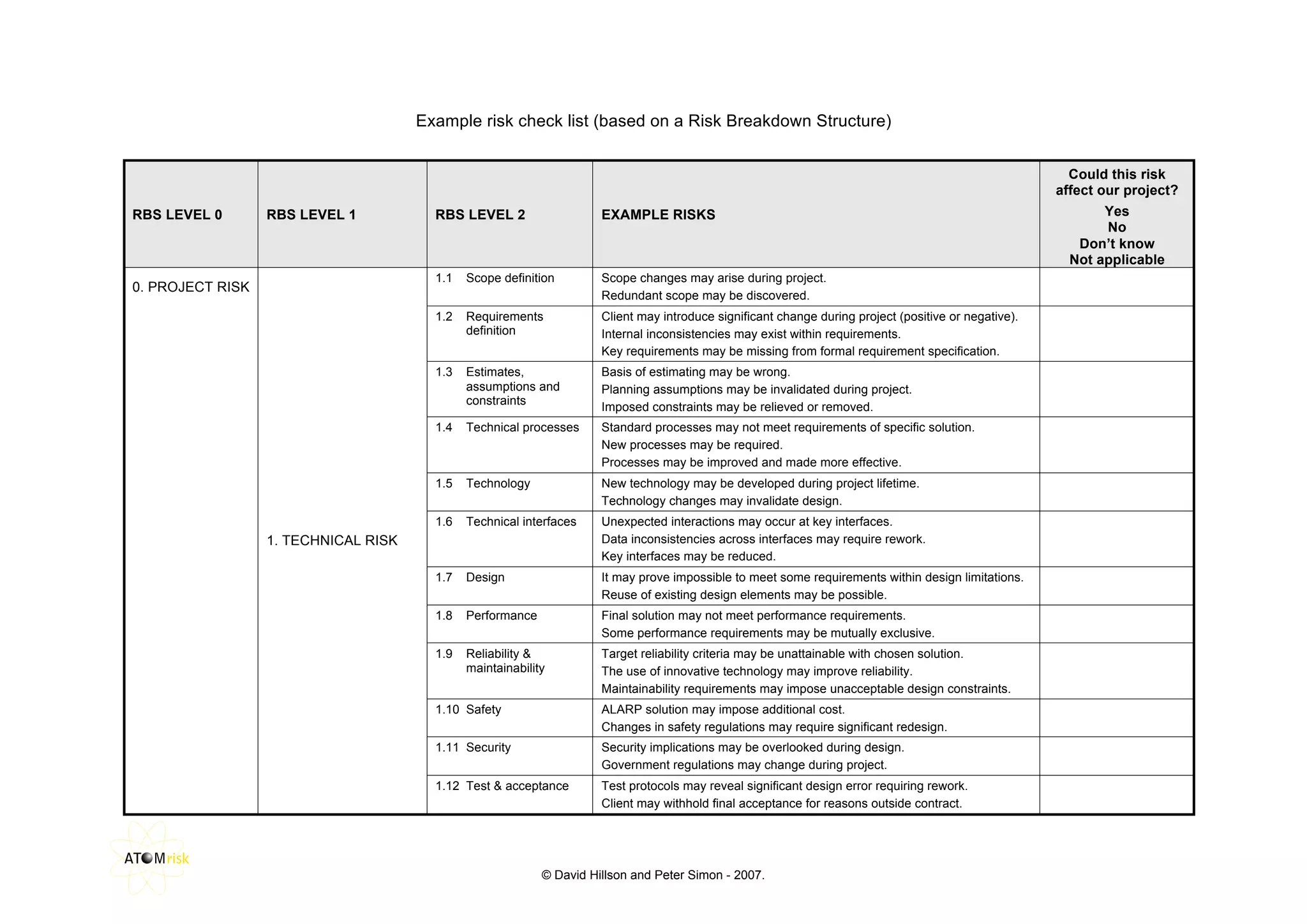
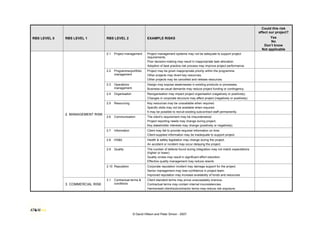
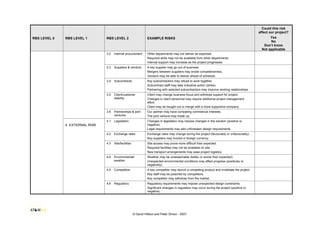
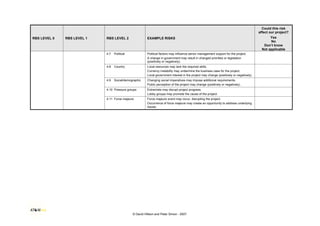
This document provides a risk breakdown structure and example risks for a project. It lists risks across four levels - project risks, technical risks, management risks, and external risks. Example risks listed include scope changes, requirement changes, cost estimate inaccuracies, resource availability issues, regulatory changes, and other factors that could positively or negatively impact the project. The document is intended to help identify risks that could affect a given project.