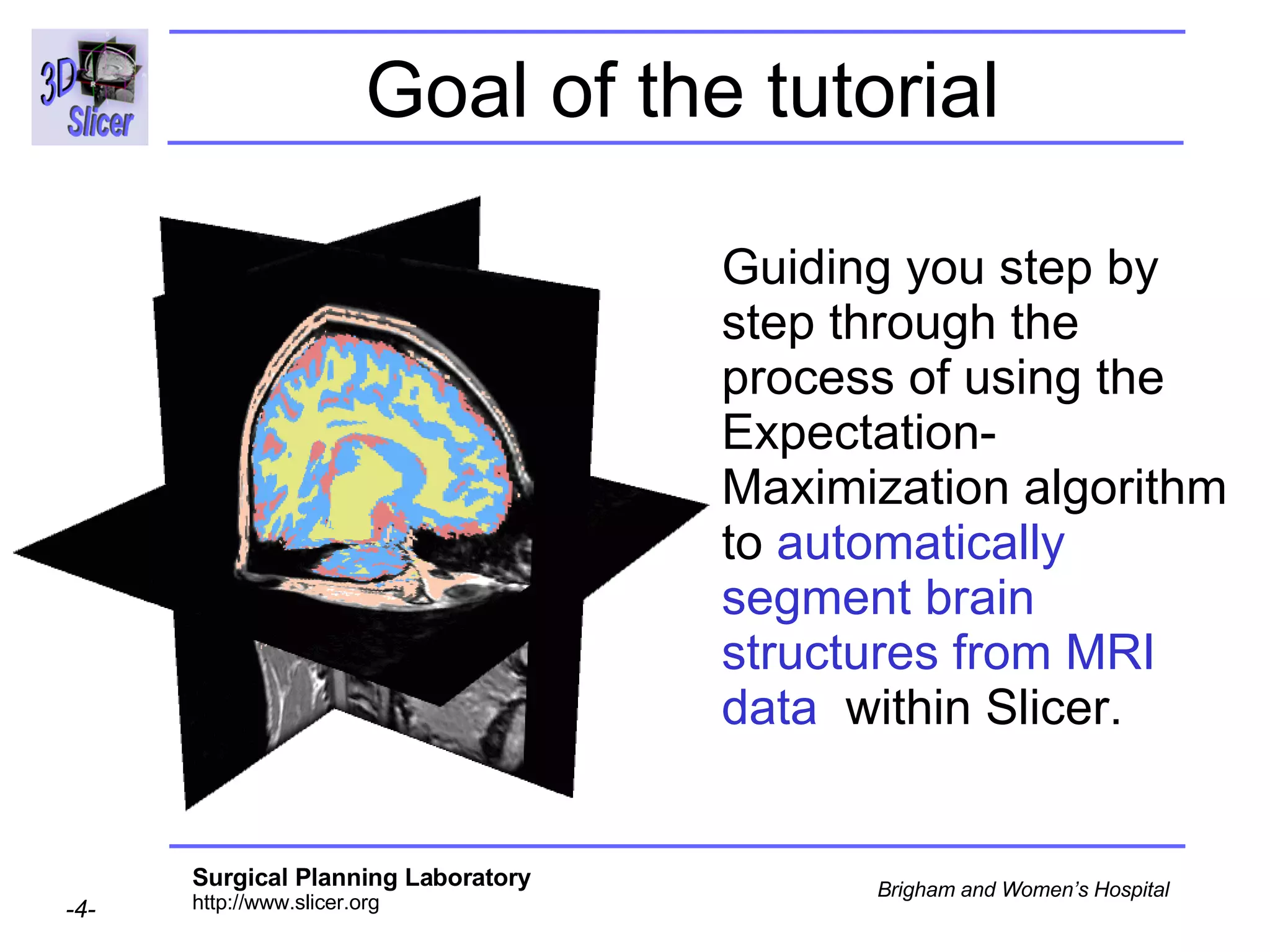
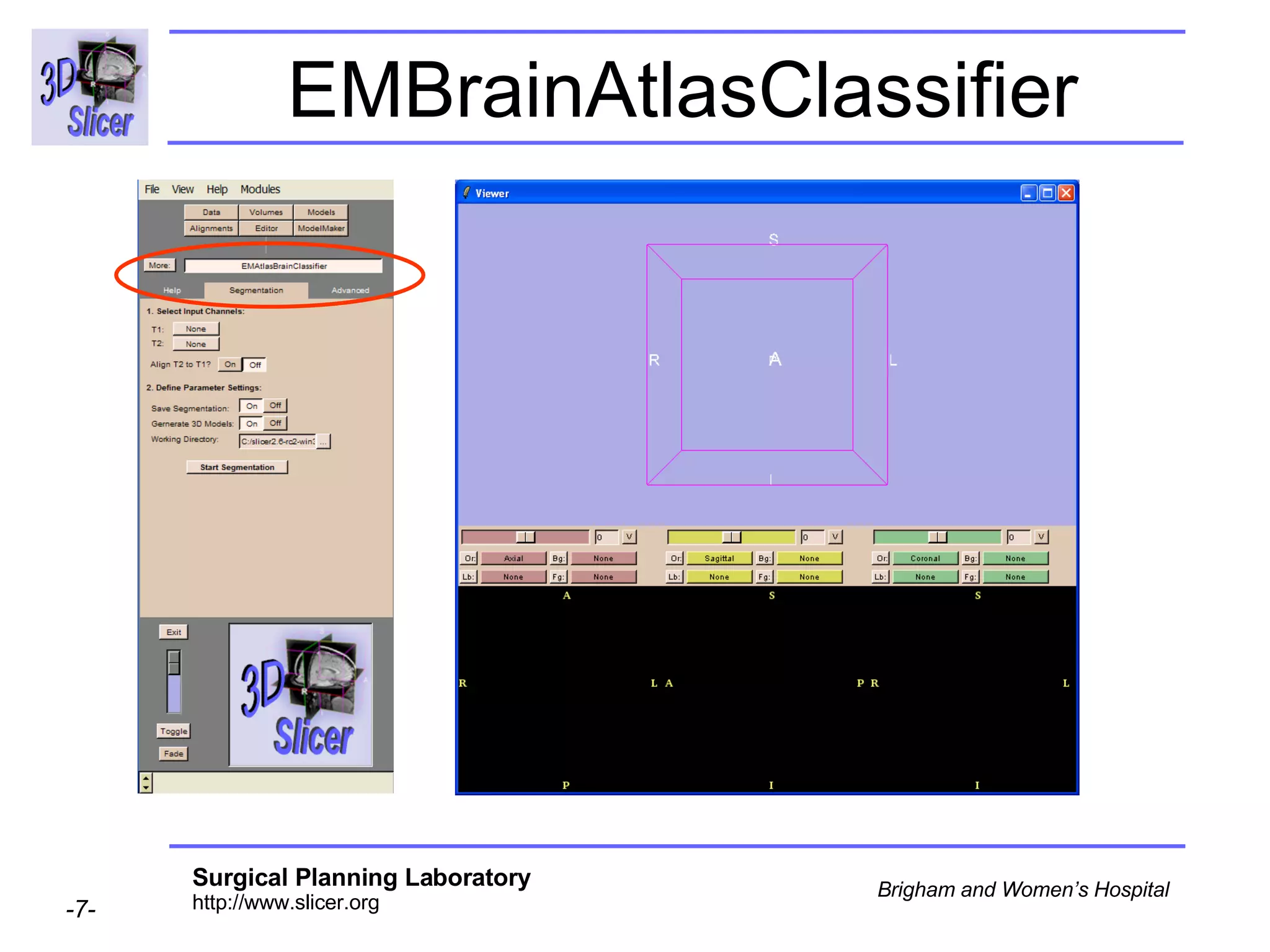
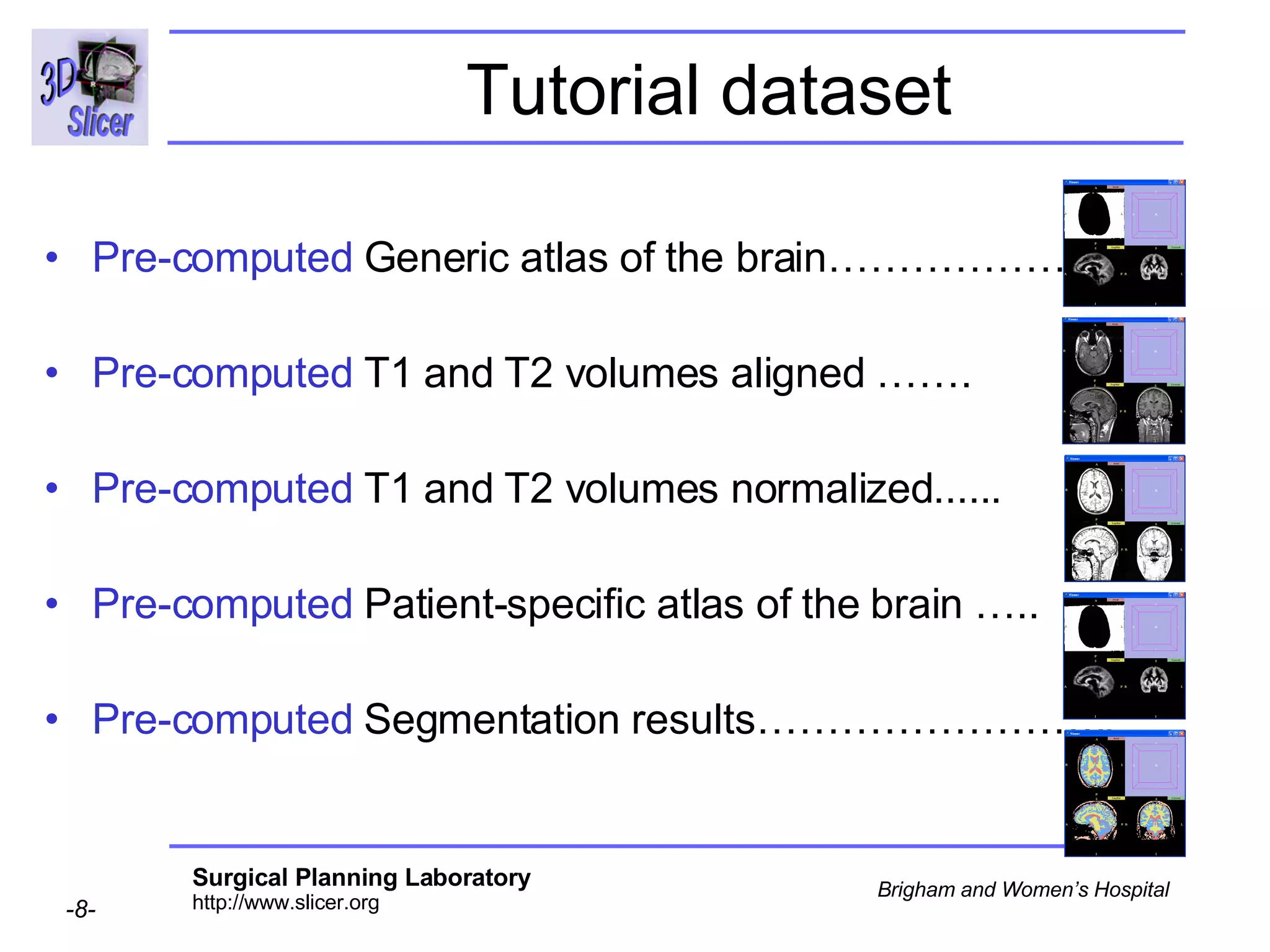
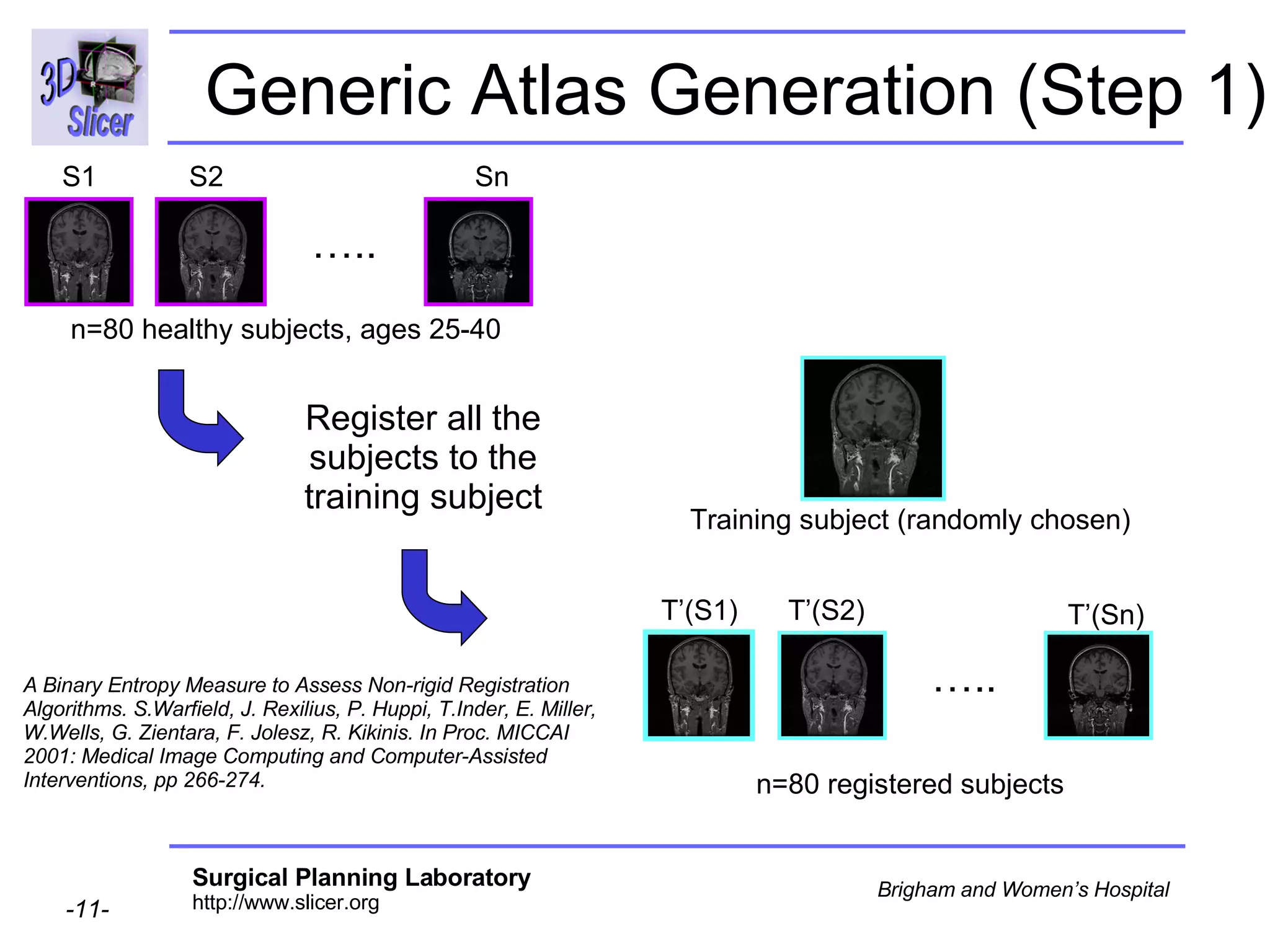
