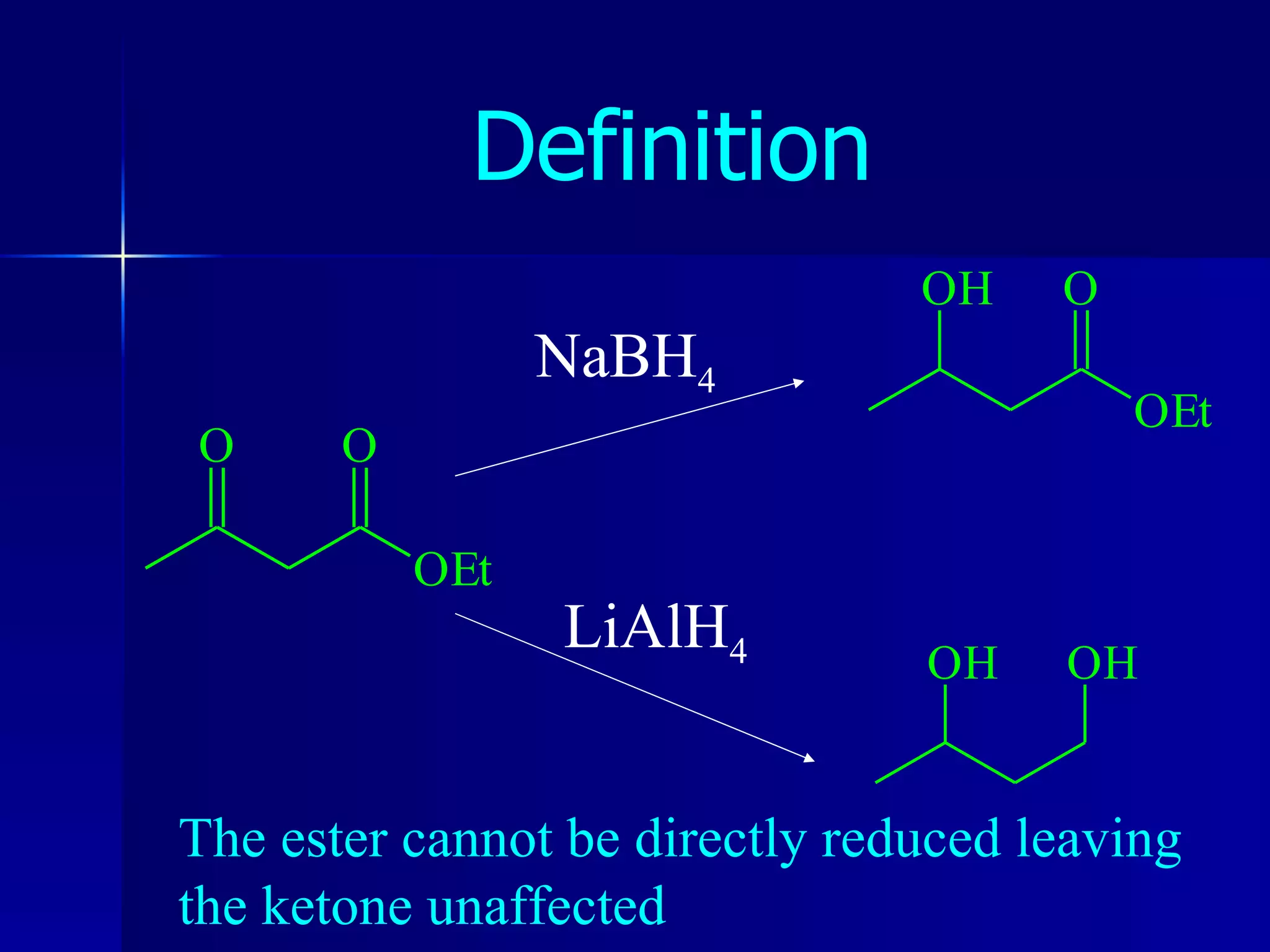
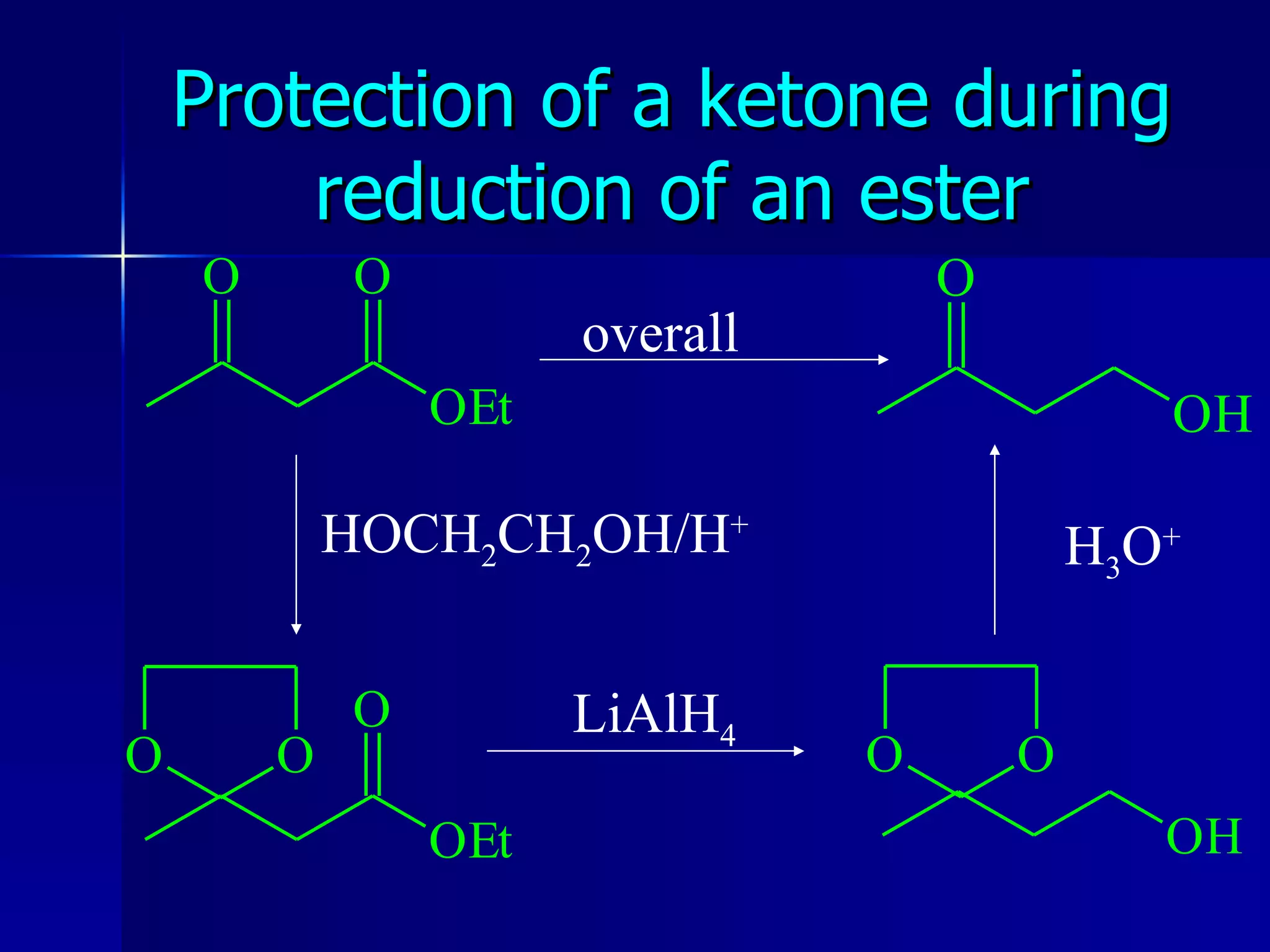
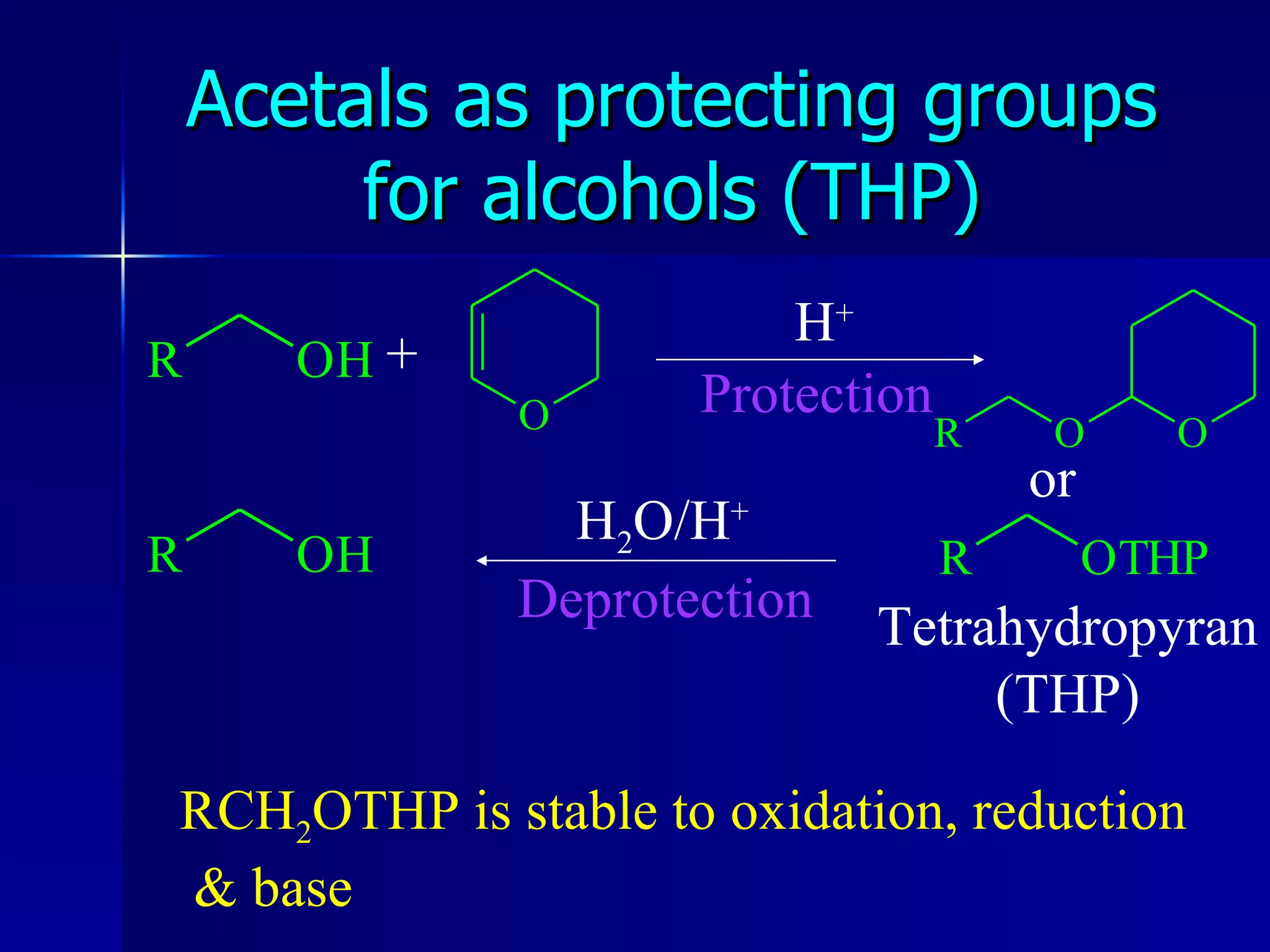
