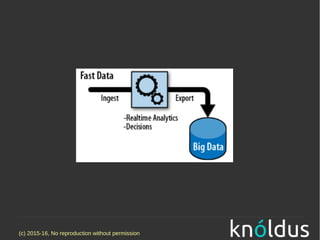
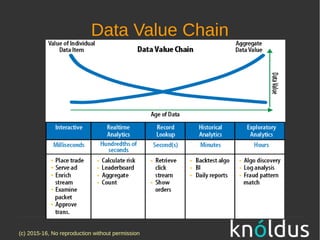
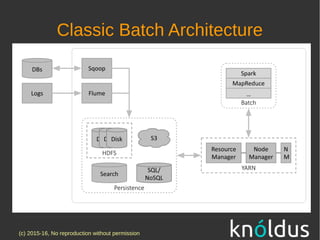
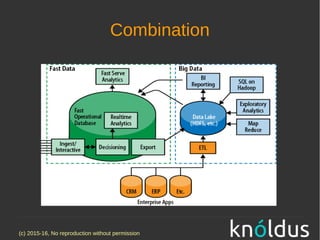
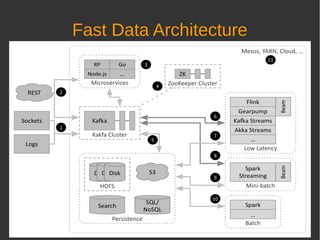
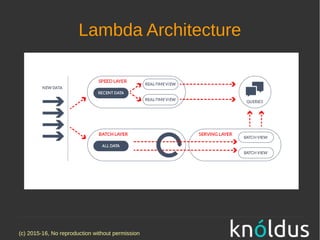
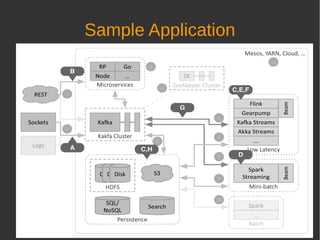
The document discusses fast data architectures. It notes that data is doubling every two years and will grow exponentially over this decade. Fast data involves streaming data from sources like IoT sensors, clicks, and interactions that can occur hundreds to millions of times per second. This requires an architecture that can process data in real-time versus traditional batch processing. An effective fast data architecture incorporates streaming data sources, microservices, stream processing tools like Kafka and Flink, and batch processing for analytics. The core principles involve treating all data as events, using message queues for integration, and ensuring message processing guarantees.