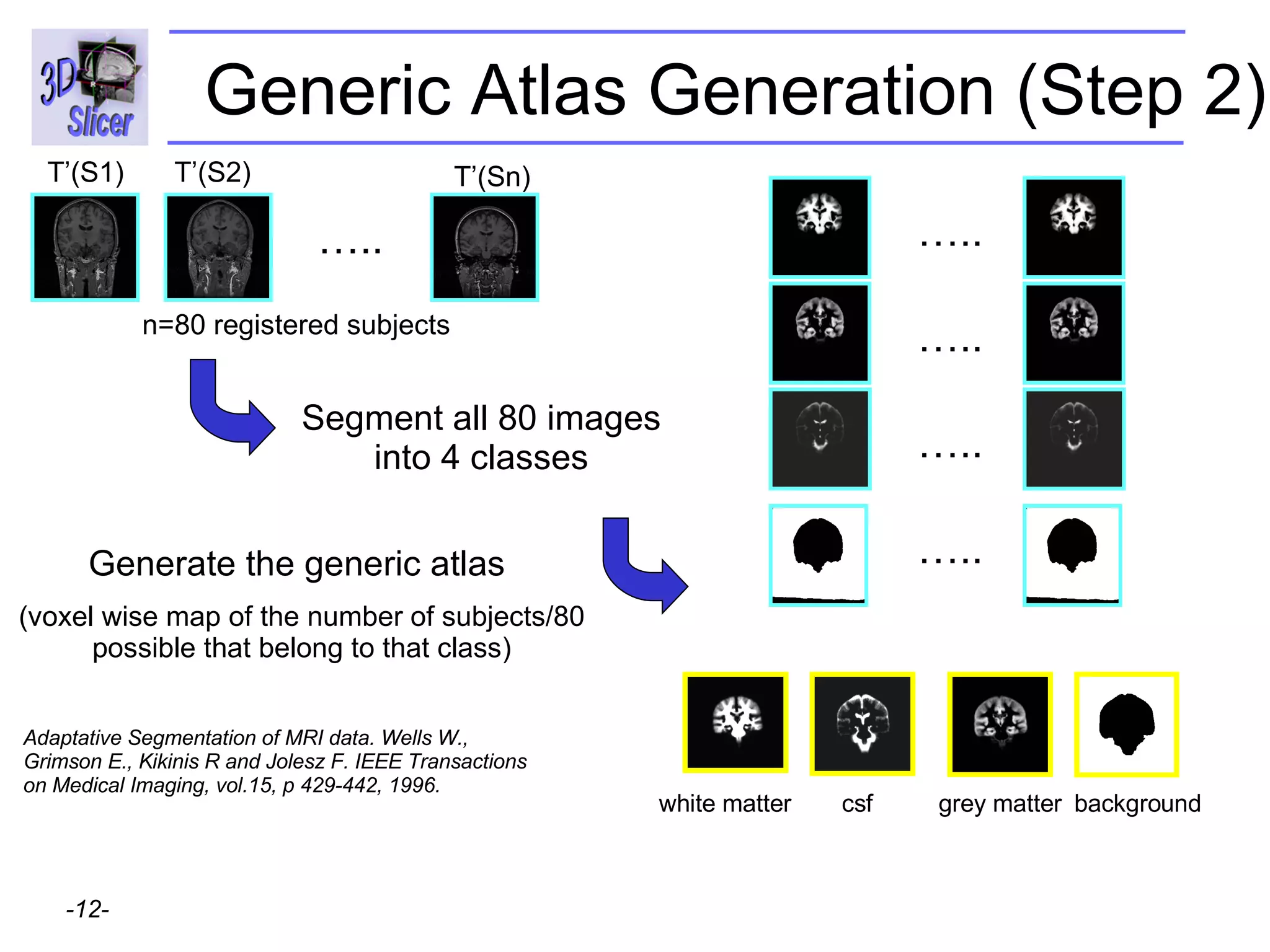
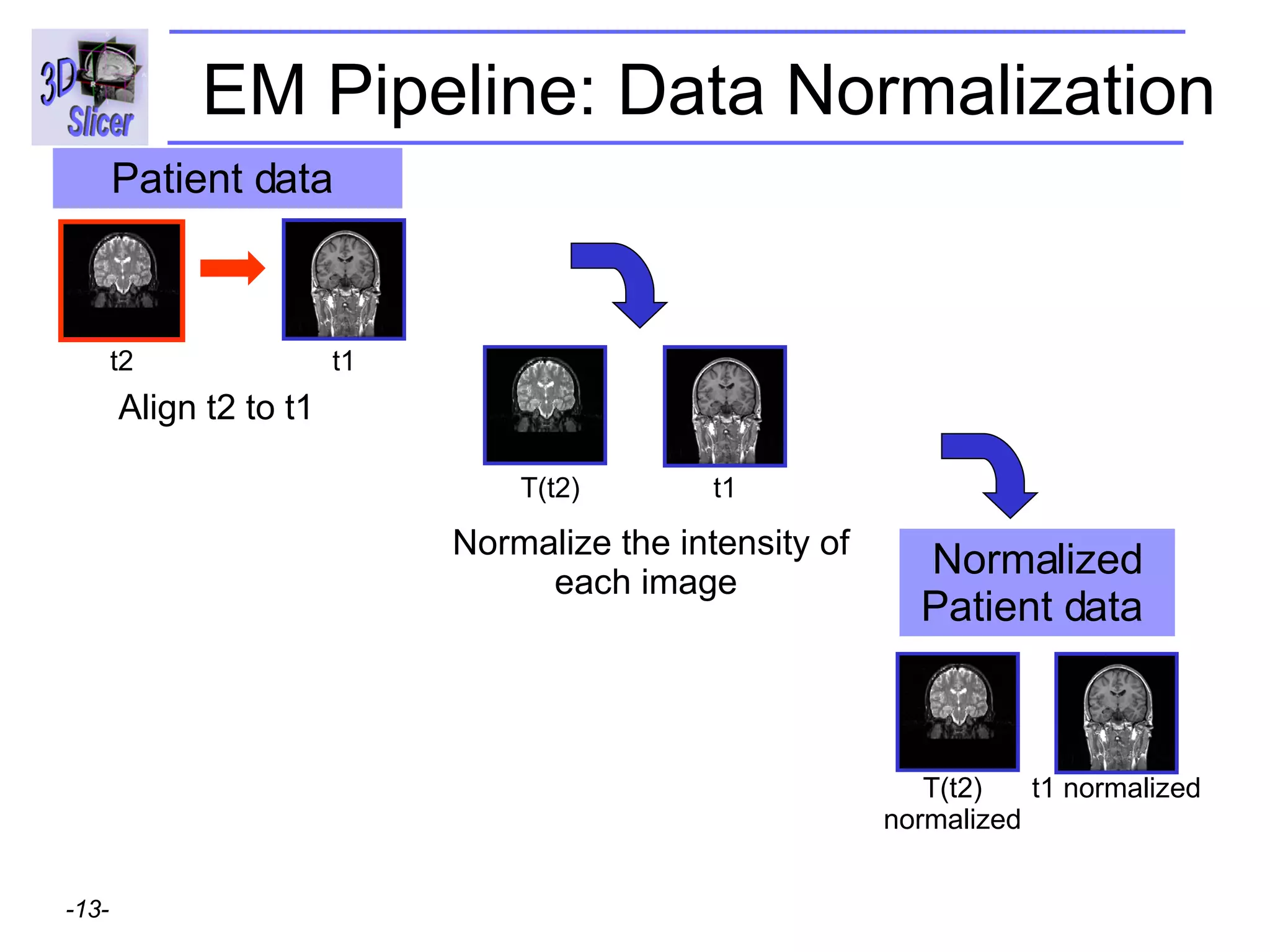
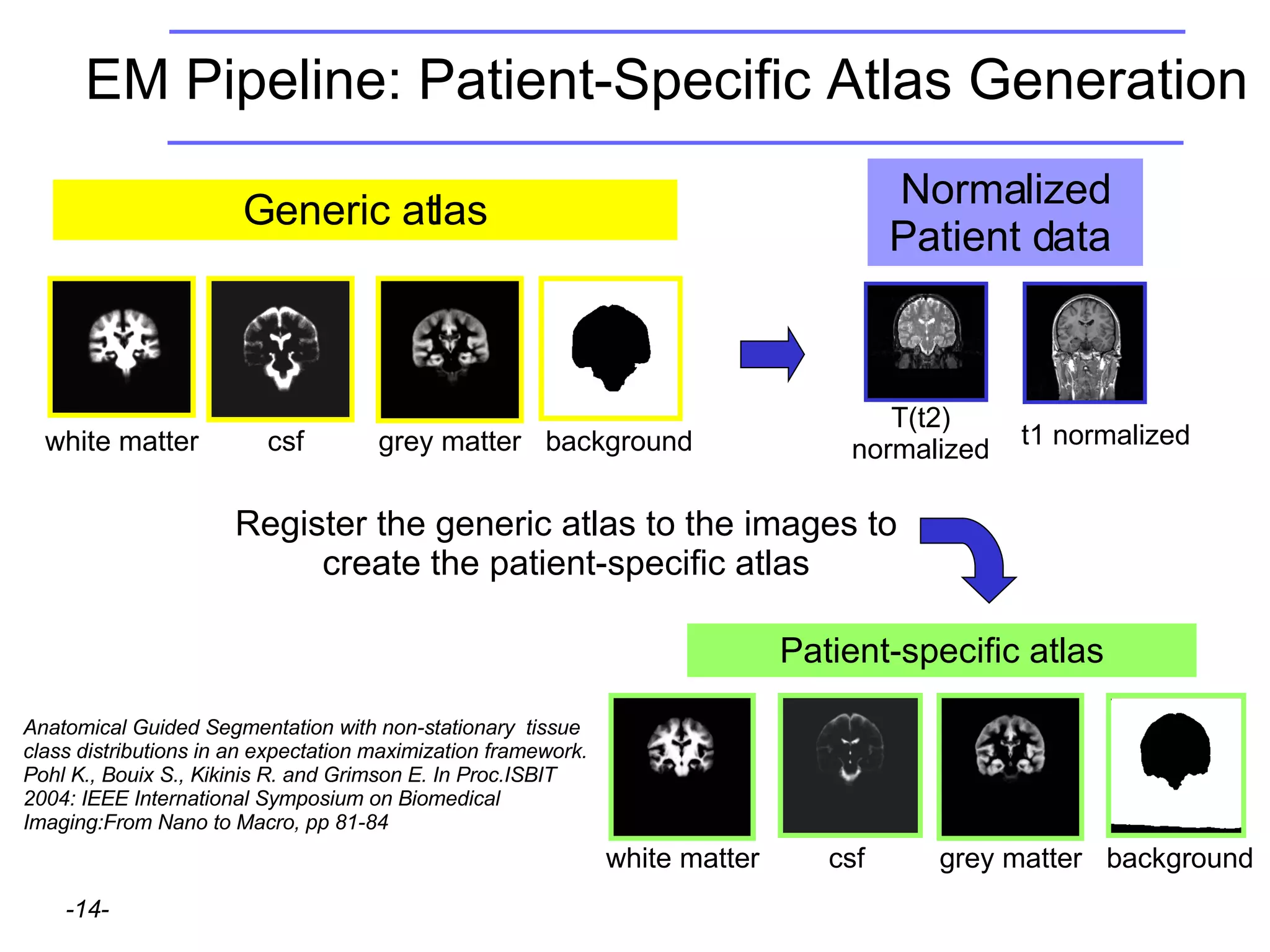
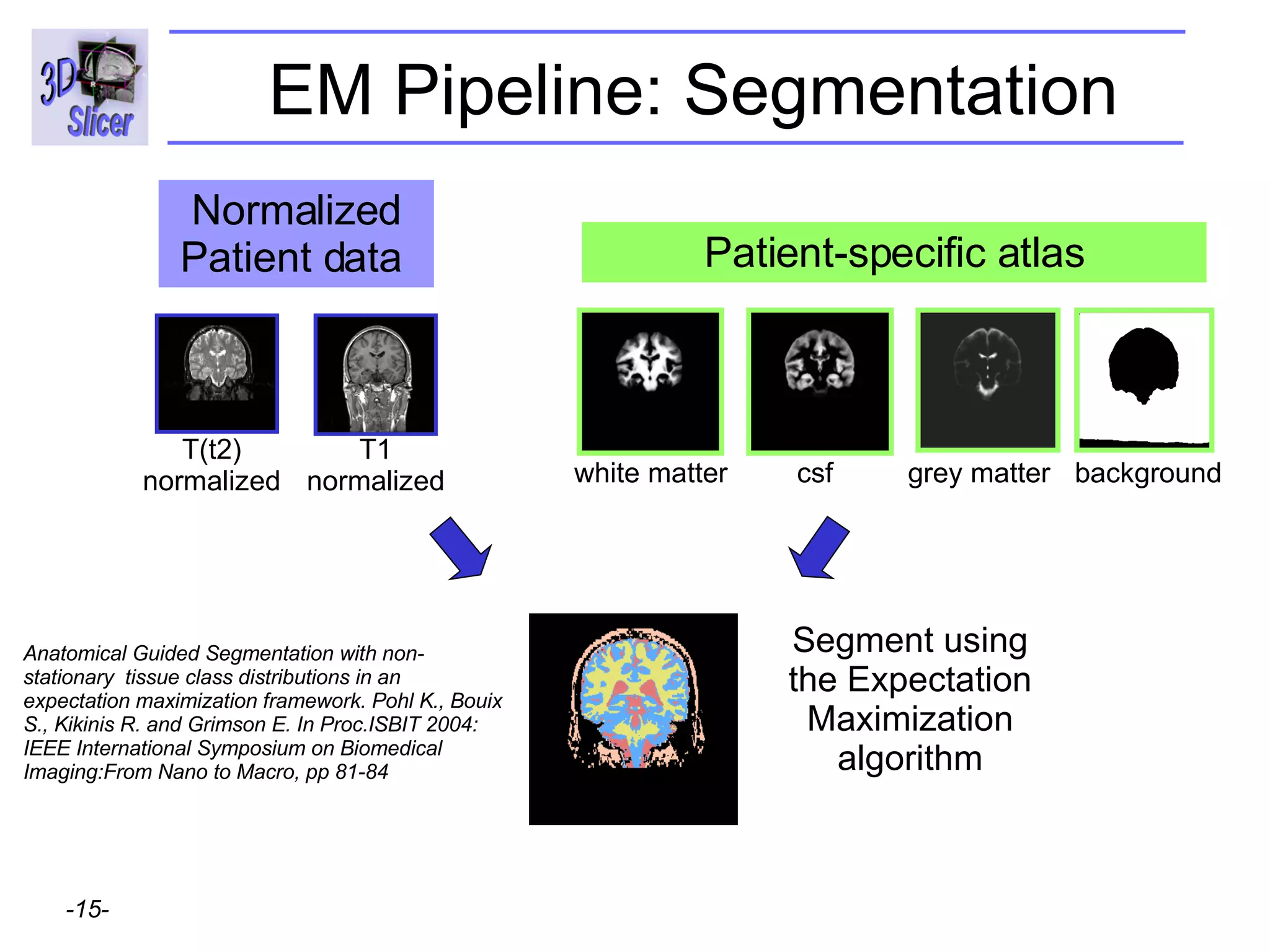
