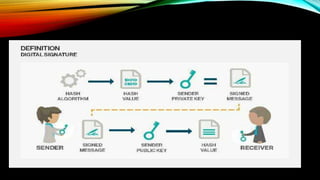
The document provides an overview of cyber laws, emphasizing their importance in regulating the internet and protecting individuals from cybercrime, which encompasses various offenses against persons, property, and society. It details aspects such as electronic signatures, intellectual property rights, data protection, and the Information Technology Act of 2000 in India, highlighting key provisions and offenses under these laws. Cyber laws aim to balance the rights of individuals with the requirements of commerce and technology in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.