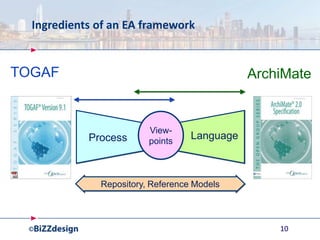
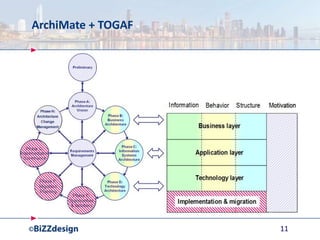
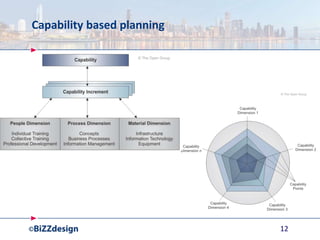
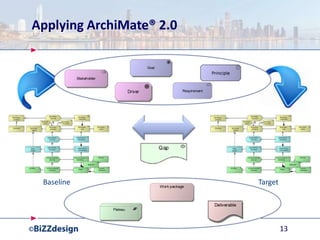
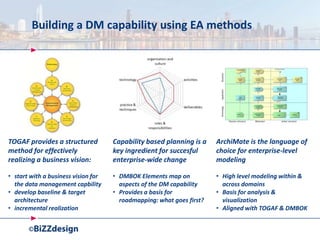
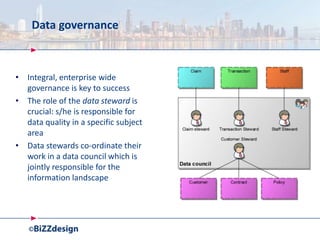
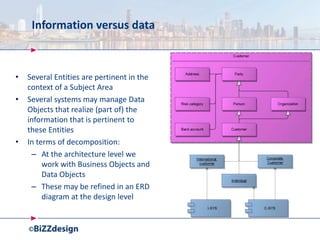
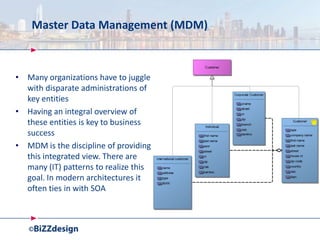
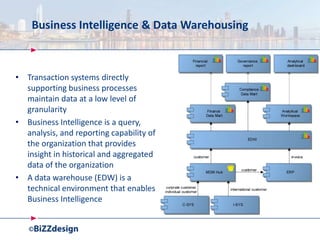
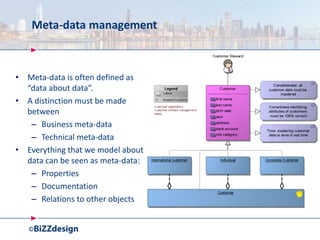
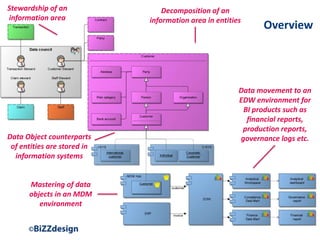
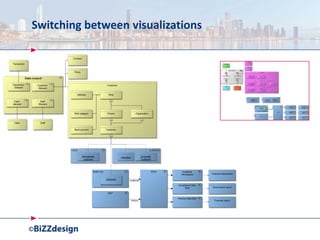
The document discusses building a strong data management capability using TOGAF and ArchiMate frameworks. It emphasizes the importance of data governance, master data management, and the role of data stewards in maintaining data quality across organizations. The continuous nature of data management is highlighted as crucial for sustainable business success and operational efficiency.






![Map out the enterprise
[Master] Data Management programs cause change: to
data, to systems, to business process, to people and to
the enterprise. An organization should map out their
organization to identify the data, systems, process and
people affected by the initiative and how they will be
affected.
-- Whitepaper “Why MDM projects fail and what this means for big data” by Entity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingastrongdmcapabilitywitheam-130604015141-phpapp02/85/Building-a-strong-Data-Management-capability-with-TOGAF-and-ArchiMate-8-320.jpg)