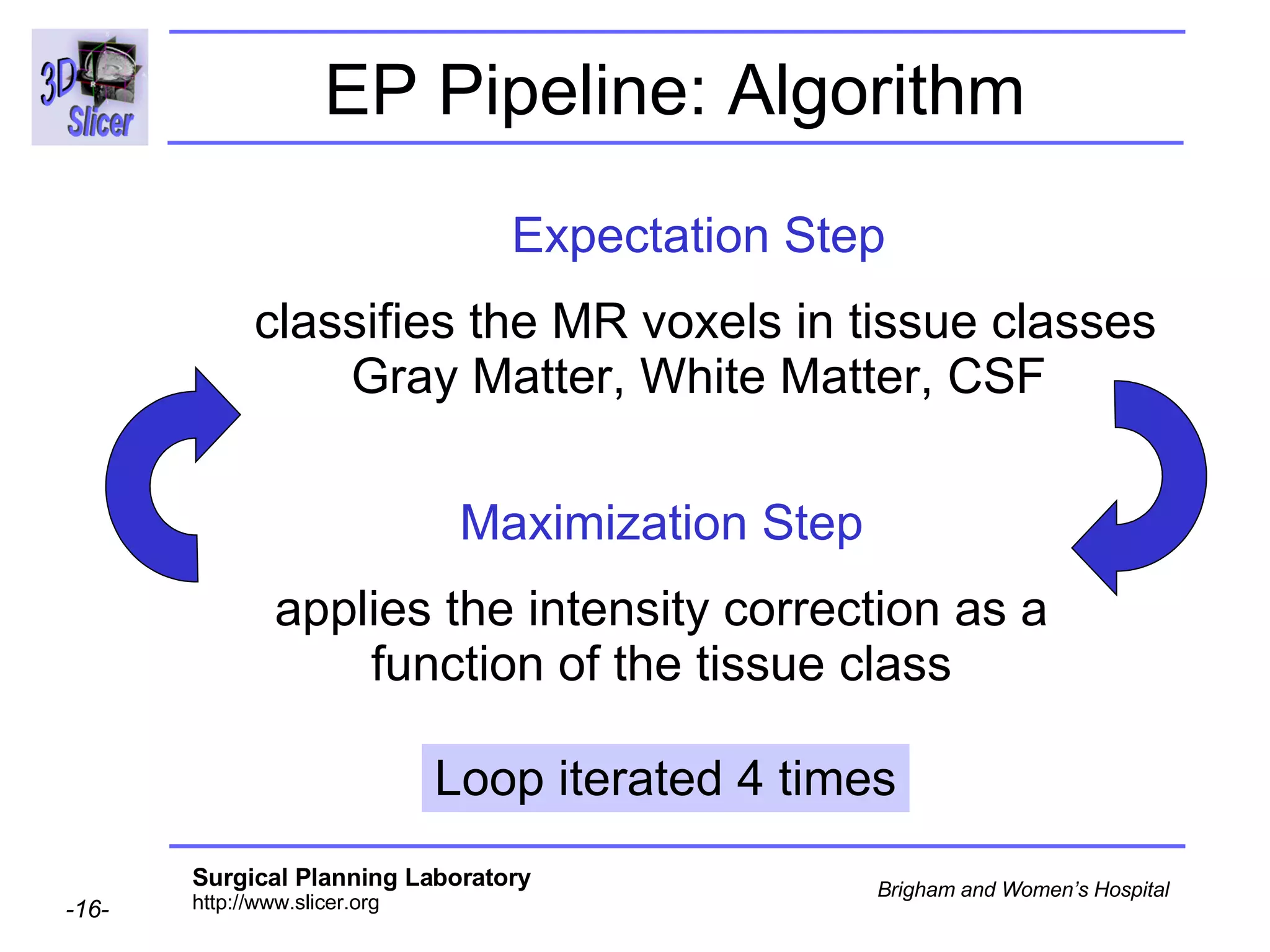
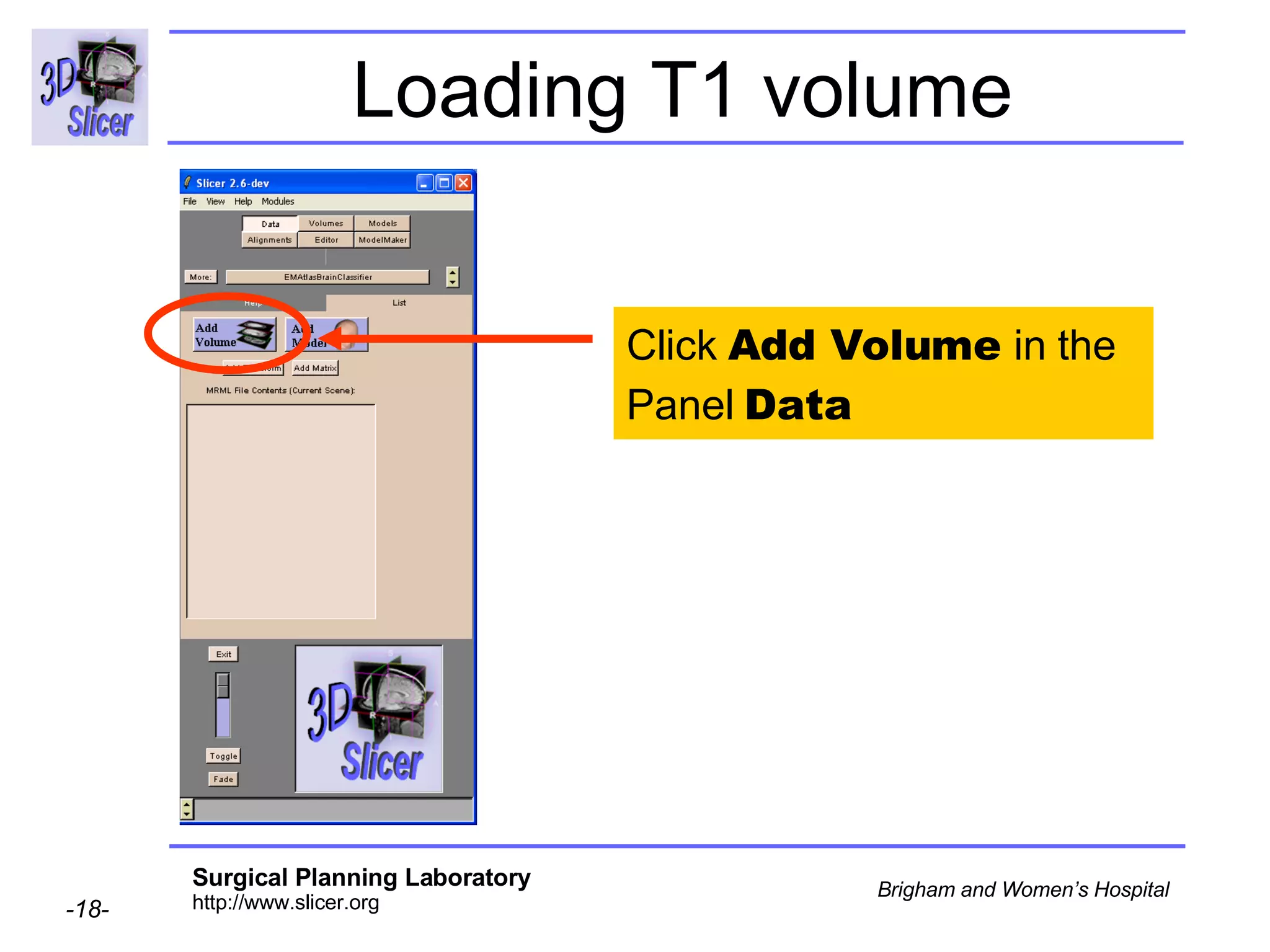
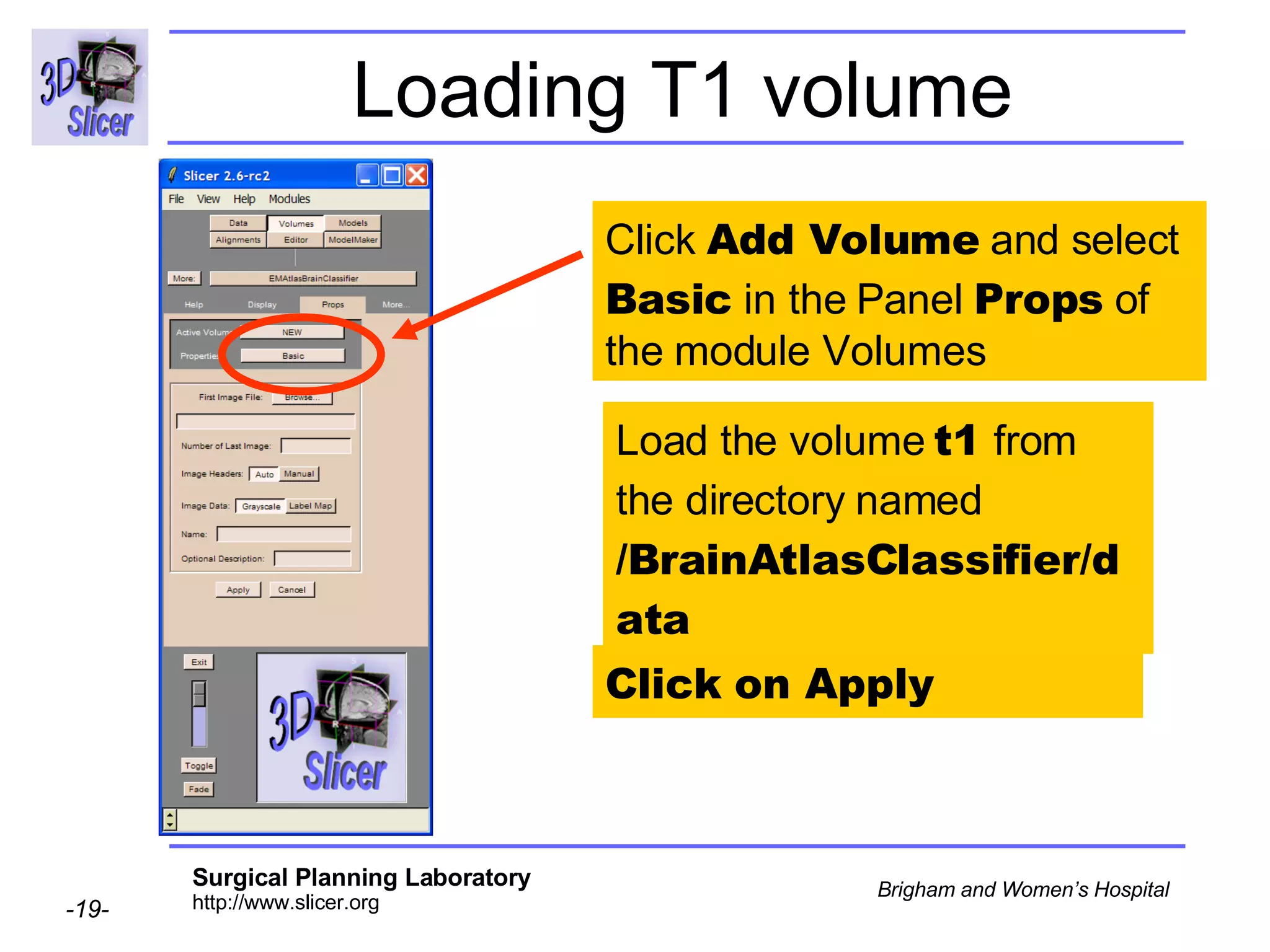
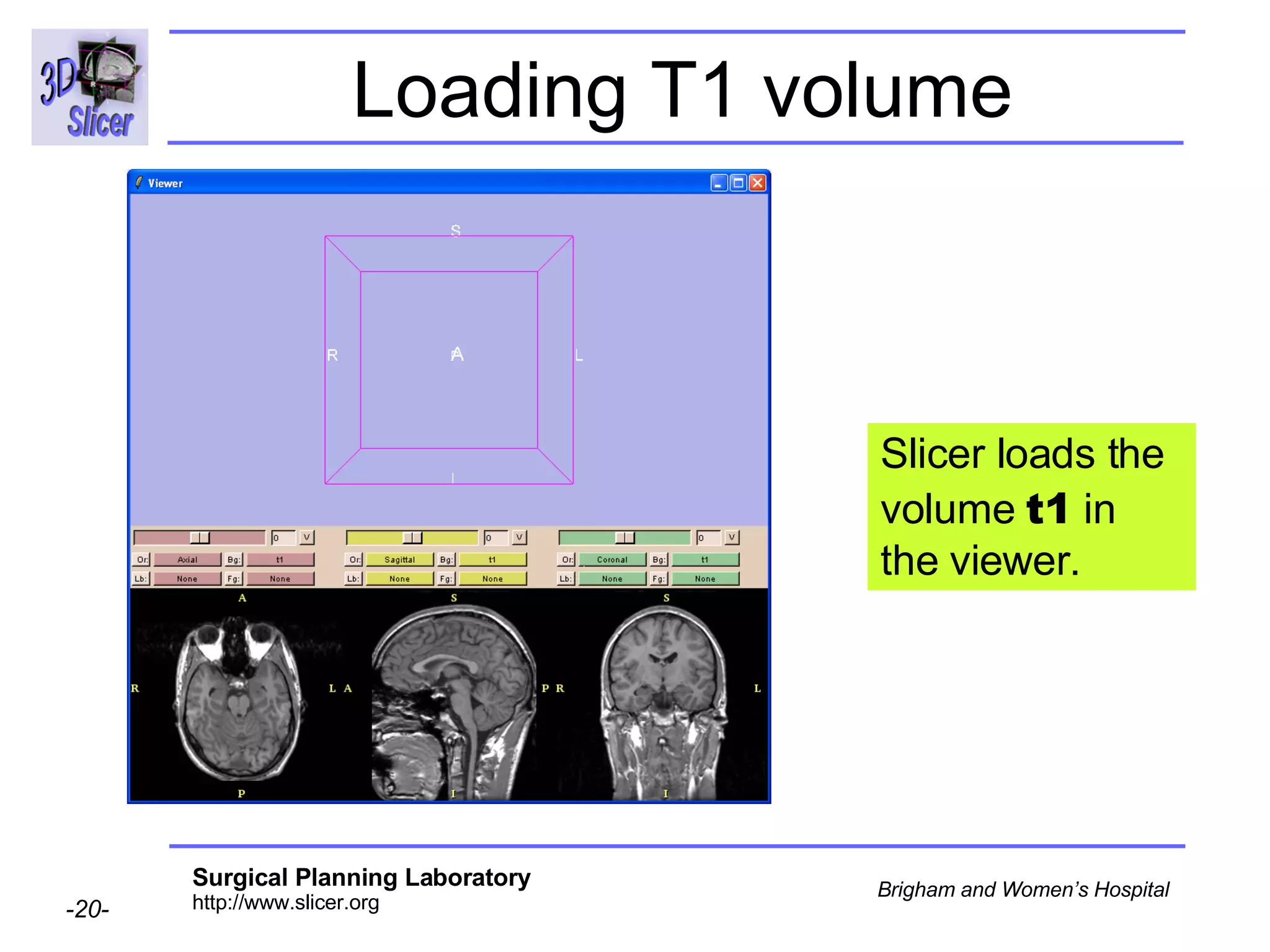
