on month of Shrawan/ Bhadra • Markets mainly focused on products especially for Teej Lakhe Nach • Celebrated by some Newars of Tarkughat in Bhadra for a day • Festival not continued till date - may be due to lack of interest of people towards their tradition & culture and influence from modern society
- 89. MONUMENTS • Dhamilikuwa (historically important kuwa) after which the name of the place was put as Dhamilikuwa • Ram Mandir in Dhamilikuwa • Dewa Chhambo Gumba in Syauli- Dhamilikuwa • Chakratirtha Mandir • Kalika Mandir in Bhalayakharka • Gorakhnath Temple in Pyarjung • Siddha Baba Temple in Mohoriyakot • Historical Fort: Rainaskot is also a cultural place in Mohriyakot • Rainas Peace Church in Dhamilikuwa
- 90. MONUMENTS
- 91. MONUMENTS Dewa Chhambo Gumba in Syauli, Dhamilikuwa Shiva Mandir of Chakratirtha Kalika Temple in Panthi danda, Bhalayakharka Kalika Temple, Rainaskot
- 93. Infrastructure Development 1. Road and Accessibility Condition 2. Bridges 3. Electricity 4. Communication 5. Irrigation 6. Water Supply 7. Residence and Building Materials
- 94. 1.Road and Accessibility Condition •Basic mode of transportation •Connects the whole municipality area and helps in further development. •mostly earthen road in the municipality • Road has almost connected whole part of the municipality but there is no frequent transportation facility and the routes are limited. •many are under construction.
- 95. 1.Road and Accessibility Condition
- 96. ROAD NETWORK MAP
- 97. 1.Road and Accessibility Condition
- 98. 2.Bridges In hills suspension bridges are mostly built for connecting across the rivers. Different bridges constructed in the municipality are as follows: Name of Bridge VDC Connection Wooden bridge Suspension Bridge Motarable Bridge Length Okhle Dhamelikuwa Bhandarithok Gorkha 1 63.7 Naringhat Dhamelikuwa Purkot Tanahu 1 124.6 Chepeghat Dhamelikuwa Palungtar Gorkha 1 91 Kaliraha Dhamelikuwa Palungtar Gorkha 1 Chilli Khola Pyarjung Kolki 1 36.5 Dhulpure Bridge Pyarjung Kolki 1 35 Borang Khola Bhalyakharka Bhalyakharka-7 - 1 - Borang Khola Bhalyakharka Bhalyakharka 4-9 - 1 - Borang Khola Bhalyakharka Bhalyakharka 4- Gorkha - 1 - 49 Soti Bhalyakharka Bhalyakharka-Harmi Gorkha - 1 - Dobhan Bhalyakharka Bhalyakharka -Kolki 1 - Ekle Julunge pool Chakratirtha Aapiple Gorkha 1
- 99. 3.Electricity •Most of the people living here are facilitated with electricity from national electricity grid . •Some use solar energy and gas plant for electricity service. •Many people of Pyarjung and Mauriyakot are deprived of electricity service.
