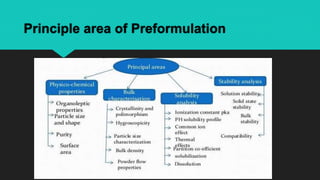
The document discusses the importance of pharmaceutical preformulation in Bangladesh, detailing its goals, usefulness, and various classes involved in the preformulation process. It highlights the significance of characterizing the physicochemical properties of drug substances to ensure the development of safe and effective dosage forms. Furthermore, it outlines the steps and parameters evaluated during preformulation studies, emphasizing their role in successful drug formulation and development.