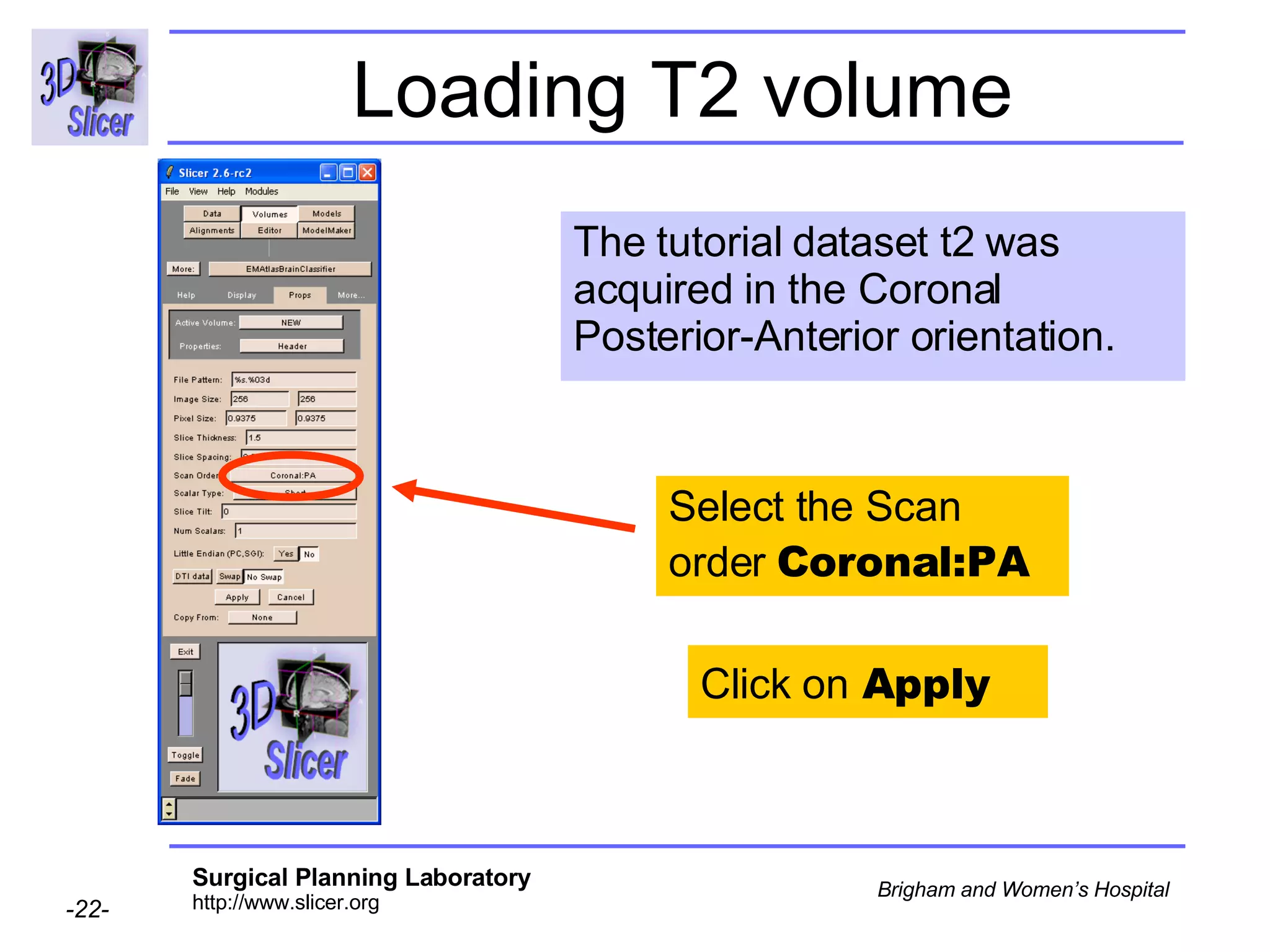
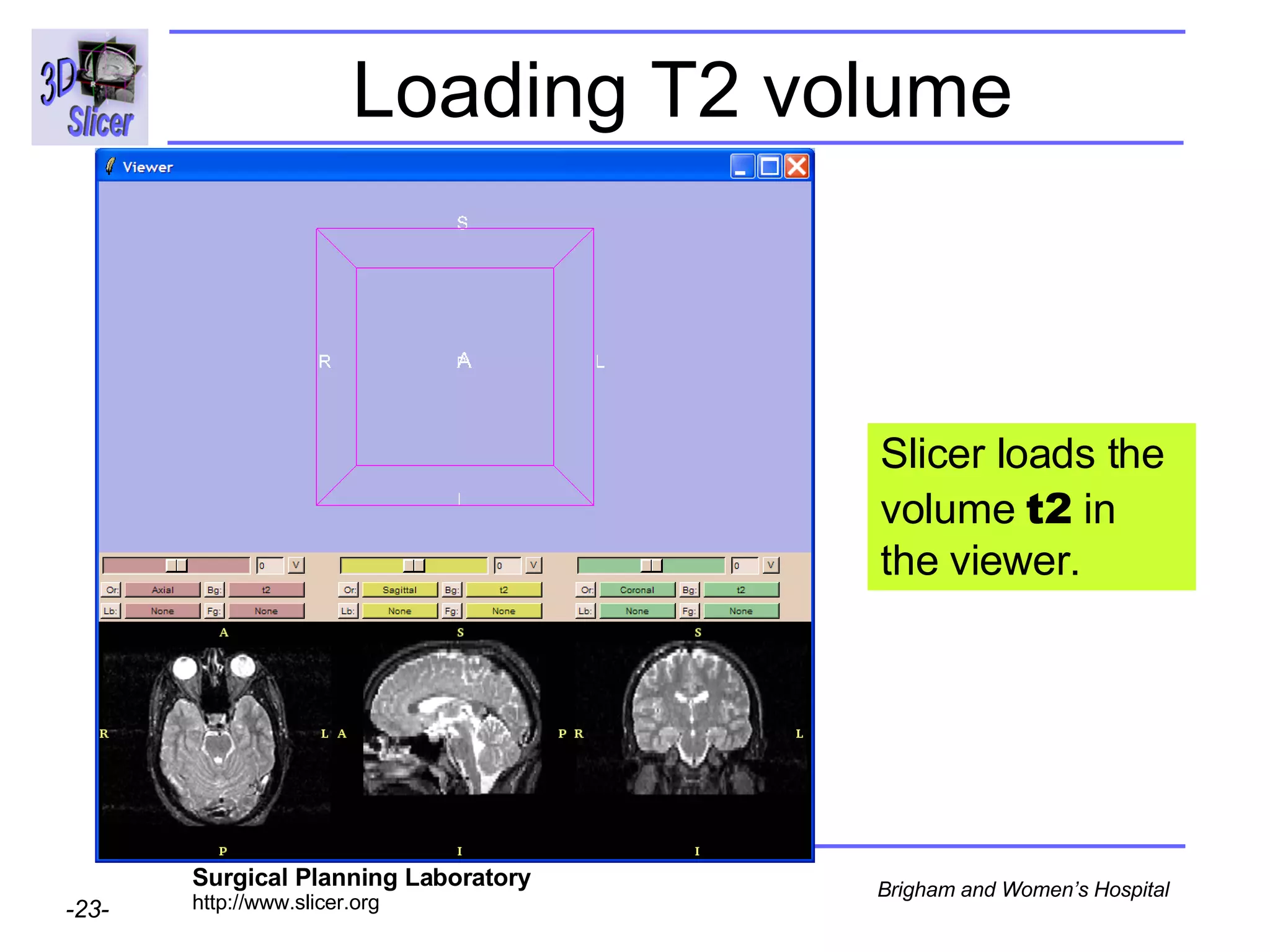
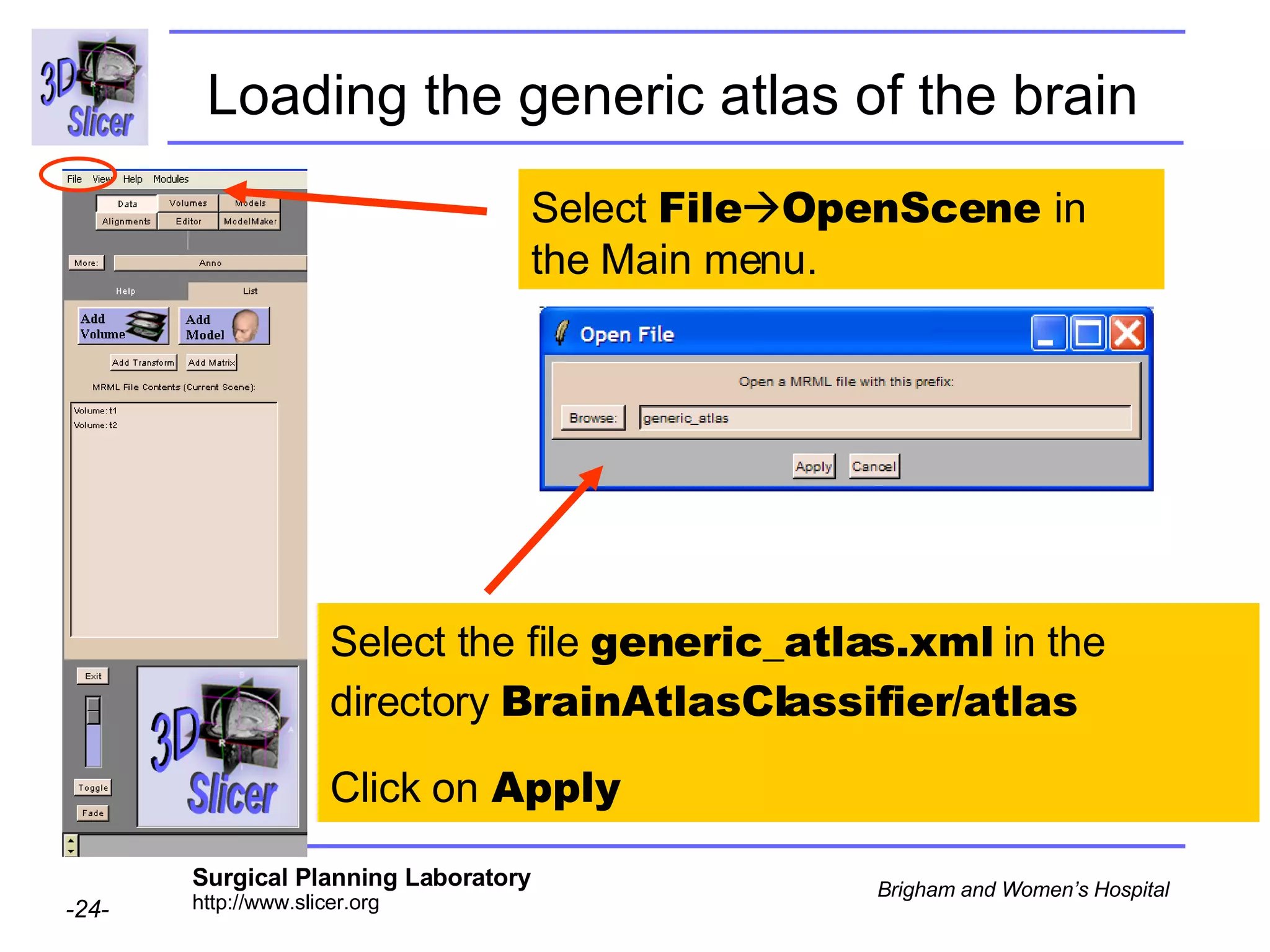
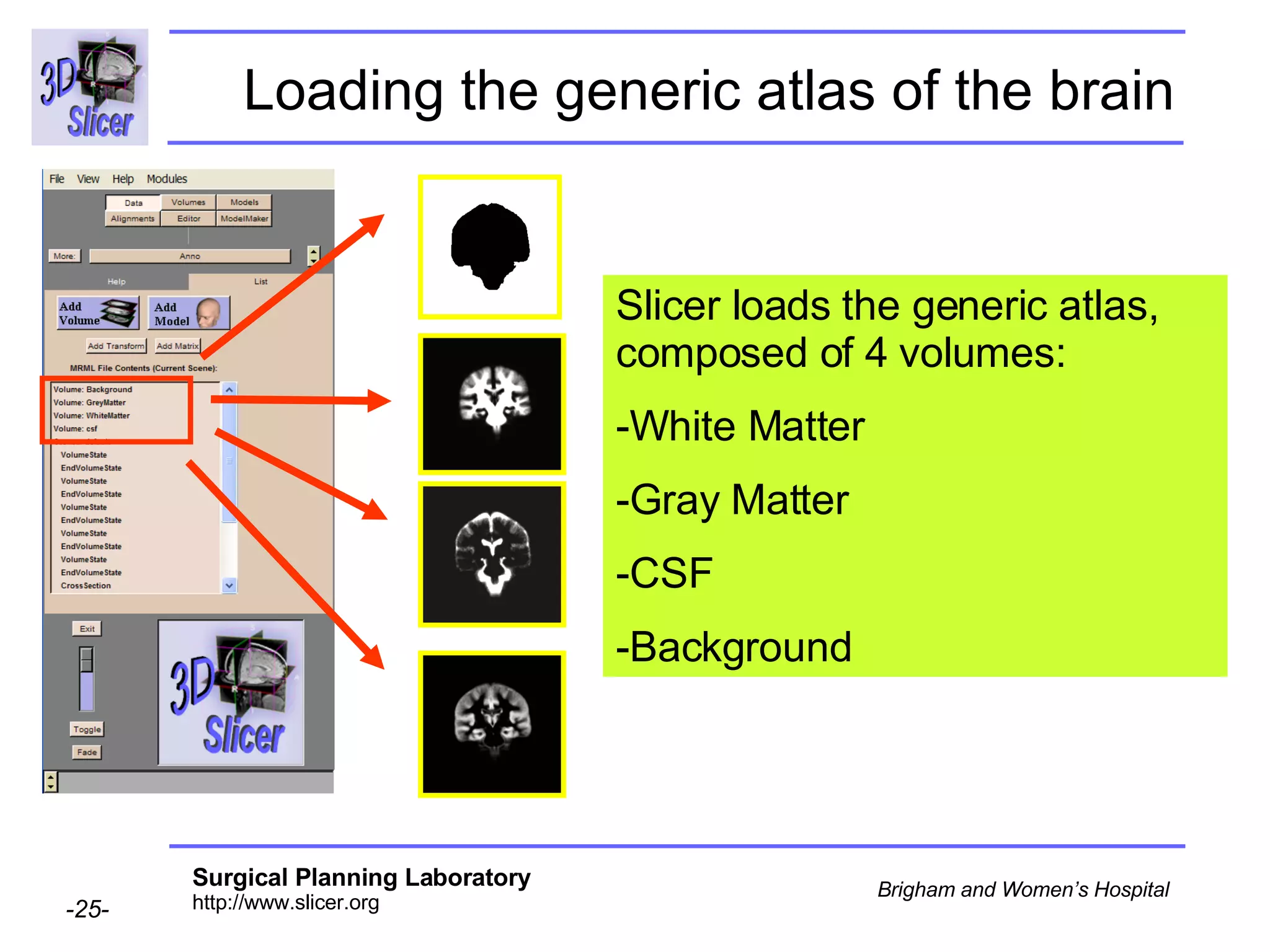