- 100. 4.Communication •Major means of communication -mobile phone. •no landline -municipality. Graph showing the communication Medium in Rainas Municipality
- 101. 5.Irrigation Rainas Irrigation planning: •Water source : Chepe River •Main Canal: 14.5km. , Branch Canal: 5km. •Command Area: 850 hectare •Benefitted land: Rainas Municipality, ward no.: 3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 (Bhalayakharka, Chakratirtha, Dhamilikuwa) •Benefitted Population: 11666 •Main crops: wheat, maize, potato, paddy, mustard, seasonal vegetable. •Cropping Intensity: 230% (before: 100%)
- 102. 5.Irrigation Pangre-Harrabot Irrigation Planning: •Water source: Tardi Khola •Main canal: 8km., Branch canal: 500km. •Command area: 390 hectare • Benefitted land: Rainas Municipality, ward no.: 1,2 (Tarkughat) •Benefitted population: 2893 •Main corps: wheat, maize, potato, paddy, mustard, seasonal vegetable. •Cropping Intensity: 200% (Before: 130%)
- 103. 6. Water Supply Source •Piped water •Well/ Kuwa •River/Pond/Canal
- 104. 6. Water Supply Graph showing Source of Water Supply
- 105. 6. Water Supply Graph showing Ward wise Distribution of Source of water supply
- 106. 6. Water Supply Graph showing Water Purification method used
- 107. 7. Residence and Building Materials Graph showing Building Construction Type
- 108. 7. Residence and Building Materials Graph showing Construction material of Load Bearing Building
- 110. INSTITUTIONS
- 111. •Health post / Sub health Post •Post Office •Pashu Sewa Kendra •Krishi Bikash Bank •Jila Aayurbed Aausadhalaya •Police station – 2nos Government institutions Rainas Municipality OfficePolice Station at Chakratirtha
- 112. Non-Government institutions Child Club • 20 child club according to VDC profile (2067 B.S) Youth Club • Samaj Kalyan Yuwa Club • Navikaran Yuwa Club • Savya Srijan Yuwa Club • Sunaulo Bihani Yuwa Club
- 113. Non-Government institutions Community Based Organization (CBO) • Numerous child clubs, women’s group, and cooperatives working in the municipality. • Women’ group also known as Aama Samuha has been established for increasing income of the women and for their empowerment. • There are other community based organizations working for welfare of housing old aged group.
- 114. Educational institutions Table showing list of Educational institute Source :VDC profile (2067 B.S)
- 115. BACKGROUNDLAND USE
- 116. LANDUSE •Rainas Municipality can broadly be divided into various land use category • Land use of agriculture and Forests area, with compact settlement on various designated area, and water body as Marsyangdi, Chepe and Tarte River. •The built-up areas can be divided into residential, commercial, institutional, industrial, and recreational areas. Land Use Area (Ha) %age Built-up 665.76 9.12 Bush 86.14 1.18 Cultivation 3747.81 51.34 Forest 2588.51 35.46 Grass 50.17 0.69 Orchard 0.94 0.01 River/ Stream 76.54 1.05 Sand 82.87 1.14 Others 1.27 0.02 Total 7300.00 100.00
- 117. LANDUSE
- 118. LANDUSE MAP
- 119. SETTLEMENT PATTERN •settlement has developed on the plain areas along the main road to the upper slopes of Rainaskot. •settlement clusters emerging as the ribbon development -Along the roads connecting Dhamilikuwa to Bhalayakharkha
- 120. SETTLEMENT PATTERN •emerging commercial areas are Tarkughat, Panchbhai Chautari, Syauli, Tinpiple, Alkatar, Borangkhola, Kundule and Borang.
- 122. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT • consists of Jungle, slope hills, plain flat land and river • warm climate in plains in lower altitude and cooler climate up hills • Rich in natural resources like forest, flora and fauna, herbs, water bodies, wildlife etc
- 123. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT Forest • help to keep ecosystem in balance • one of the main resources of Rainas municipality • Almost 35.46% of municipality area is occupied by forest • Well preserved • forest area is covered with trees such as Bankarela, Harro, Bari, Tetepati, Bet, Gurjo, Gurjango etc
- 124. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT S.N Name of Community Forest VDC Name Area (Hector ) 1 Rani ban Bhalayakharka 34.25 2 Odalpato Bhalayakharka 14 3 Kaprechaur Bhalayakharka 54.15 4 Suryodaya Bhalayakharka 31.78 5 Satidevi Bhalayakharka 136.45 6 Dundure Dhanpakha Bhalayakharka 16.25 7 Pangate Community Forest Pyarjung 40.54 8 Lama gaun Community Forest Pyarjung 57.54 9 Samlekot Community Forest Pyarjung 54.43 10 Mandali Community Forest Pyarjung 16.1 11 Sani Pokhari community Forest Pyarjung 21.47 12 Silapathar Community Forest Pyarjung 7.26 13 Manichakra Community Forest Pyarjung 17.24 14 chakratirtha forest Chakratirtha 64.55 15 Deworali Chakratirtha 37.91 16 Jhakri than Chakratirtha 119.85 17 Aapchaur Dhamilikuwa 122.5 18 Lupu Gaun Dhamilikuwa 137.19 19 Salfedi Dhamilikuwa 21.11 20 Simalchau Ranighat Dhamilikuwa 61.84 21 Garambesi Dhamilikuwa 23.55 22 Chamfawoti Dhamilikuwa 37.7 23 Gauritar Dhamilikuwa 28.14 24 Shree Marshyandi Community Forest Majhigaun 25 Shree Kataharbari Community Forest Harrabot 26 Shree Nabojotyi Community Forest Harrabot 27 Shree Kalika Community Forest Sika 28 Shree Mahadev Community Forest Sika 29 Shree Ananpurna Community Forest Sika 30 Shree Taleju Community Forest Sika 31 Shree Pipaltari Community Forest Pipaltar 32 Shree Kalamata Community Forest Tarkughat List of Forests