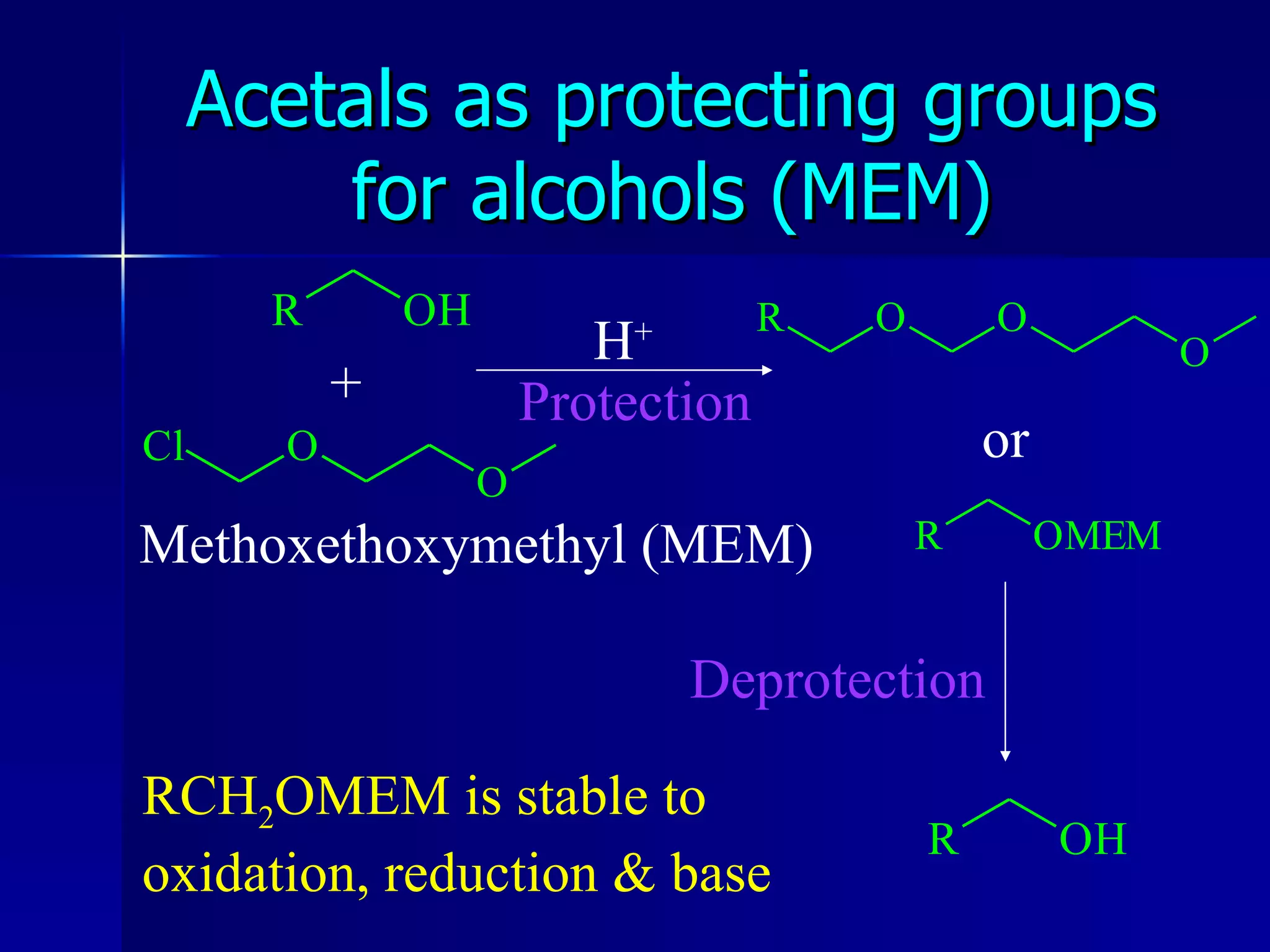
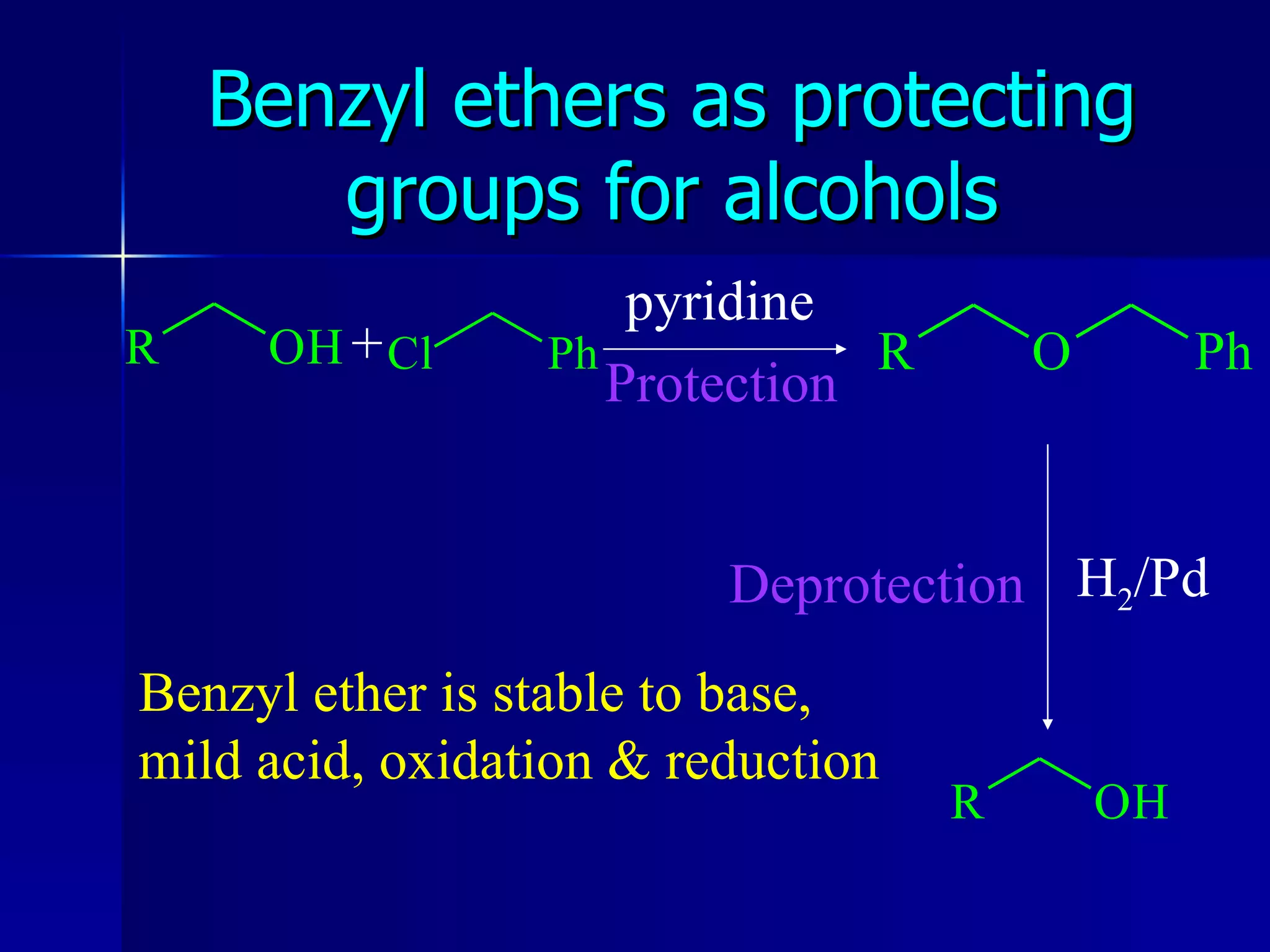
