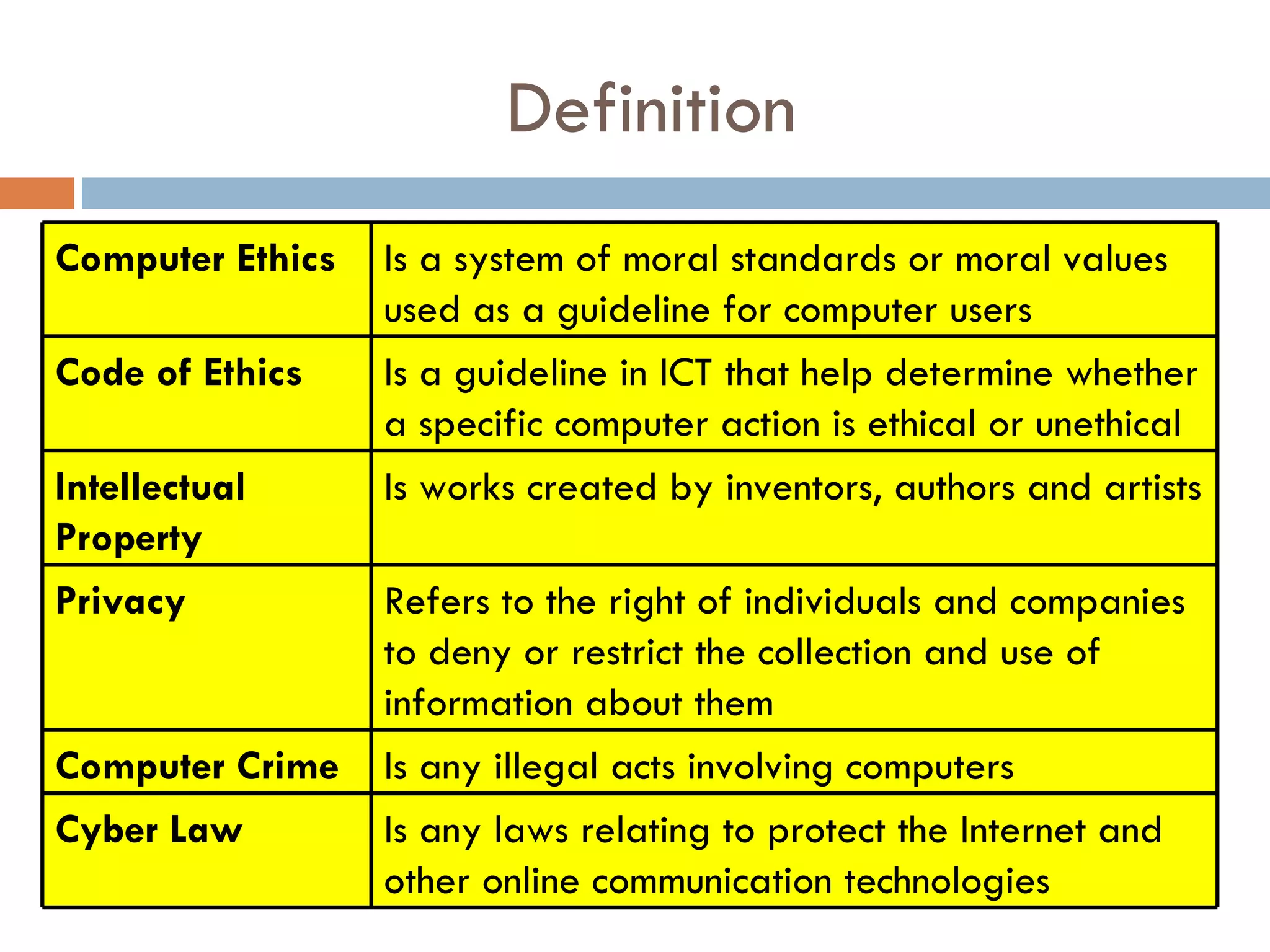
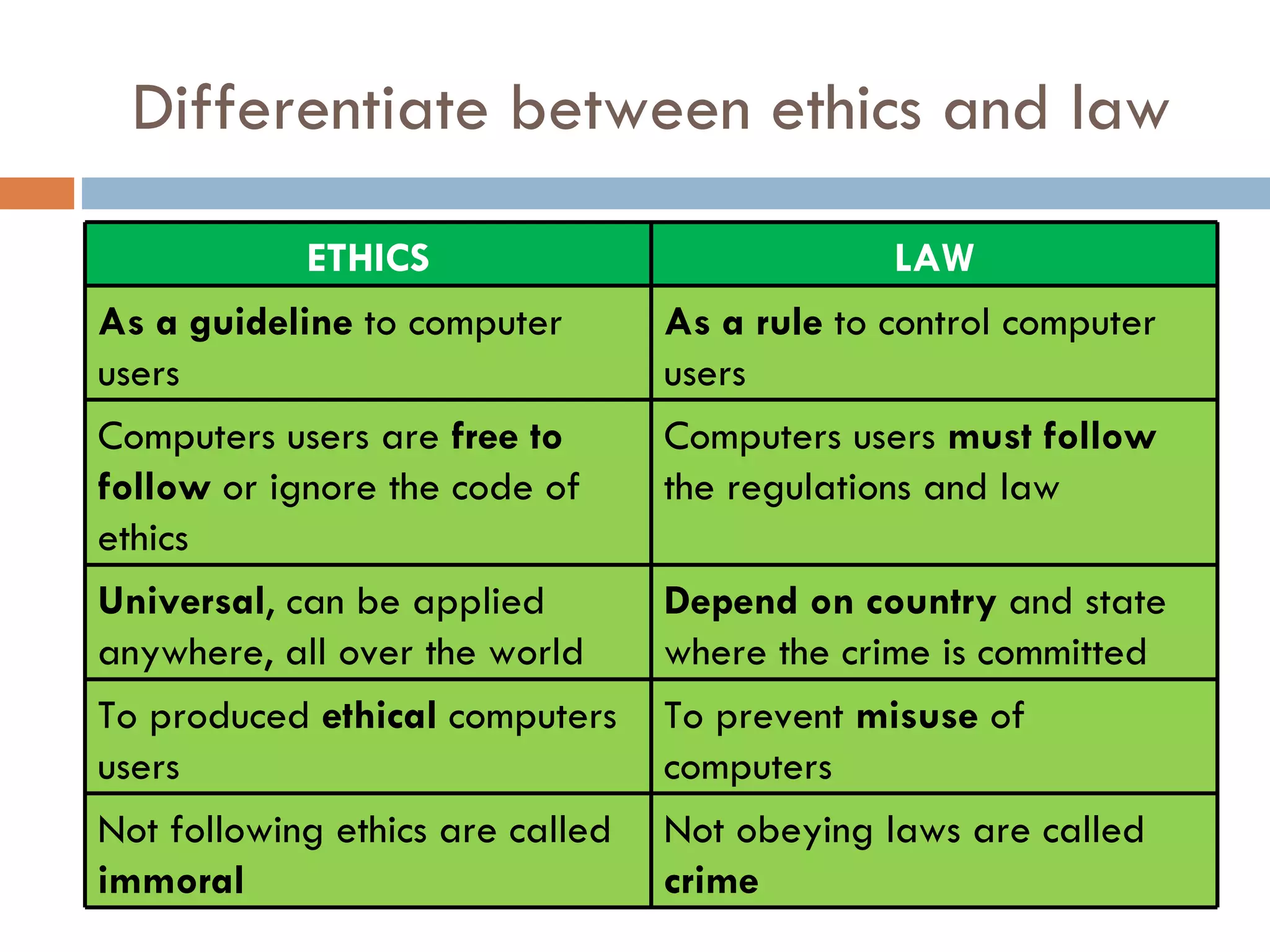
This document defines key concepts related to computer ethics, law, and crimes. It discusses the differences between ethics and law, outlines four types of intellectual property laws, and describes ways to protect privacy online. Authentication methods like passwords, smart cards, and biometrics are explained. The effects of pornography and slander are contrasted. Examples of computer crimes and the purpose of cyber laws in Malaysia are provided.