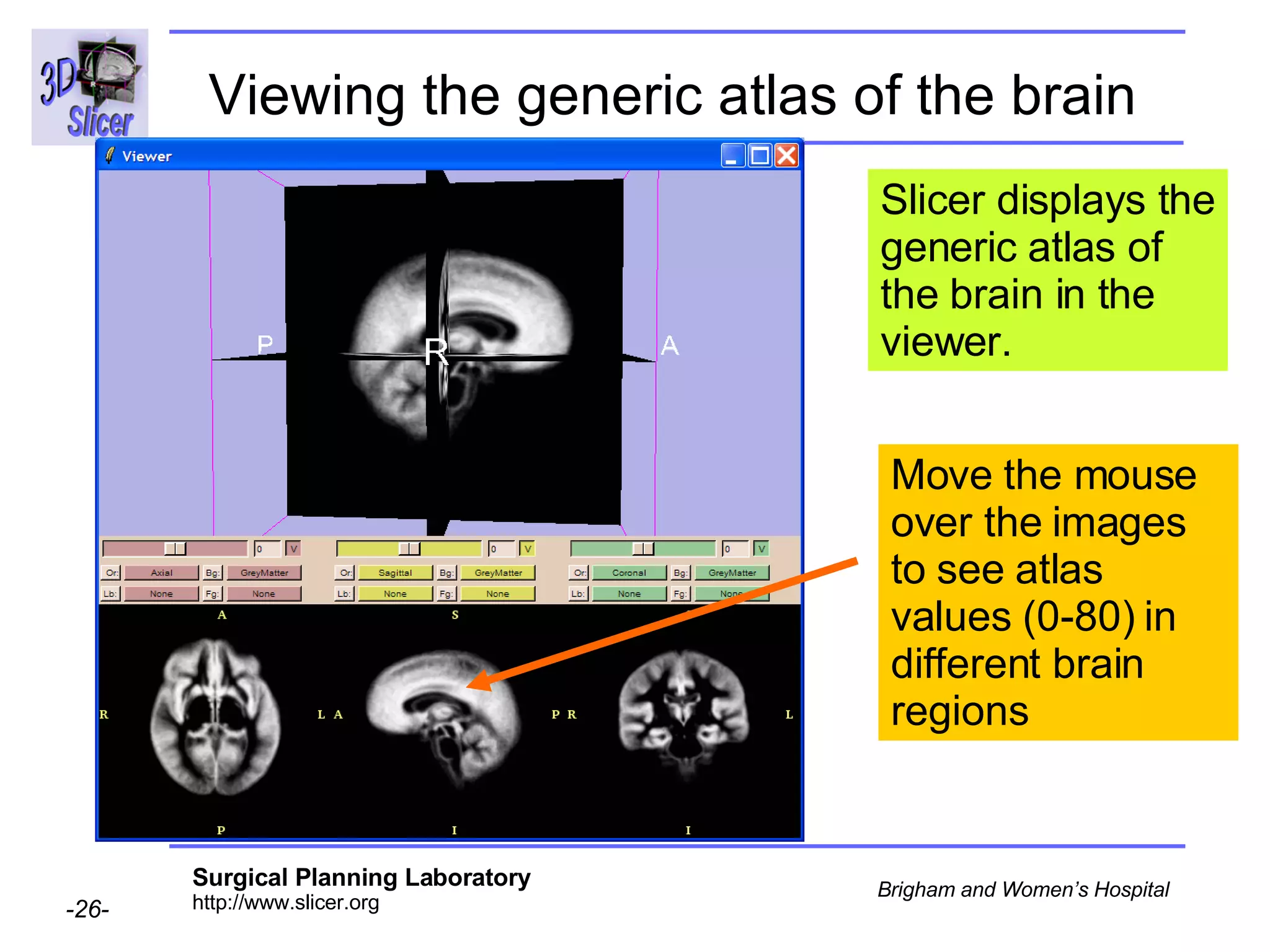
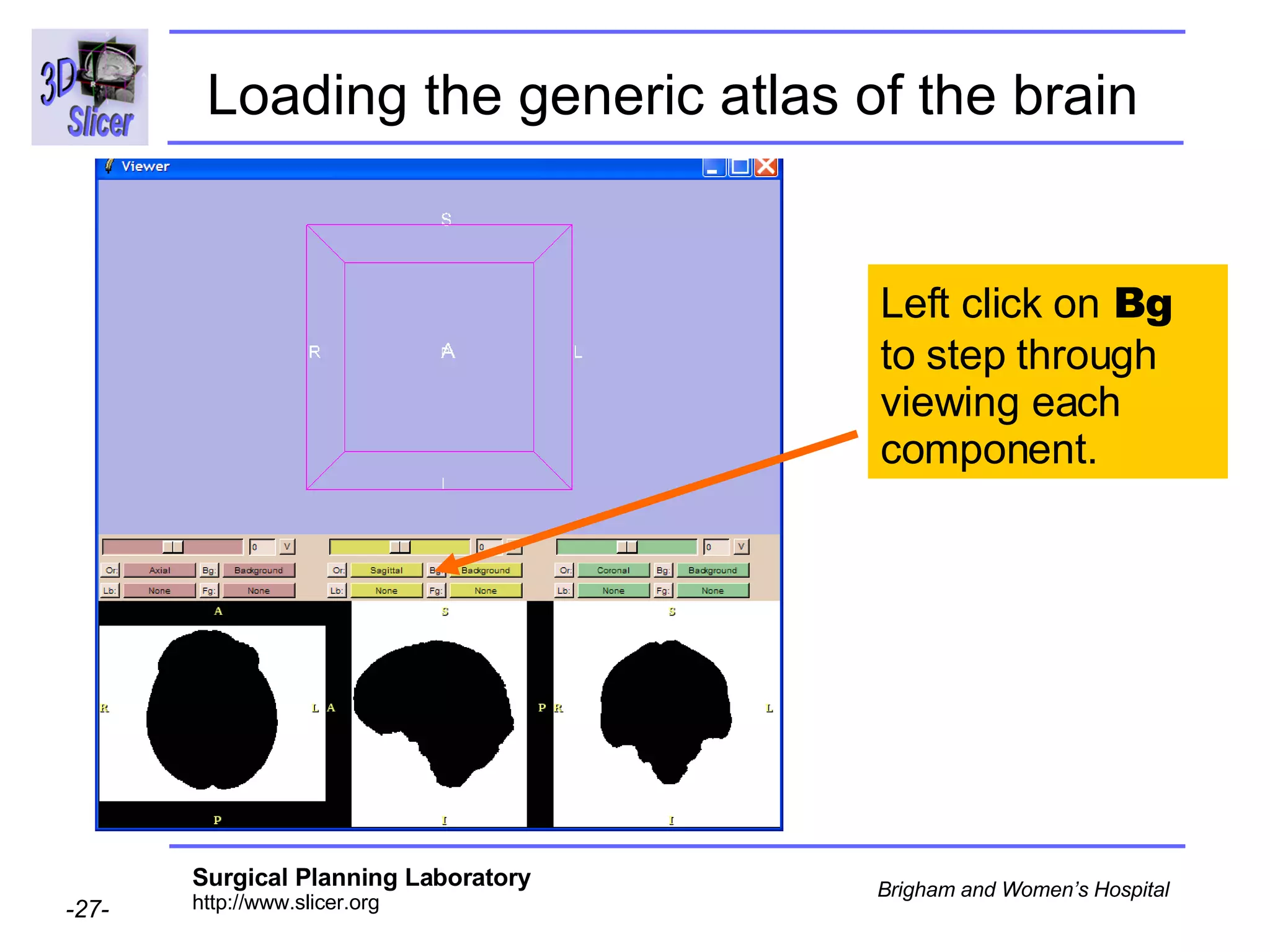
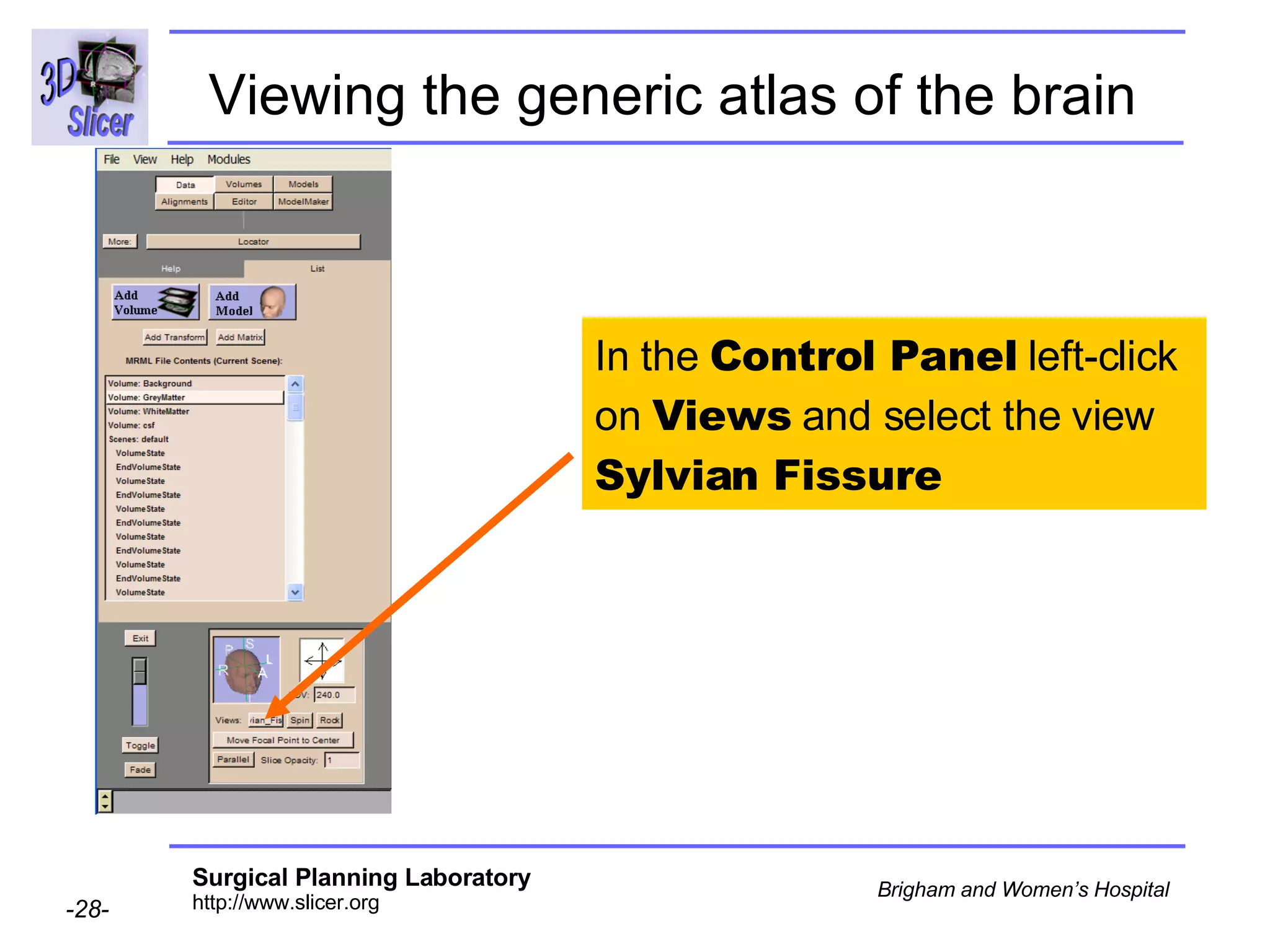
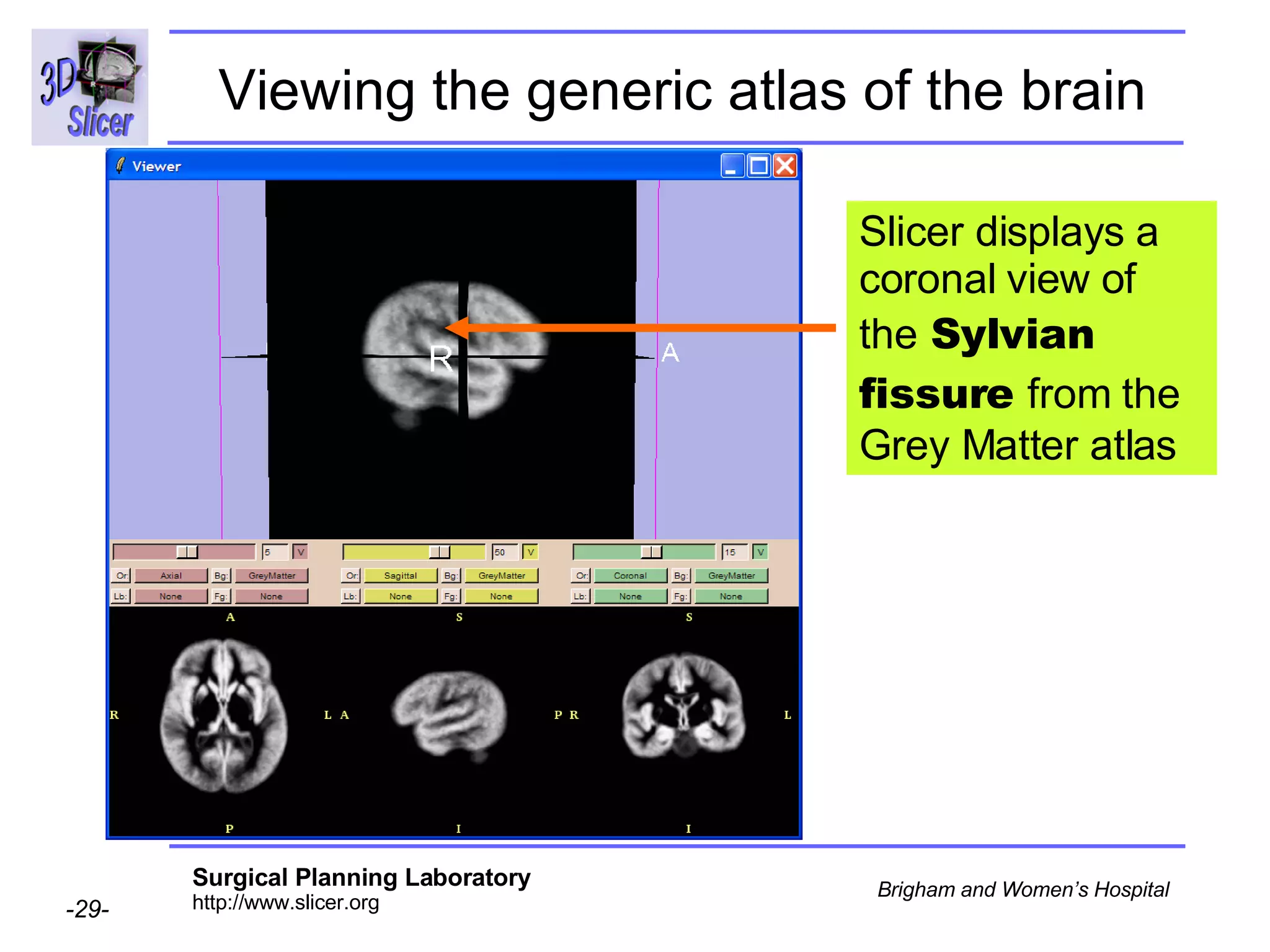
