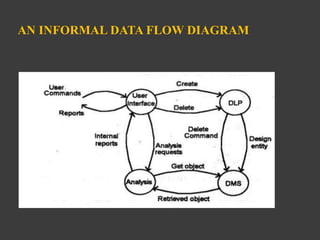
This document outlines the typical sections and contents of a software requirements specification (SRS). It discusses 12 common sections of an SRS, including an overview, development environments, external interfaces, functional requirements, performance requirements, exception handling, implementation priorities, foreseeable changes, acceptance criteria, design guidance, a cross-reference index, and a glossary. Key sections describe functional requirements using relational or state-oriented notation, performance characteristics like response times, and exception handling categories. The SRS should have properties like being correct, complete, consistent, unambiguous, functional, and verifiable.