- 125. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT Rivers and Water Bodies • Chepe River • Marsyangdi River • Various ponds and water conduits Ward-1: Kataharbari Padhero Ward-3: Dhamilikuwa Ward-9: Thuli Pokari -dried &converted into football ground Ward-10: Katkate Padhero Ward-13: Magar pani Padhero Ward-13: Ritthe pani Padhero Ward-13: Patle pani Padhero Ward-14: Kaure pani Padhero Ward-14: Kuwa pani Padhero • in critical conditions due to lack of maintenance and change in environmental condition
- 126. WATER RESOURCES MAP
- 127. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT Wild lives and vegetations • rich in biodiversity • wild animals like leopard, bear, fox, squirrel, bat, monkey, wild cat etc • major birds like crow, dove, owl, eagle, crane, duck, and swan • among 700 herbs known , 200 types of herbs are available like Dubo, Jhingeraj, Pipla, Sabo, Gurjo, Tulshi, Babari, Gudargano, Amala, Harro-barro, Simali, Bell, Akashay Beli, Gaitihare, Aloe Vera, Pudina etc • rich in flora and fauna • dozens of flowers found like Rhododendron, rose, lily, hibiscus, jasmine, marigold, lalupate, tulip etc
- 128. SITE PLAN
- 129. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT Agriculture • 51.34% of total area of the municipality is occupied by cultivation land • potential in agriculture as it has flat fertile lands along bank of the Chepe River which are facilitated by two irrigation canals • fertile land is capable of producing paddy two times a year
- 130. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT • land on the upper hills not facilitated by irrigation has to depend on monsoon rain for the cultivation • capable of producing varieties of crops, fruits and vegetables like maize, paddy, millet, wheat, mango, litchi, orange, jackfruits, cucumber etc • started growing Black cardamom (Alaichi).
- 131. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT Solid Waste Management •Almost 82% of household dispose 1-3 kg of solid waste followed by 3-6 kg and very few disposes more than 6kg of solid waste daily
- 132. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT Solid Waste Management • Majority of people themselves manage the solid waste by burning and burying it. •municipality does not have any solid waste collection system and allocated landfill site. •People in the urbanizing areas throw their garbage in the open area which has resulted in pollution
- 133. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT Solid Waste Management • Majority of people (75%) convert the solid waste into compost •Composting not only solves the environmental degradation problem and prevents pollution but also gives healthy agricultural products
- 134. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT Sewerage and Sanitation • almost every house in the municipality has their own latrines 86.62% has outside and 11.62% has inside •Only 0.88 % lack latrines especially in squatter settlement
- 135. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT Sewerage and Sanitation • 90% have permanent and almost 9% have temporary pit latrines •Rainas Municipality along with the whole Lamjung District has already been declared as Open Defecation Free Area in 2072 BS
- 136. ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT Sewerage and Sanitation • almost 96% have their own septic tank and only about 1% uses sewerage connection system •35% of the population uses their sewerage along with animal excreta to generate Gover gas •helps in managing sewerage and also making themselves sustainable
- 137. DISASTER LANDSLIDE EARTHQUAKE WIND AND STORM FLOODFIRE HAZARD
- 138. Definition •According to Wikipedia- “disaster as a serious disturbance of the functioning of a community or a society involving widespread human, material, economic or environmental losses and impacts, which exceeds the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own resources.“ • developing countries such as Nepal suffer most when disaster takes place>> 95% deaths and losses are 20 times greater • Nepal is extremely vulnerable to to the natural disaster the impacts of climatic change the unplanned development activities • Rainas municipality of Lamjung >>> located in central Nepal due to its topography and land pattern, there is significant risk of natural hazards.
