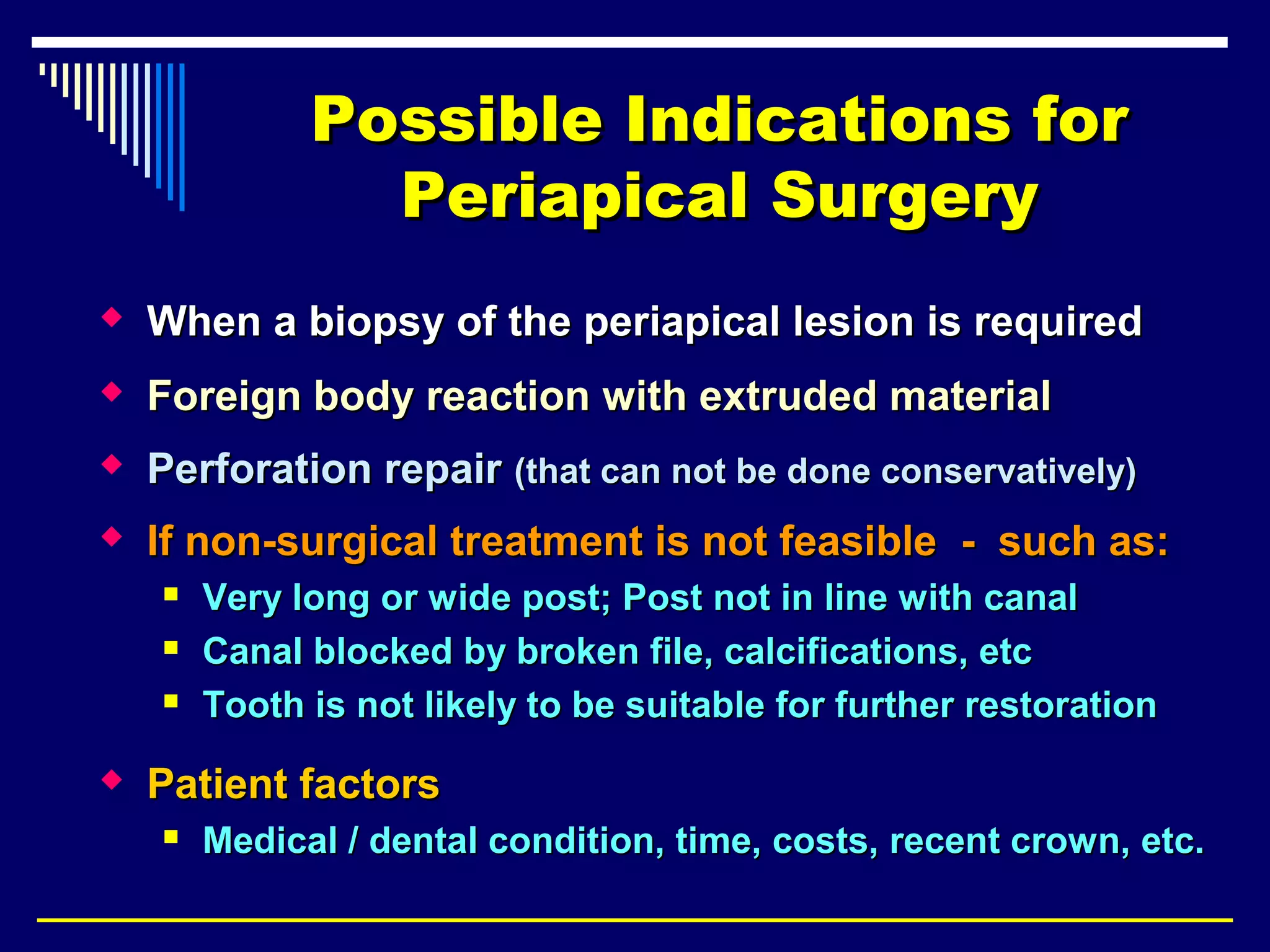
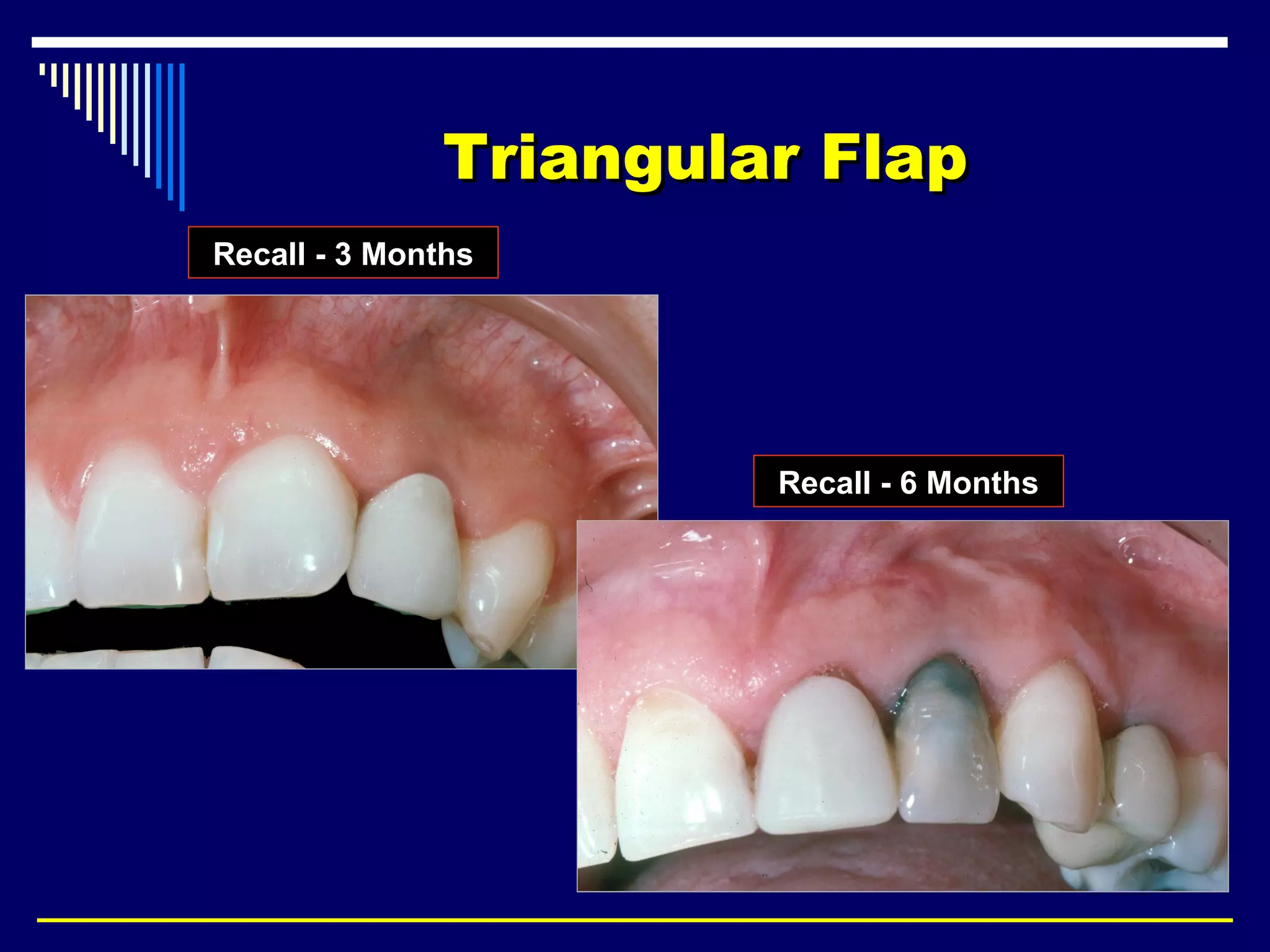
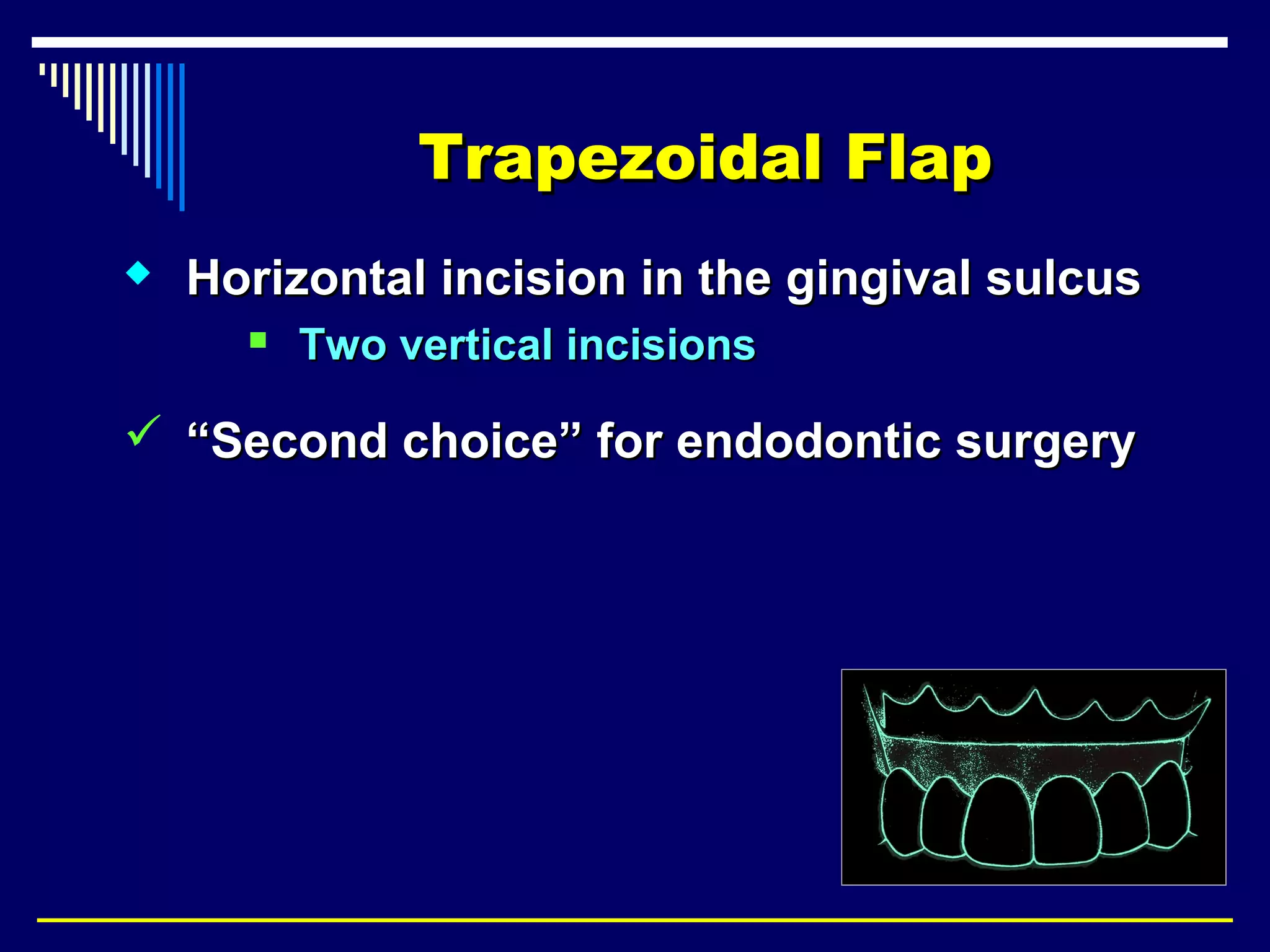
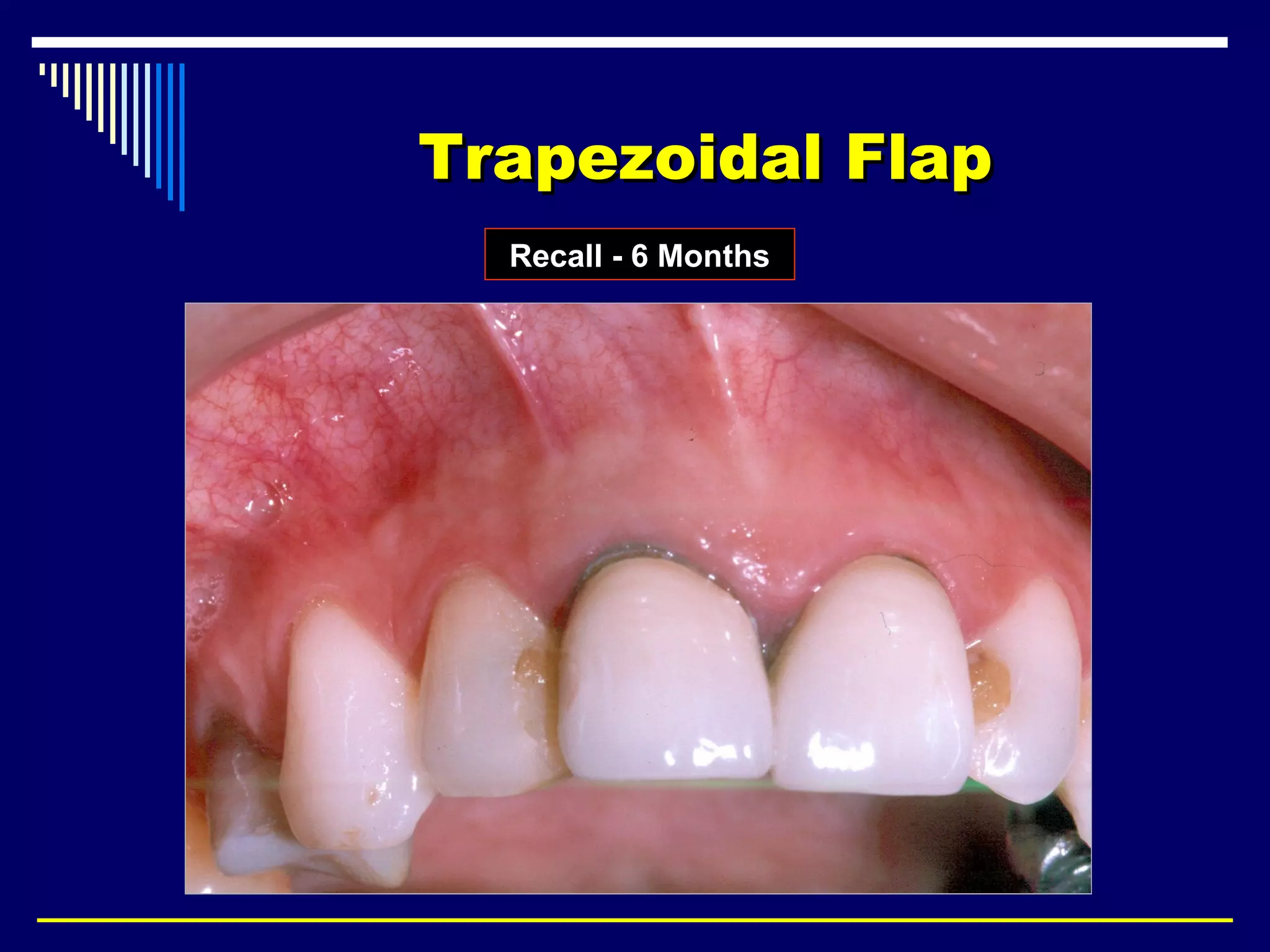