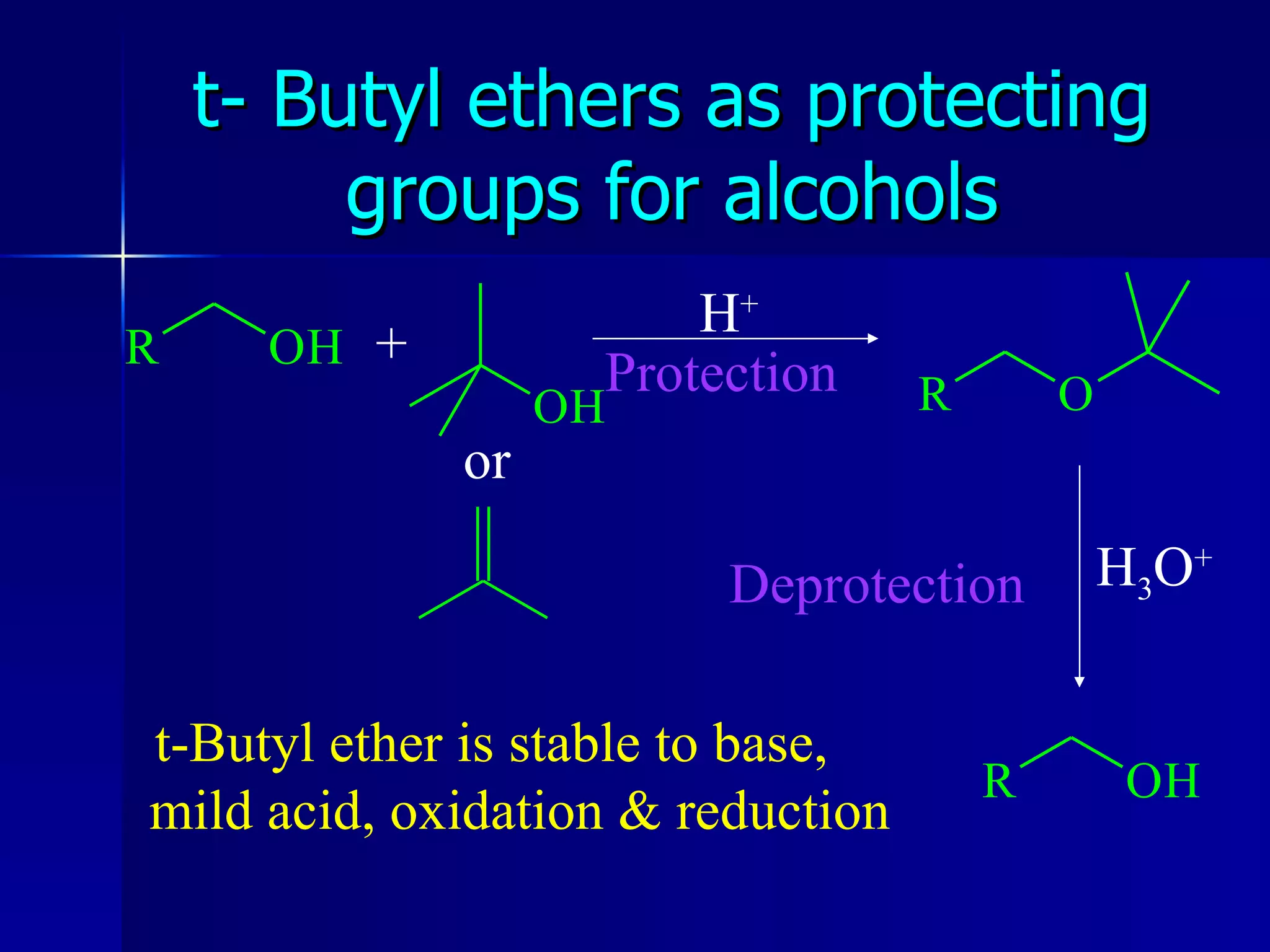
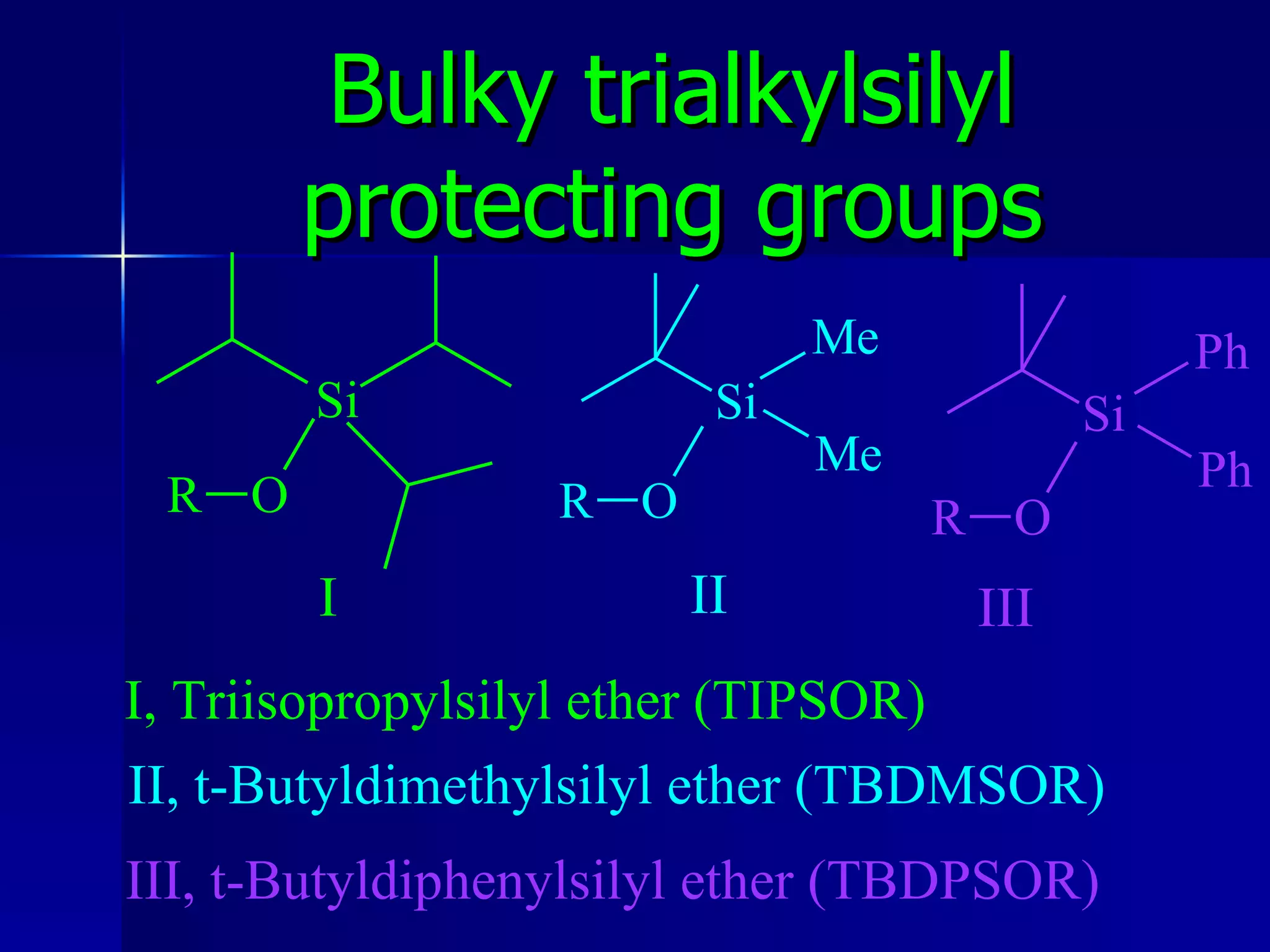
The document discusses protecting groups in organic synthesis. It defines protecting groups and lists criteria for effective protecting groups. It then discusses specific protecting groups for alcohols, including acetals like THP and MEM groups, alkyl ethers like benzyl and t-butyl ethers, and silyl ethers like trimethylsilyl ether. More bulky silyl protecting groups like TIPS, TBDMS, and TBDPS are also introduced to overcome issues with nucleophilic attack on trimethylsilyl ethers.