- 139. Flood • Marsyangdi, is the major river drains from the north to the south of the municipality. It in turn fed by numerous tributaries including Chepe River. • Flood is not the major problem • half of theriver water is passes through irrigation canal. • Also there is no settlement along the river bank which prevent loss of lives during water level increment. • However, during monsoon, river water sweeps away the land parts along the riverbank
- 140. Landslides • Landslide is the major natural disaster • series of landslides has occurred in the slopes along the Chepe River • Landslide is the result of different other natural disaster such as flood, deforestation and earthquake. • different development activities like construction of irrigation canal and of rural road also trigger the risk of landslide in this areas.
- 141. Earthquake •Mega earthquake of 25th April 2015 had affected most parts of Rainas municipality such as Mohoriyakot, Dhamilikuwa, Chakratirtha, and Tarkughat. •From building survey, we found 67.78% of housed were partially damage, 18.49% of houses were fully damaged • main reason of this destruction is the age and structure of the buildings • Load bearings buildings are Severely affected rather than RCC framed structure
- 142. Drought • Another major hazard in most of the areas of Rainas municipality •The upper area of municipality such as Mohoriyakot, Pyarjung, Tarkughat and Bhalayakharka is experiencing severe water scarcity •water resources has dried out so people have to travel a lot in order get drinking water •Lack of water has also affected the agricultural pattern of upper areas • also acts as the major reason for migration of people to lower areas such as Dhamilikuwa and Chakratirtha. • one of the reason to initiate fire in forest
- 143. Fire Hazards •fire hazard take place very occasionally in Rainas municipality • main reason of fire hazard in lack of awareness and traditional misconception. •But this year, drought act as the major reason for fire in forest Wind and Storm •Another natural hazard is wind and storm which takes place during the month of Chaitra abd Baisakh •People loss there life and property •Also create other problems such as obstruction of roads, damage of electrical poles which affect the day to day activities of local people
- 144. BACKGROUND ANALYSIS
- 145. LINKAGE • No town produces all the goods required for itself within its boundary • Transfer of goods and manpower between cities. • Rainas municipality is developing as center for undeveloped VDCs and nearby district Gorkha. • Exchange of any of such has direct impact in economic development of the region • Rainas Developing Phase • No proper road connection • Rainas can be taken as rural area
- 146. LINKAGE • Rely on other cities like Narayanghat, Kathmandu, Dumre, Besisahar and others • Linkage between cities and Rainas can be considered as urban- rural linkage • ‘Engines' that drive economic, social and cultural transformations • Rural-urban interactions include: • Linkages across space (such as flows of people, goods, money, information and wastes) • Linkages between sectors (for example, between agriculture and services and manufacturing).