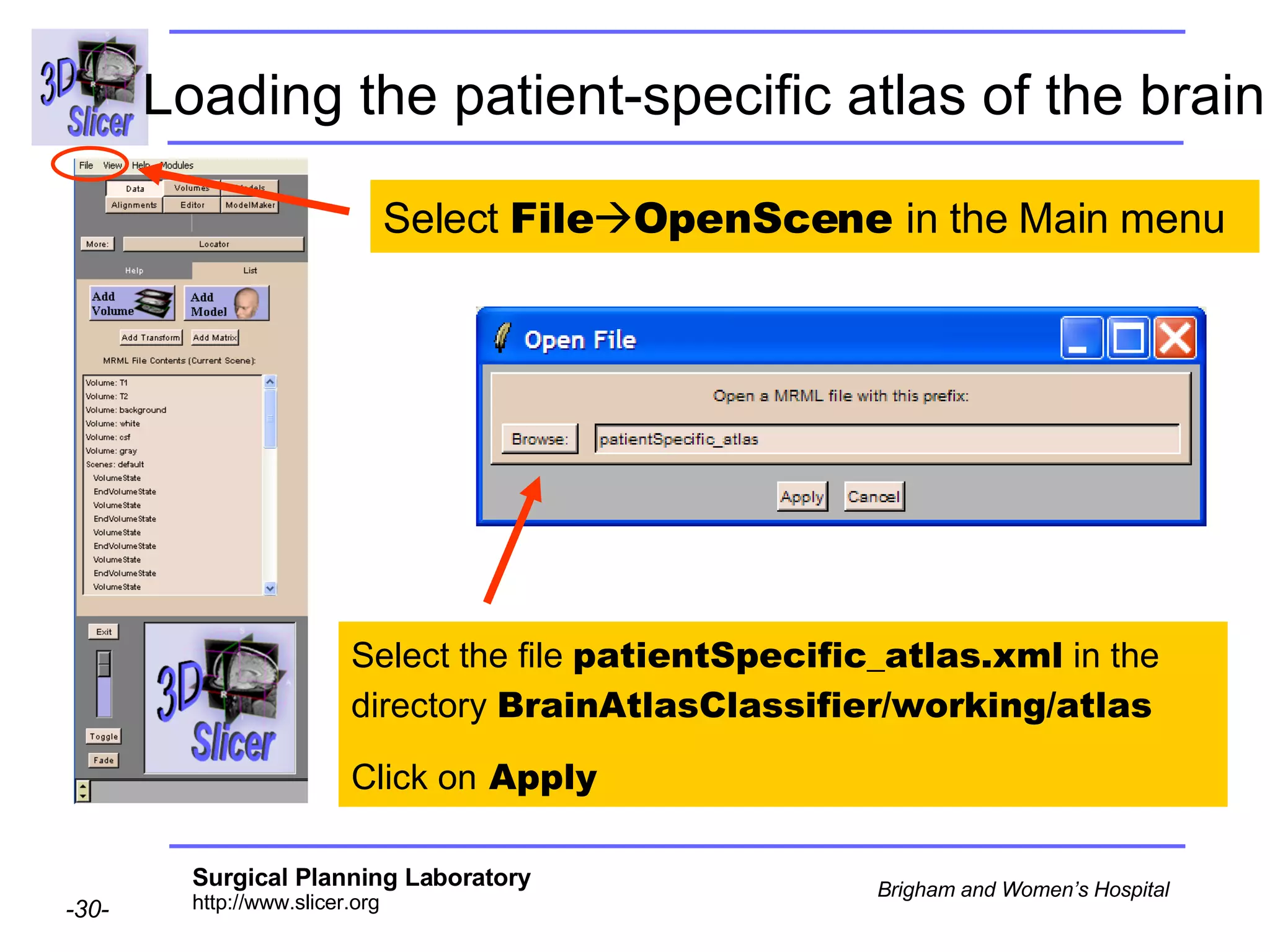
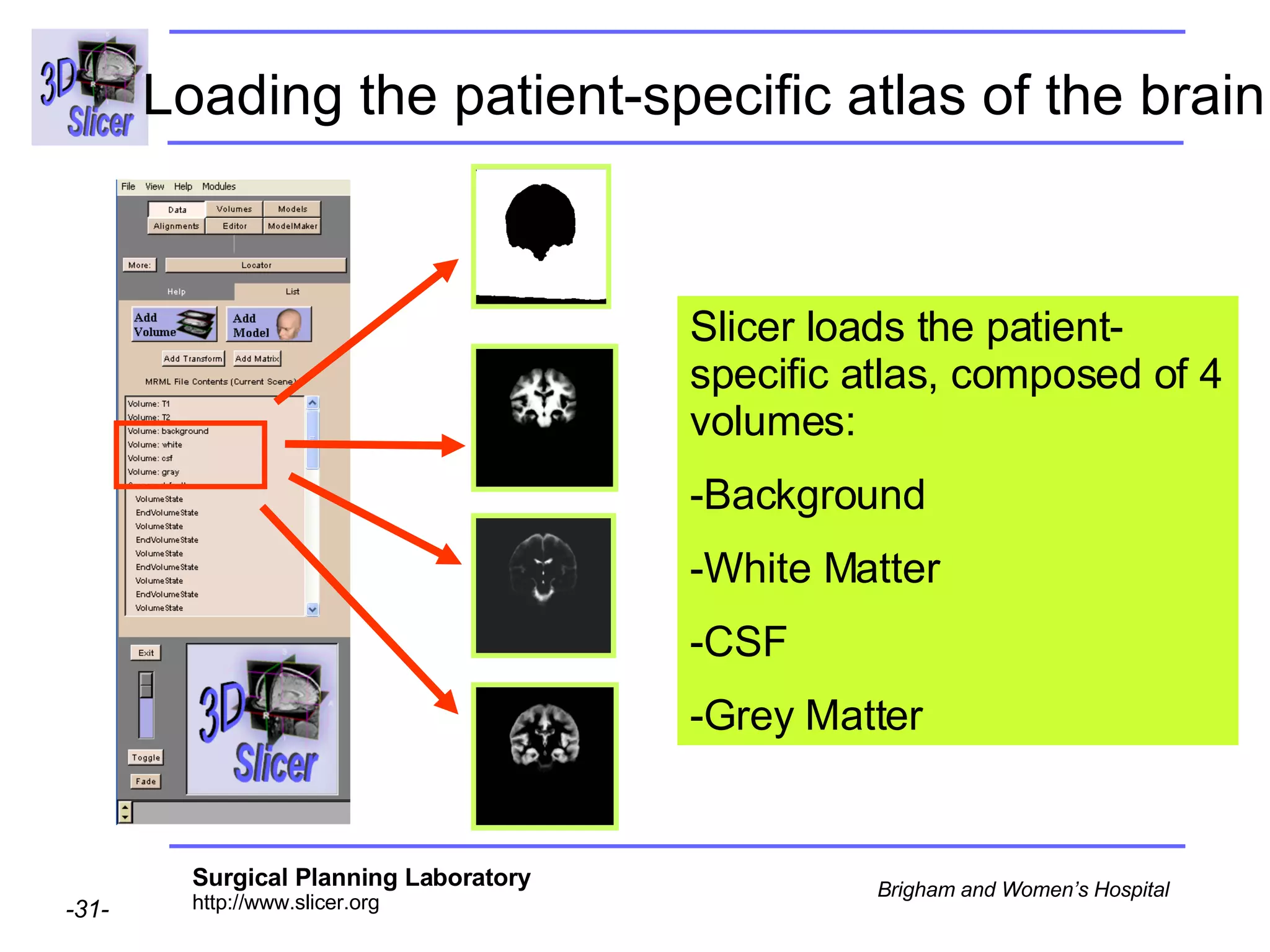
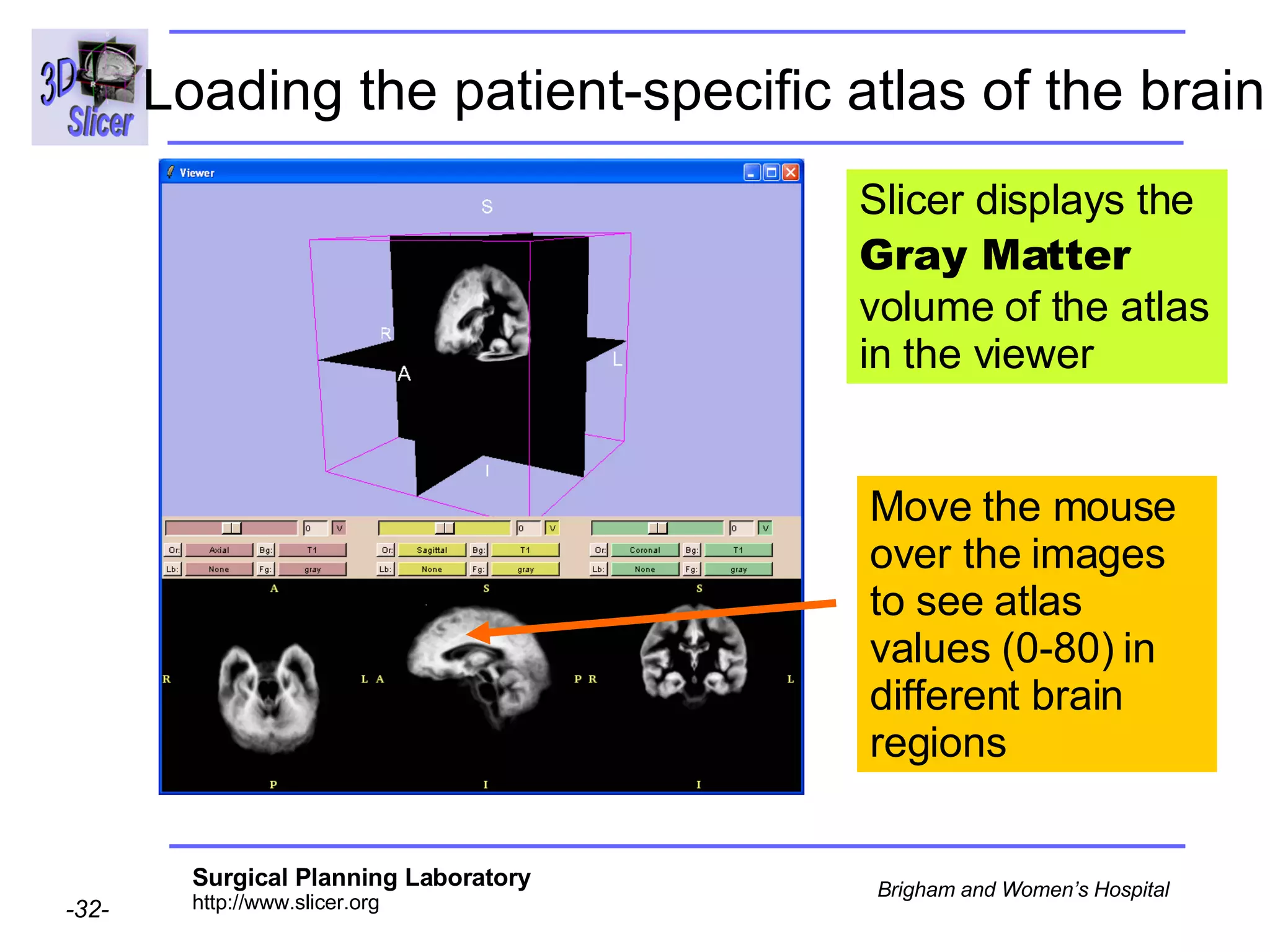
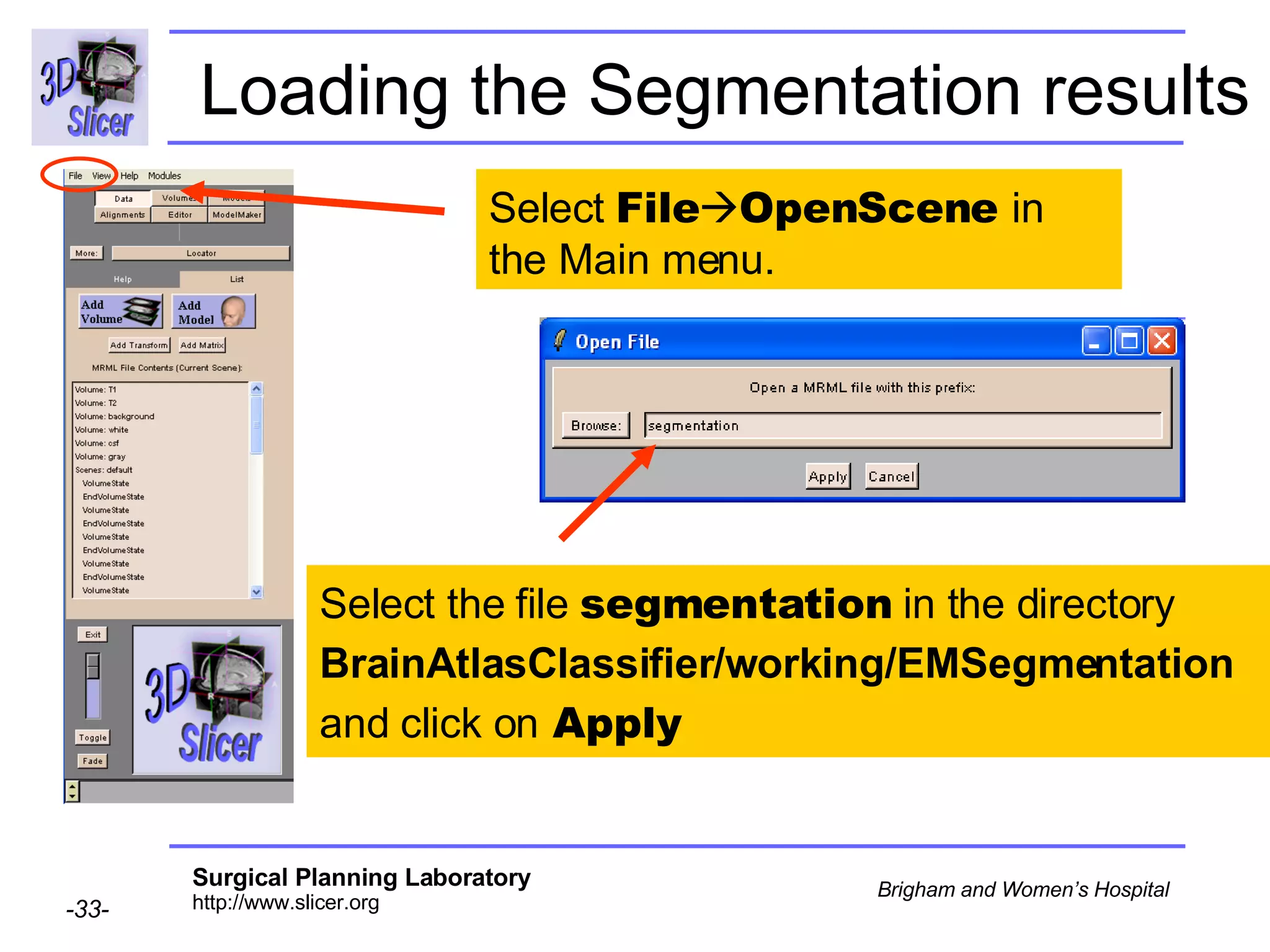