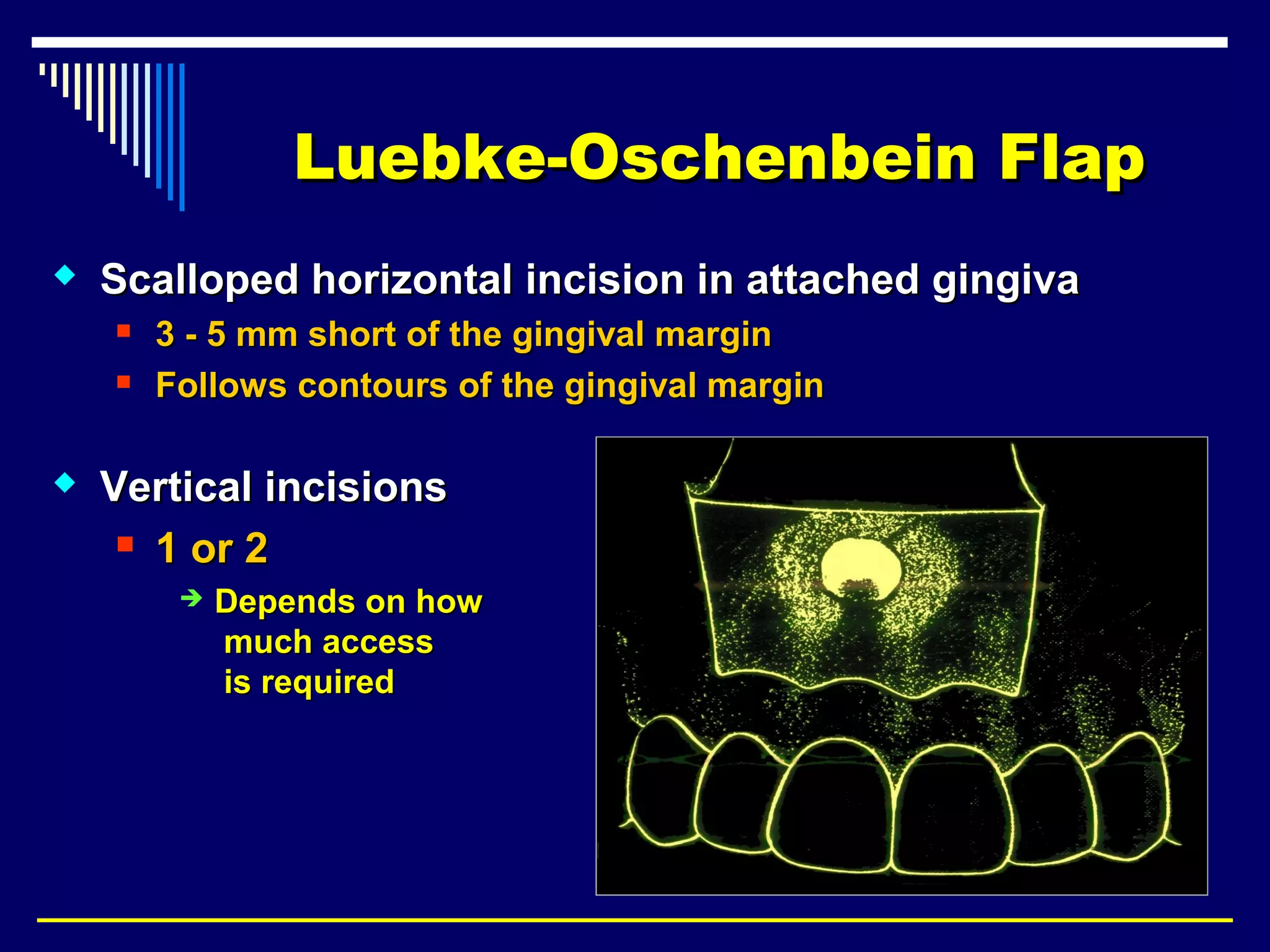
This document discusses endodontic surgical procedures and considerations for periapical surgery. It describes various endodontic surgical procedures including incision and drainage, periapical curettage, apicoectomy, retrograde endodontic treatment, perforation repair, root resection, hemisection, exploratory surgery, and intentional replantation. It also discusses possible indications for periapical surgery, considerations for surgery, flap designs including semi-lunar, gingival crest, triangular, trapezoidal, and Luebke-Oschenbein flaps. Potential post-operative sequelae and the lack of an ideal retrograde filling material are also covered.