- 147. LINKAGE
- 148. LINKAGE Rainas Municipality • Manpower • Cash Crops • Health service • Education Besi sahar Chitwan Kathmandu Dumre • Consumable Goods • Quality manpower • Technology • Cultural degradation Linkage with Cities
- 149. LINKAGE Trend Of Internal Migration
- 151. PROBLEMS AND ISSUES • Identified through data collected from household survey and its analysis 1. Water supply problems • 36.09% - Sever water problem • 25.18% - No water problem • 38.56% - House hold taps • 21.65% - Community tap • Remaining fetch directly from source 2. Solid waste disposal problems • 81.87% produce 1-3 kg waste • 14.79% produce 3-6 kg • 96.83% buries in their own compound • 75.18% converts into compost
- 152. PROBLEMS AND ISSUES 3. Problems of health facilities • 46.03% - Uses hospital • 49.03% - Uses clinic and health post • 76.23% - Uses maternal health services • 100% children were vaccinated 4. Problem of educational facilities • 20.60% - Literate • 21.23% - Illiterate • 5.28% - Primary education • 8.97% - Lower secondary education • 27.46% - Secondary education • 10.74% - Higher secondary education • 4.40% - Bachelor’s degree • 1.05% - Master’s degree
- 153. PROBLEMS AND ISSUES 5. Problem of accessibility • 0% - Blacktopped • 13.73% - Stone paved • 20.95% - Graveled • 41.20% - Earthen • 23.94% - Trial • 30.99% - <1 m • 36.30% - 1-3.5m 6. Unemployment problem • Vicious circle is created due to this problem • 63% outside municipality
- 154. PROBLEMS AND ISSUES 7. Migration problem Upper part of municipality to lower part of municipality • 35.66% - Domestic reason • 9.79% - Education • 13.29% - Employment • 11.89% - Business • 2.09% - Marriage Outside municipality • 56.17% - Kathmandu • 4.53% - Besisahar • 3.02% - Gorkha • 5.48% - Pokhara • 0.56% - Biratnagar • 0.37% - Birgunj
- 155. PROBLEMS AND ISSUES • 0.56% - Nepalgunj Outside Nepal • 58.36% - Middle East • 16.09% - India • 45.77% - Responded migration as problem 8. Farming • No trainings and subsidiary for farmers – Banana farming • Bananas infested by insects and discourage • No agriculture meter for fish farmers by NEA • Have to pay more due to this • No permanent source of water for fish farming
- 156. PROBLEMS AND ISSUES • Identified through data collected from household survey and its analysis 1. Water supply problems • 36.09% - Sever water problem • 25.18% - No water problem • 38.56% - House hold taps • 21.65% - Community tap • Remaining fetch directly from source 2. Solid waste disposal problems • 81.87% produce 1-3 kg waste • 14.79% produce 3-6 kg • 96.83% buries in their own compound • 75.18% converts into compost
- 159. PROBLEMS AND ISSUES 3. Problems of health facilities • 46.03% - Uses hospital • 49.03% - Uses clinic and health post • 76.23% - Uses maternal health services • 100% children were vaccinated 4. Problem of educational facilities • 20.60% - Literate • 21.23% - Illiterate • 5.28% - Primary education • 8.97% - Lower secondary education • 27.46% - Secondary education • 10.74% - Higher secondary education • 4.40% - Bachelor’s degree • 1.05% - Master’s degree
- 163. PROBLEMS AND ISSUES 5. Problem of accessibility • 0% - Blacktopped • 13.73% - Stone paved • 20.95% - Graveled • 41.20% - Earthen • 23.94% - Trial • 30.99% - <1 m • 36.30% - 1-3.5m 6. Unemployment problem • Vicious circle is created due to this problem • 63% outside municipality
- 166. PROBLEMS AND ISSUES 7. Migration problem Upper part of municipality to lower part of municipality • 35.66% - Domestic reason • 9.79% - Education • 13.29% - Employment • 11.89% - Business • 2.09% - Marriage Outside municipality • 56.17% - Kathmandu • 4.53% - Besisahar • 3.02% - Gorkha • 5.48% - Pokhara • 0.56% - Biratnagar • 0.37% - Birgunj
- 167. PROBLEMS AND ISSUES • 0.56% - Nepalgunj Outside Nepal • 58.36% - Middle East • 16.09% - India • 45.77% - Responded migration as problem 8. Farming • No trainings and subsidiary for farmers – Banana farming • Bananas infested by insects and discourage • No agriculture meter for fish farmers by NEA • Have to pay more due to this • No permanent source of water for fish farming
- 171. SWOT ANALYSIS • Acronym for Strength, Weakness, Opportunity and Threat • Developed for business for adopted for planning too. • Data collected to be arranged as • Strength : Characteristics that give advantage over others. • Weakness : Characteristics at a disadvantage relative to others. • Opportunities : element that could exploit to its advantage • Threats : element that could cause trouble • Strength and Weakness are internal, Opportunity and Threats are external
- 172. SWOT ANALYSIS OPPORTUNITY THREATS STRENGTH Strength – Opportunity Strategies Strength – Threat strategies WEAKNESS Weakness – Opportunity Strategies Weakness – Threat Strategies
