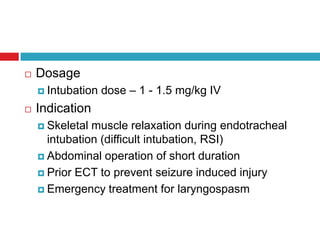
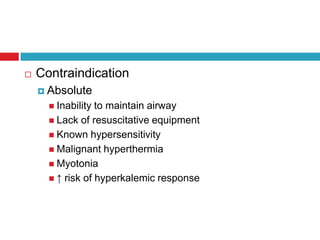
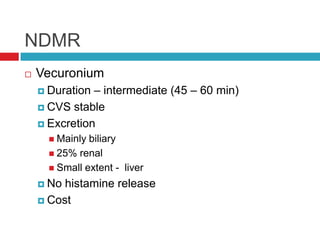
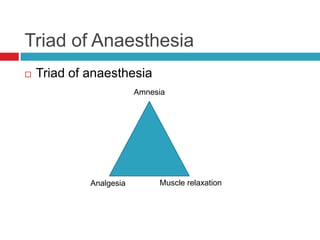
Muscle relaxants are used as part of the triad of anesthesia to induce muscle relaxation. They are classified based on their type of neuromuscular blockade and duration of action. The choice of muscle relaxant depends on factors like duration of action, cost, side effects, and route of excretion. Succinylcholine is a depolarizing muscle relaxant that acts quickly but has a short duration, while non-depolarizing muscle relaxants like vecuronium and atracurium have intermediate durations and are commonly used. Contraindications for muscle relaxants include inability to maintain an airway and prior conditions affecting neuromuscular function or potassium levels.


![HyperkalemiaUsually ↑ plasma [K+] 0.5 mEq/LAbnormal high flux of K+ occurs in Extensive third degree burnsNerve damage or neuromuscular diseases](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musclerelaxants-110826083636-phpapp02/85/Muscle-relaxants-9-320.jpg)