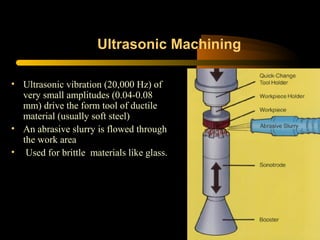
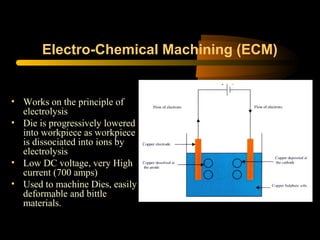
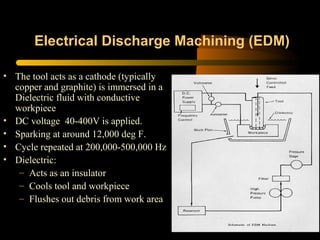
This document provides an overview of non-conventional machining processes including ultrasonic machining, water jet machining, electro-chemical machining, electro-chemical grinding, and electrical discharge machining. The objective is to make audiences aware of the merits of these non-conventional processes over traditional machining for machining complex, less machinable, or brittle materials in a faster and more economical way using computer-controlled processes with minimal human intervention. An outline and brief description is given for each non-conventional machining technique.