- 173. SWOT ANALYSIS STRENGTH WEAKNESS • Agriculture • Availability of water for irrigation • Natural beauty • Presence of historical places like mohariya kot and Rainash kot • Forest and medical herbs • Greenery of the municipality • Lack of infrastructures like water supply, health services, drainage system and road networks • Unemployment • Improper waste disposal • Less no of schools • Landline telecommunication not available • High terrain topography • Low institutional capacity OPPORTUNITY THREATS • Market of besisahar Kathmandu and nearby towns • Tourism, paragliding • Located approximately at the middle of country • Virgin land for development • Pokhara and Bandipur attracting more tourist • Out migration to large cities • Barren agricultural land • Haphazard development due to lack of bye laws • Besisahar as a threat
- 174. SWOT ANALYSIS STRENGTH – OPPORTUNITY STRATEGIES • Supplying agricultural products to nearby towns • Developing historical places as tourism centers • developing trekking routes on the upper part of municipality • Supplying forest products and medical herbs to nearby towns • These nearby towns can be used as base for exporting products mentioned in above points • Central location of Lamjung can be used for supplying local products all over Nepal • Optimum use of land through land use planning STRENGTH – THREAT STRATEGIES • Developing tourism center in municipality to attract some tourist going to nearby towns so that their visit to can be prolonged in Nepal • Creating job opportunities from agriculture, herbs and forest products so as to minimize the out migration from municipality • Using job opportunities generated from tourism development to stop the out migration form the municipality • Converting barren agricultural land back to agriculture land through the initiation of local government with participatory approach
- 175. SWOT ANALYSIS WEAKNESS – OPPORTUNITY STRATEGIES • Taking help from nearby towns to develop infrastructure • Reducing unemployment from the jobs created through newly developed sectors WEAKNESS – THREAT STRATEGIES • Initially providing home stay facilities for tourists so as to improve the initial condition of municipality and developing tourist facilities on long run to develop tourism on full capacity
- 176. SWOT ANALYSIS Short term strategies • Flowing of information about historical places and natural beauties of municipalities through different medias • Tourism related training to the people which includes tourist guide training, guides for he trekkers tourism institutes related training • Concession in different kinds of tax imposed in municipality so that agriculture and tourism can be promoted in municipality.
- 177. SWOT ANALYSIS Long term strategies • Establishing of forest and agriculture product collection centers at different locations along the ring road as per the requirement in the municipality • Development of trekking routes on the upper part of the municipality • Government helping private sectors for preparing base for exporting products form Rainash which can be exported outside Nepal .
- 178. SWOT ANALYSIS Long term strategies • Since lower part of municipality have good quality of soil with good irrigation facility, agricultural land at those places to be preserved and settlement to be provide at the upper part of the municipality • Since there are high amount of agricultural land barren, facilities and encouragement programs should be created for the farmers to convert them into agriculture land. This will in turn increase the productivity of the municipality and help in generating revenue of the municipality.
- 179. SWOT ANALYSIS Long term strategies • Since municipality don’t have required qualified manpower and resources to develop the infrastructures like communication, water supply etc, and helps from nearby towns should be taken so as to initiate their development. • After the development of new sectors which is tourism and improvement of existing sector which is agriculture different new sectors can be created like tourist guides, paragliding, trekking guides, hotels for tourist, restaurants, selling local products to tourists. In case of agriculture, different kinds of cash crops suitable according to season, transportation of agriculture products to different towns nearby.
- 180. SWOT ANALYSIS Long term strategies • After the development of new sectors which is tourism and improvement of existing sector which is agriculture different new sectors can be created like tourist guides, paragliding, trekking guides, hotels for tourist, restaurants, selling local products to tourists. In case of agriculture, different kinds of cash crops suitable according to season, transportation of agriculture products to different towns nearby.
- 181. CONCLUSION •SWOT analysis showed that agriculture, tourism and central location of Lamjung are one of the strong factor that can help Rainas to self- sustain and develop further •Water supply, solid waste, health facilities, educational facilities, accessibility, unemployment and migrations were detected as problems of Rainas municipality •no ward offices in respective wards and it is very difficult for people to reach the municipality office due to lack of vehicular accessibility. •People not satisfied with declaration of municipality due to insufficient infrastructure available •Due to unemployment active population are migrating to areas with more employment opportunities. •Health services are not sufficient and are not accessible to people in remote areas.