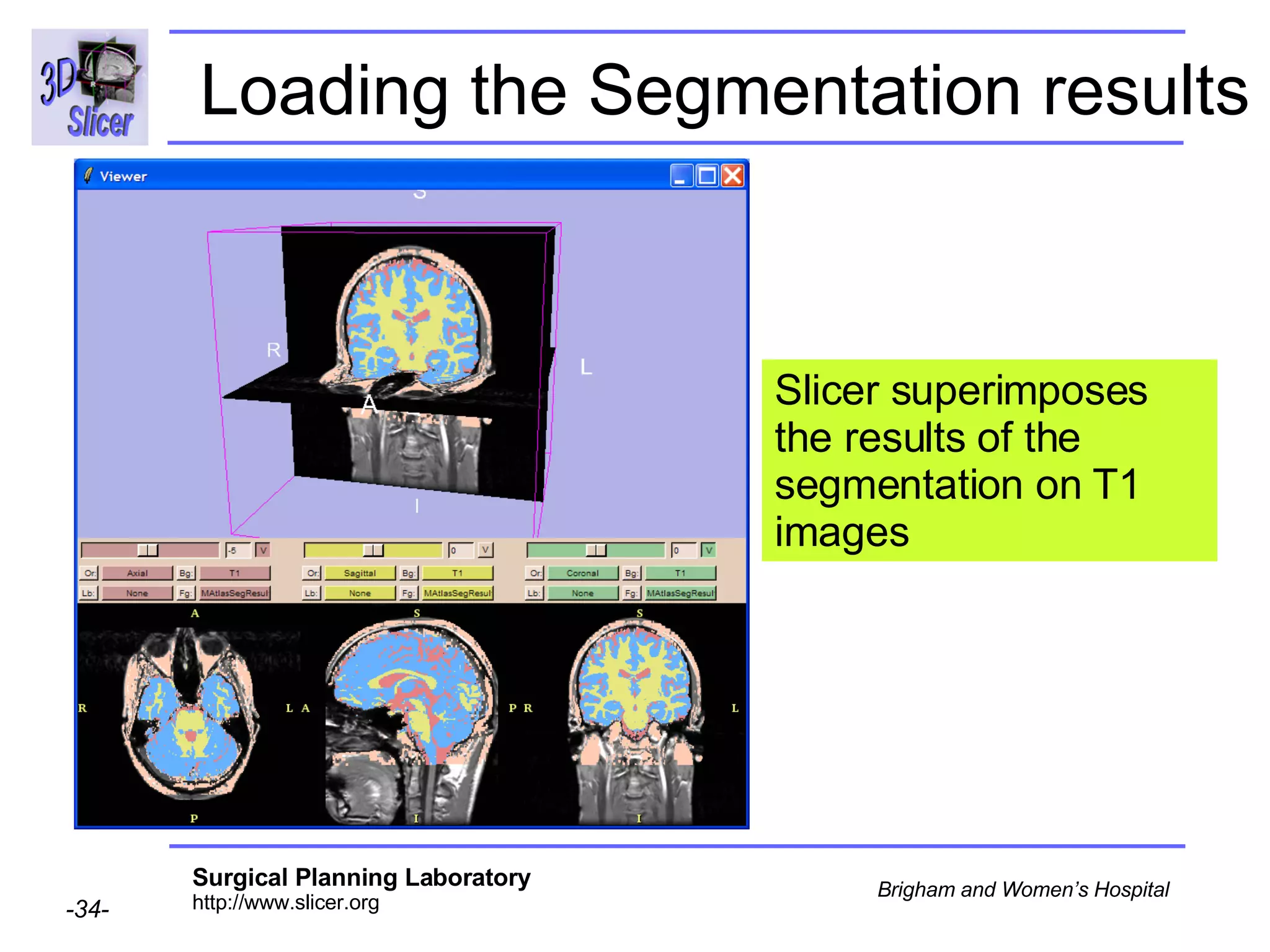
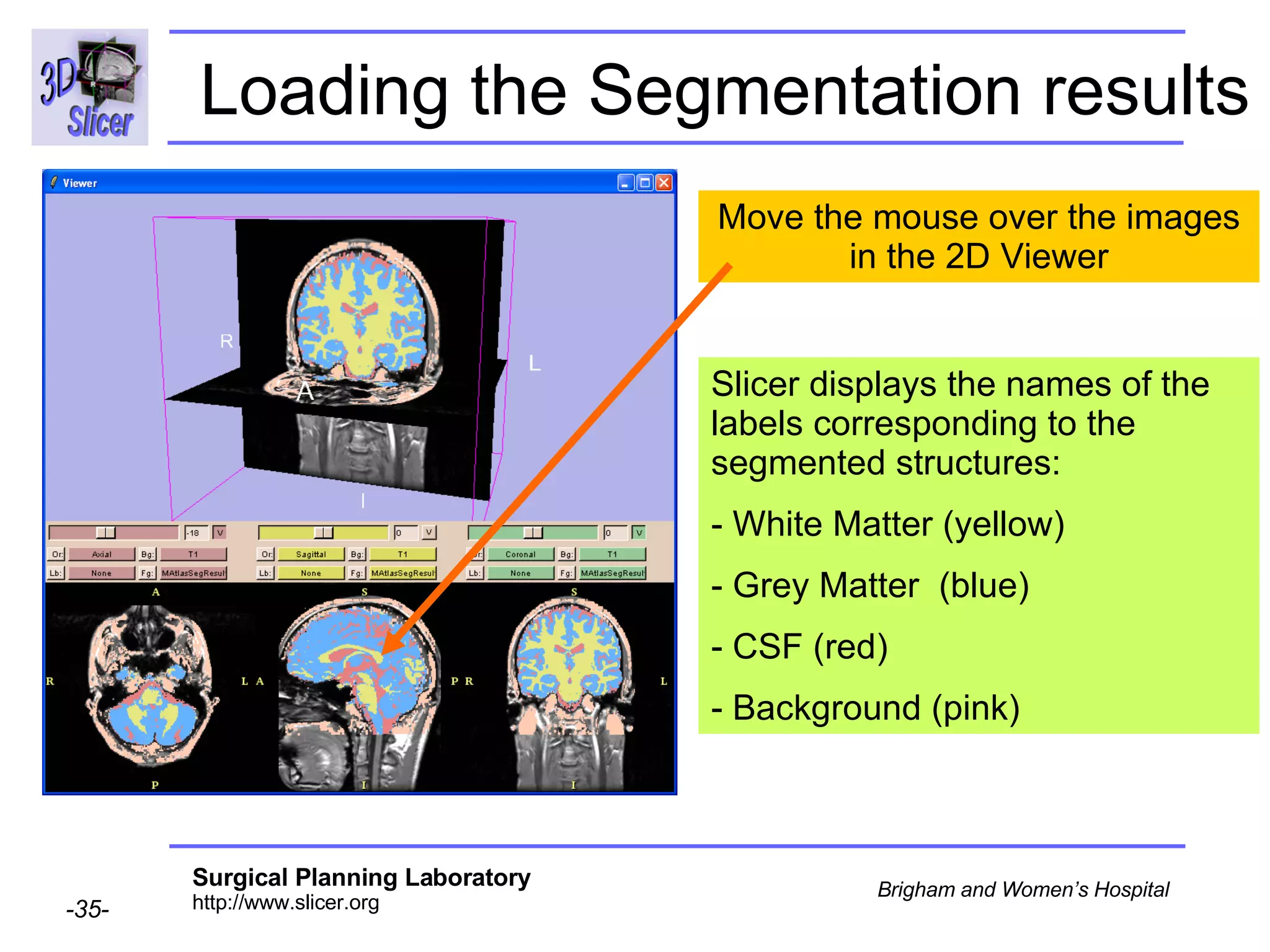
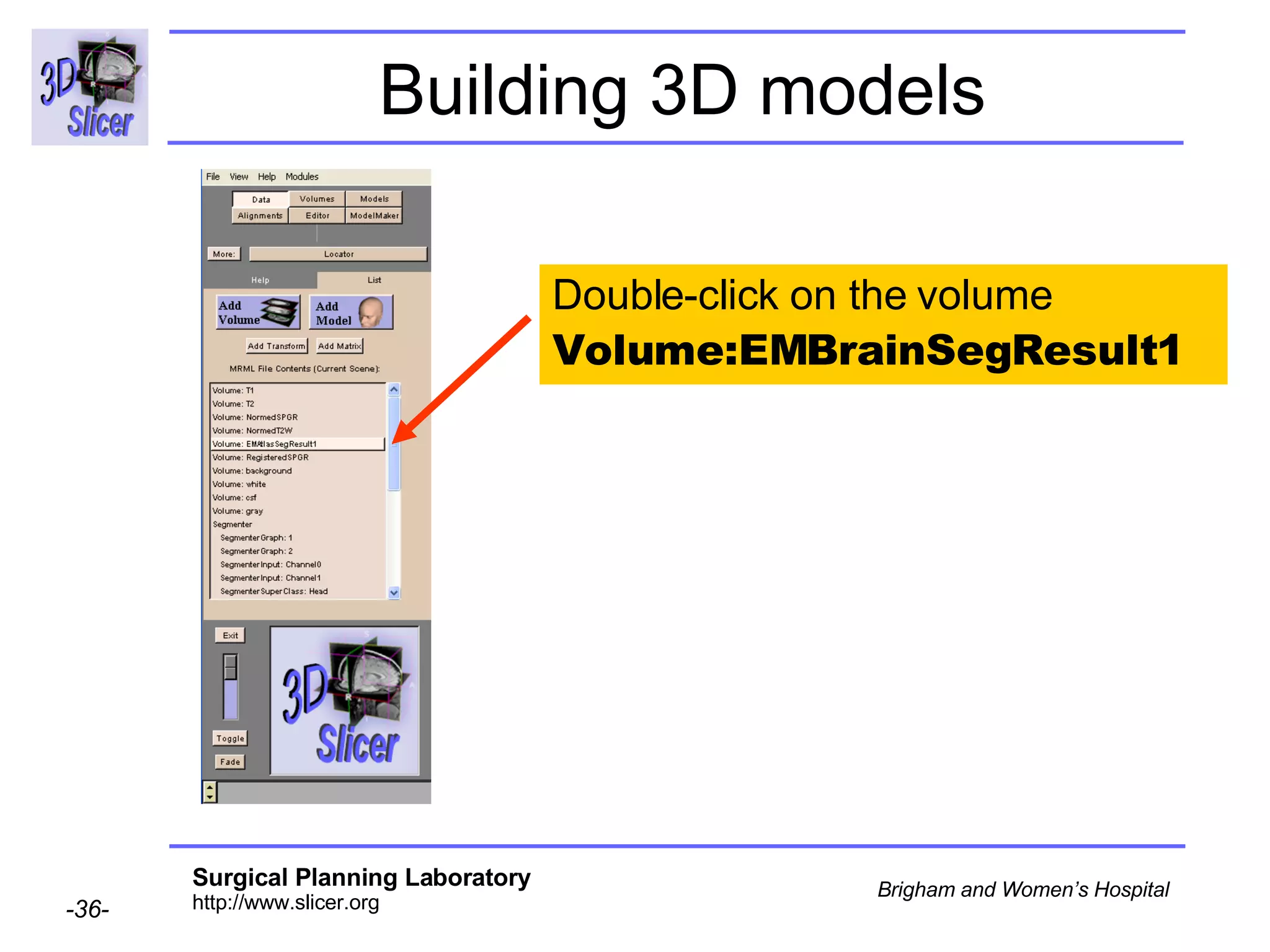
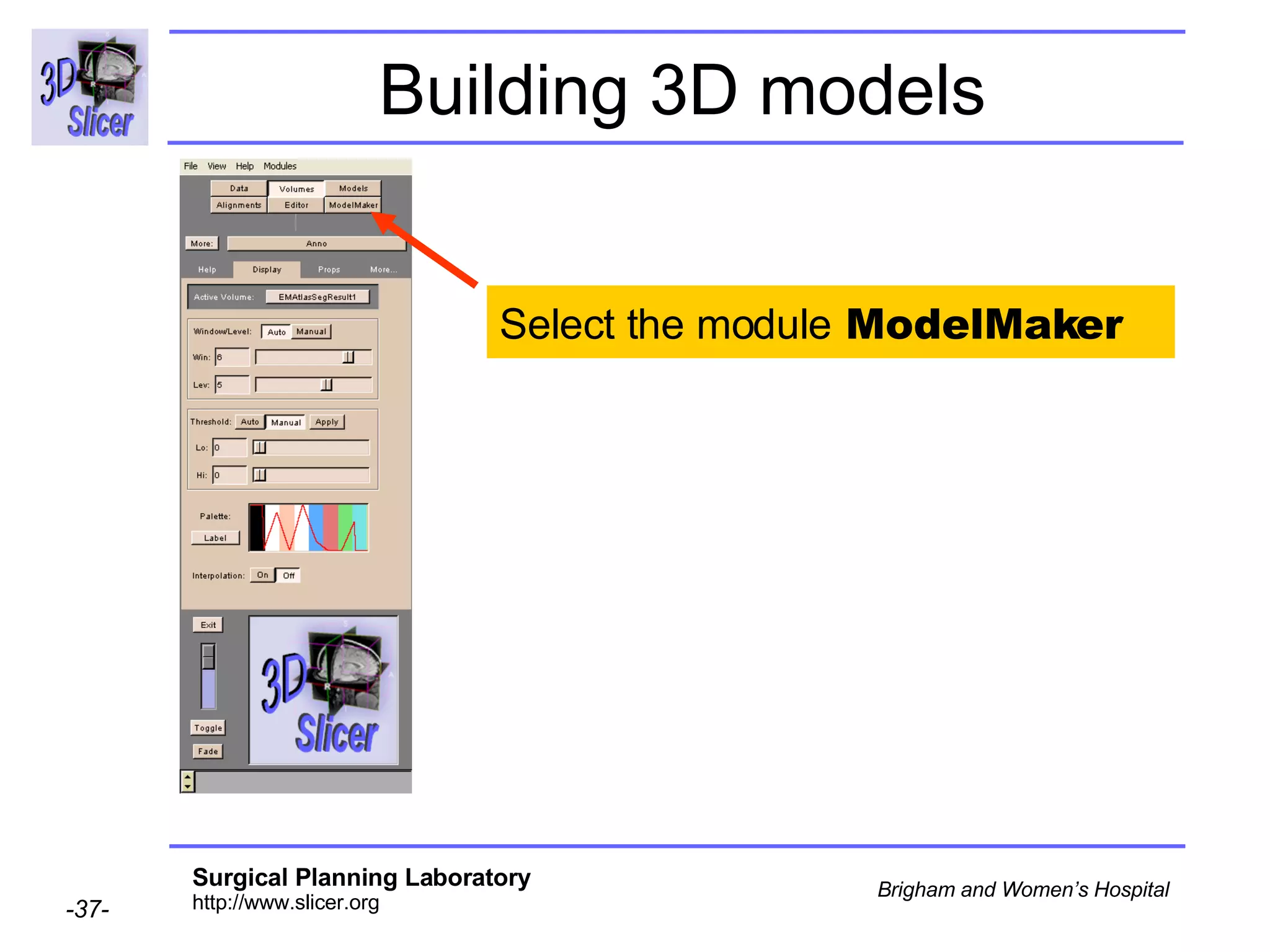
