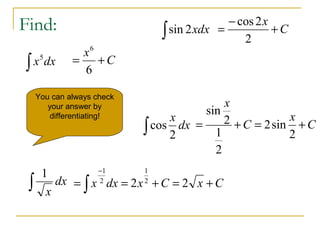
This document discusses antiderivatives and basic integration rules and formulas:
- The antiderivative of a function is the function whose derivative is the original function. Antiderivatives differ by a constant term.
- Basic formulas are provided for finding antiderivatives of common functions like polynomials, trigonometric functions, and their inverses.
- Integration rules allow for evaluating integrals of sums and products of functions using properties of antiderivatives.
- Worked examples demonstrate applying formulas and rules to find antiderivatives of given functions.