- 182. CONCLUSION SNO FACILITES PERCENTAGE 1 Water supply to house hold 38.65 23 People using water without filtration 68.31 4 Waste buried in compound by households 96.83 5 Household using hospital 46.03 6 Household using maternal service 76.23 7 Illiterate population 21.13 8 Earthen road 41.20 9 Road width less than 1 meter 36.80 10 Outside country migration 37 •Although people of Rainas are engaged in agriculture, they are not able to benefit economically due to absence of market for agricultural products. •Children have to walk for hours everyday for education. • High level education facility is not available in the area. •So proper planning has to be done in order to solve these problems.
- 183. PRESENTED BY: 072/MSU/BATCH THANK YOU
Editor's Notes
- According to our survey, 87.852% people do not own any vehicles, 7.7465% people use motor bike or scooter, 3.3451% people own bicycle, 0.88% own Tractors and 0.1761% own other kind of vehicles.
- As an indicator of physical development municipality has various infrastructure such as roads, bridges, electricity, communication system, etc. There are basic facilities in the municipality but the services are yet not satisfactory in the municipality. Some of the Physical infrastructures developed are as follows:
- Roads are basic mode of transportation. It connects the whole municipality area and helps in further development. There are mostly earthen road in the municipality. Road has almost connected whole part of the municipality but there is no frequent transportation facility and the routes are limited. Most of the roads here, are of earthen type and many are under construction. Following table shows list of roads in use in Rainas Municipality along with its length in km.
- According to our sample survey, 41.20% of the houses have earthen road as access, 23.94% houses have trail as access, 20.95 % have gravel access road, 13.73% have stone paved access road and 0.176% have brick paved access road.
- According to our sample survey, in all the wards most of the roads are earthern, followed by gravel, and stone paved.
- According to our survey, we found that the highest percentage of people i.e. 38.616% use both NTC and NCell sim. 34.606% of people use NTC sim only and 25.137% of people use NCell sim only. In the same way 0.7286% use CDMA, 0.5464% use other services and 0.3643 use landline telephone. Among the people we surveyed, 65.487% of people have TV cable at home and 34.513% of people do not have TV cable at home. In the same way 84.902% of people do not have Internet facility and 15.0698% of people have internet connection.
- Our sample survey showed 38.556% of Municipal Connection as source of water supply, 25.88% use spring water, 21.655% use Community Tap, 5.45% use other source of water, 5.8% use Stone taps and 2.64% use well as source of water.
- Our sample survey showed 38.556% of Municipal Connection as source of water supply, 25.88% use spring water, 21.655% use Community Tap, 5.45% use other source of water, 5.8% use Stone taps and 2.64% use well as source of water.
- According to the survey, we found that most of the people i.e. 68.31% do not treat the water for drinking. About 17.606% of people filter the drinking water, 10.739% boil the water before drinking, 2.2887% use chlorination and 1.05% use Sodis.
- According to our survey, 84.859% of people have Load Bearing Building, 11.44% have RCC Frame Structure and 3.69% have Temporary buildings. About 84.232% of Load Bearing Type of building are of Stone Mud Masonary, 10.581% are of Brick Mud Mortar, 2.07% are of Stone Cement Mortar, 1.65% are of Brick Cement Mortar, 1.24% are of Sundried Brick and 0.20% of Stone Cement Mortar.
- About 84.232% of Load Bearing Type of building are of Stone Mud Masonary, 10.581% are of Brick Mud Mortar, 2.07% are of Stone Cement Mortar, 1.65% are of Brick Cement Mortar, 1.24% are of Sundried Brick and 0.20% of Stone Cement Mortar.
- There are number of government organizations set up for providing facilities to the general public. People generally go to Health post for medical checkup; they were established in each former VDCs. Pashu Sewa Kendra has been established to provide information to related animal husbandry. There are two police stations within the municipality at Chaktatirtha and Tarkughat.