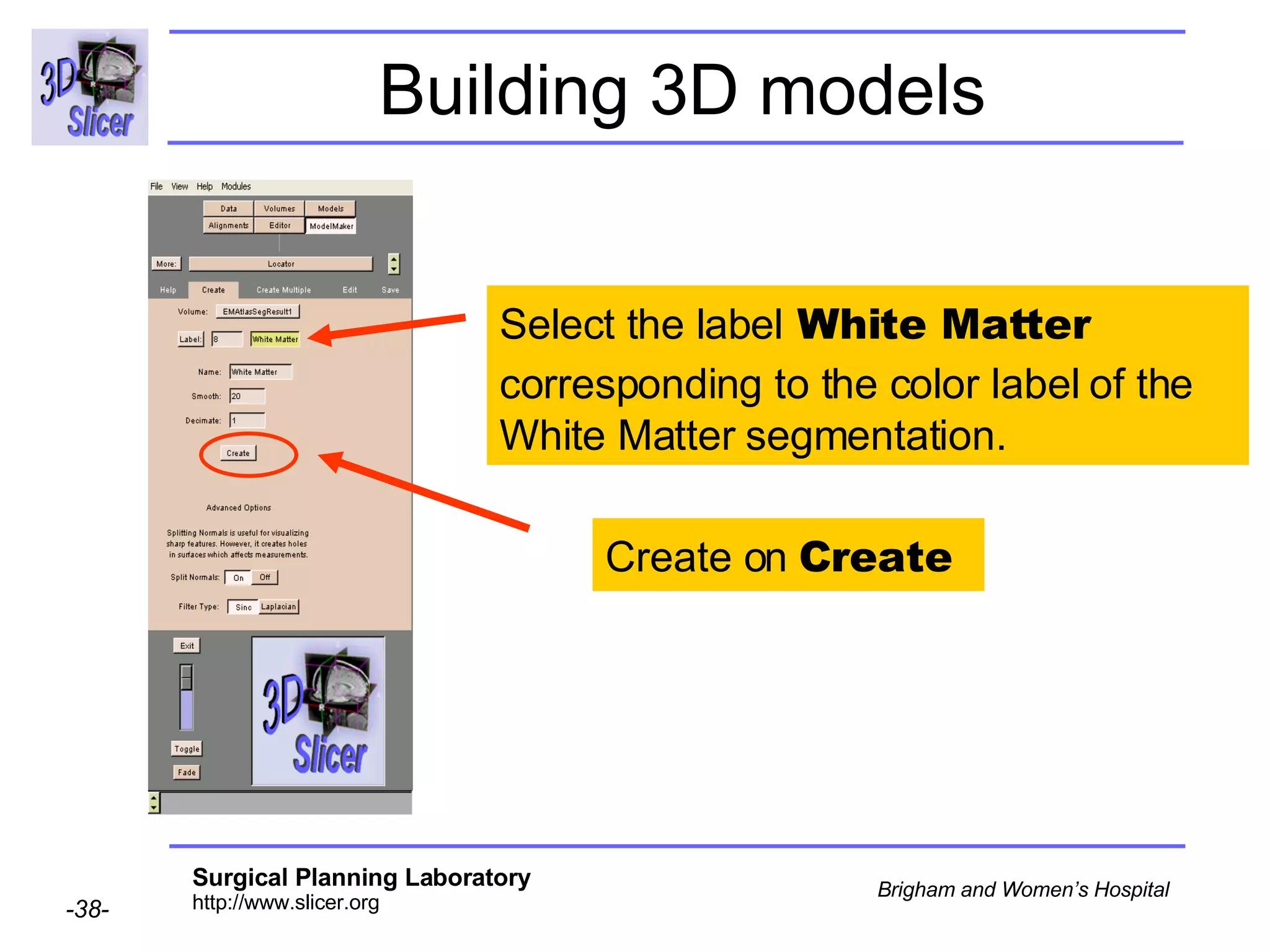
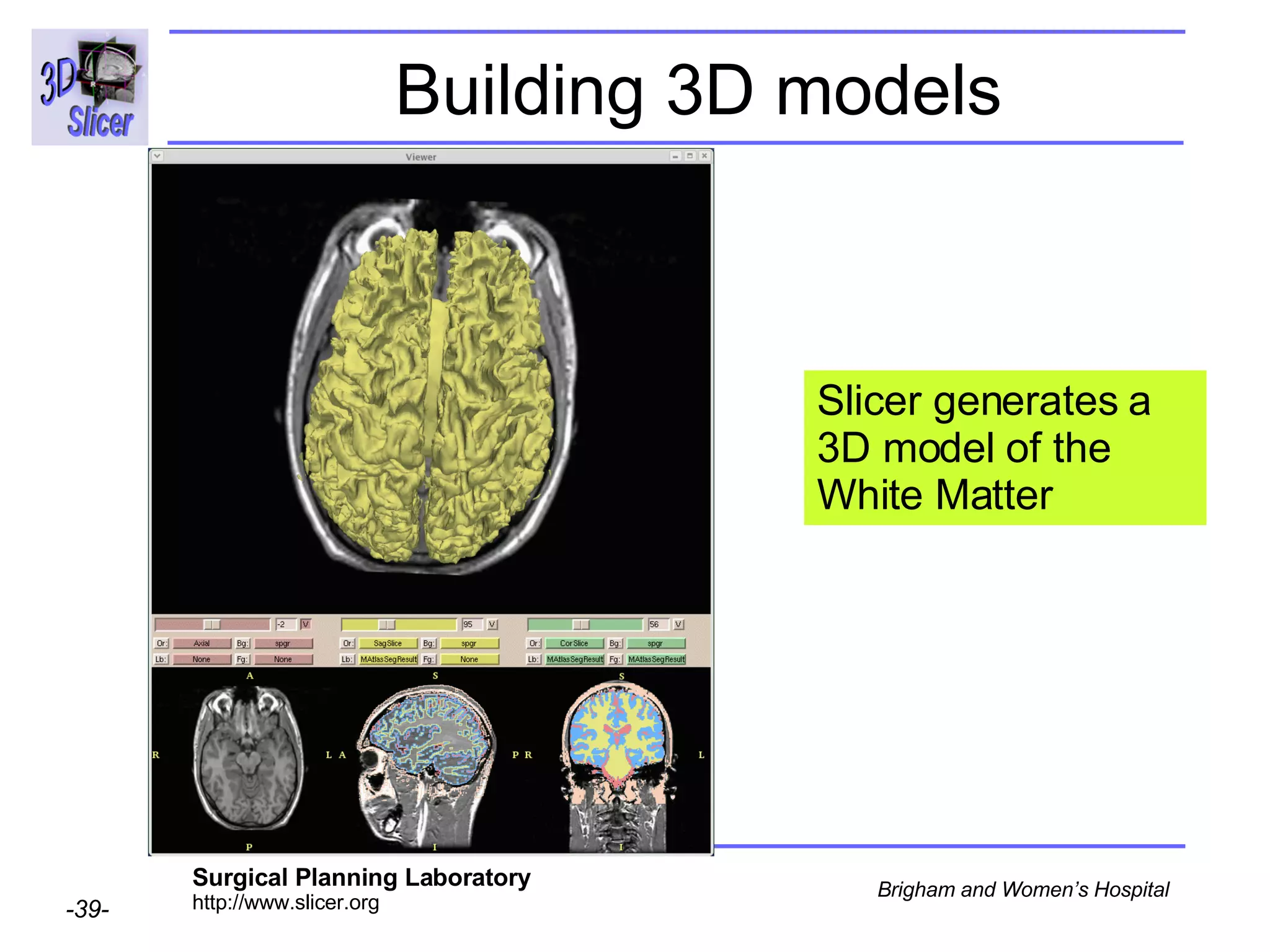
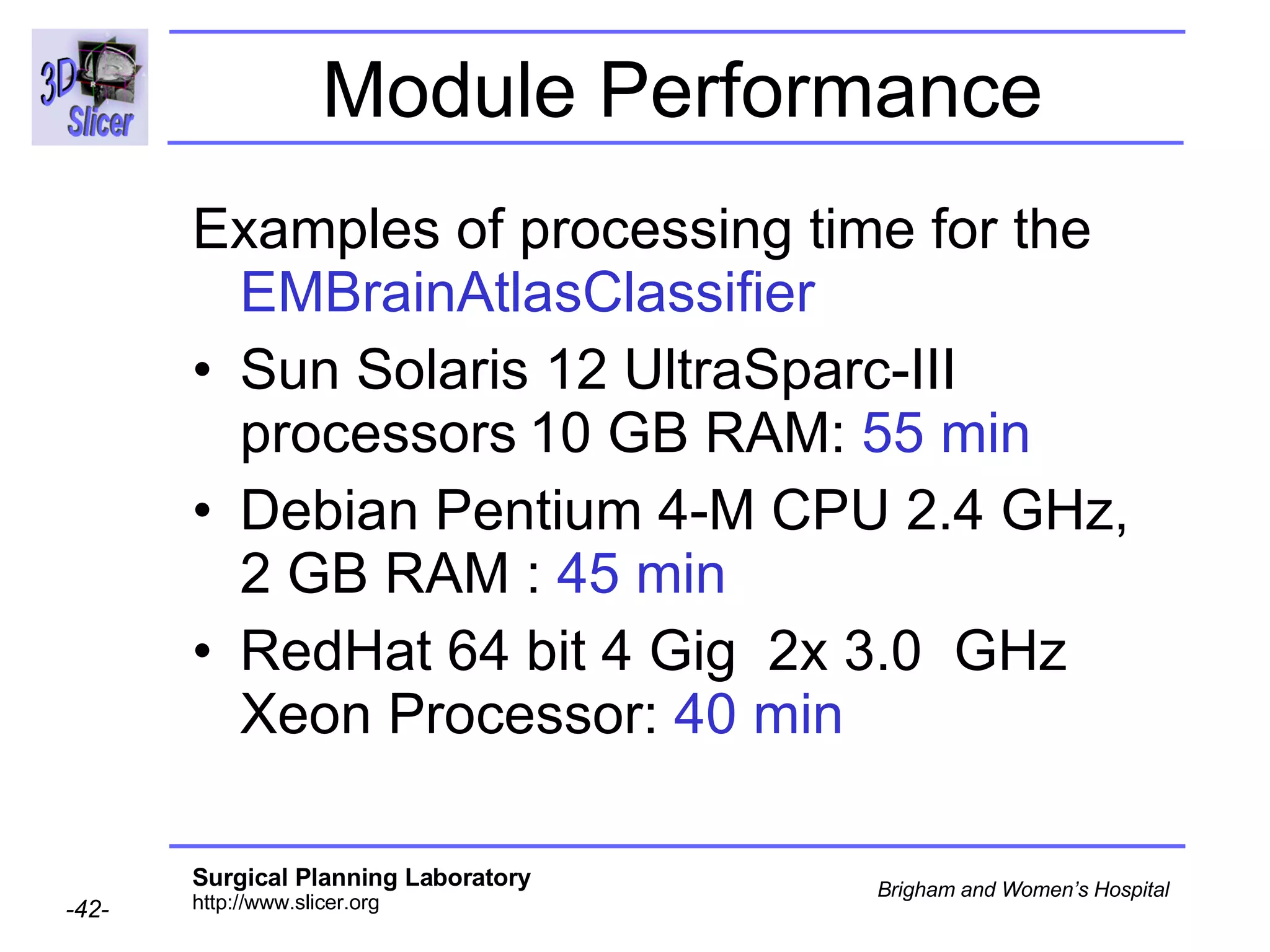
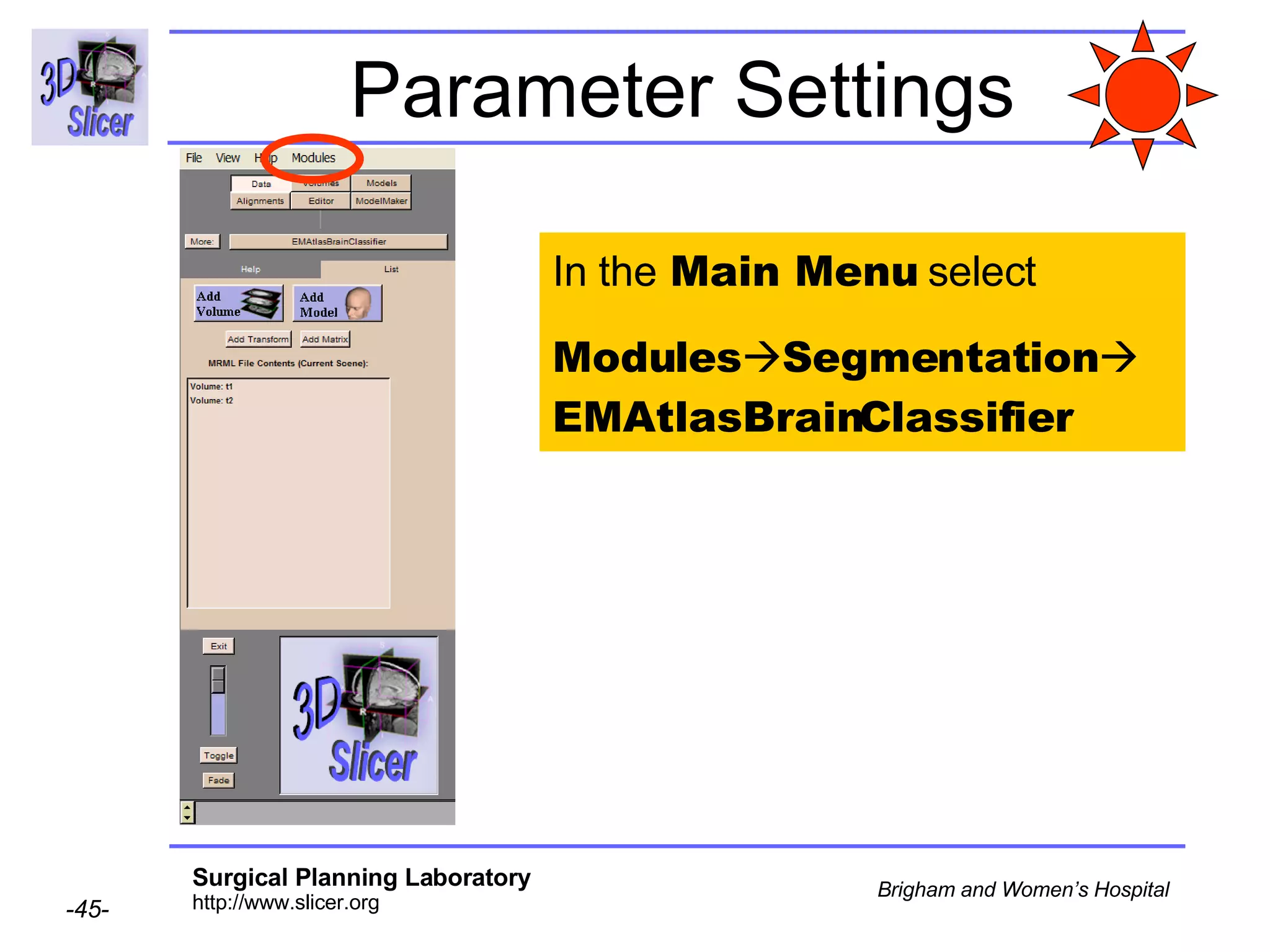
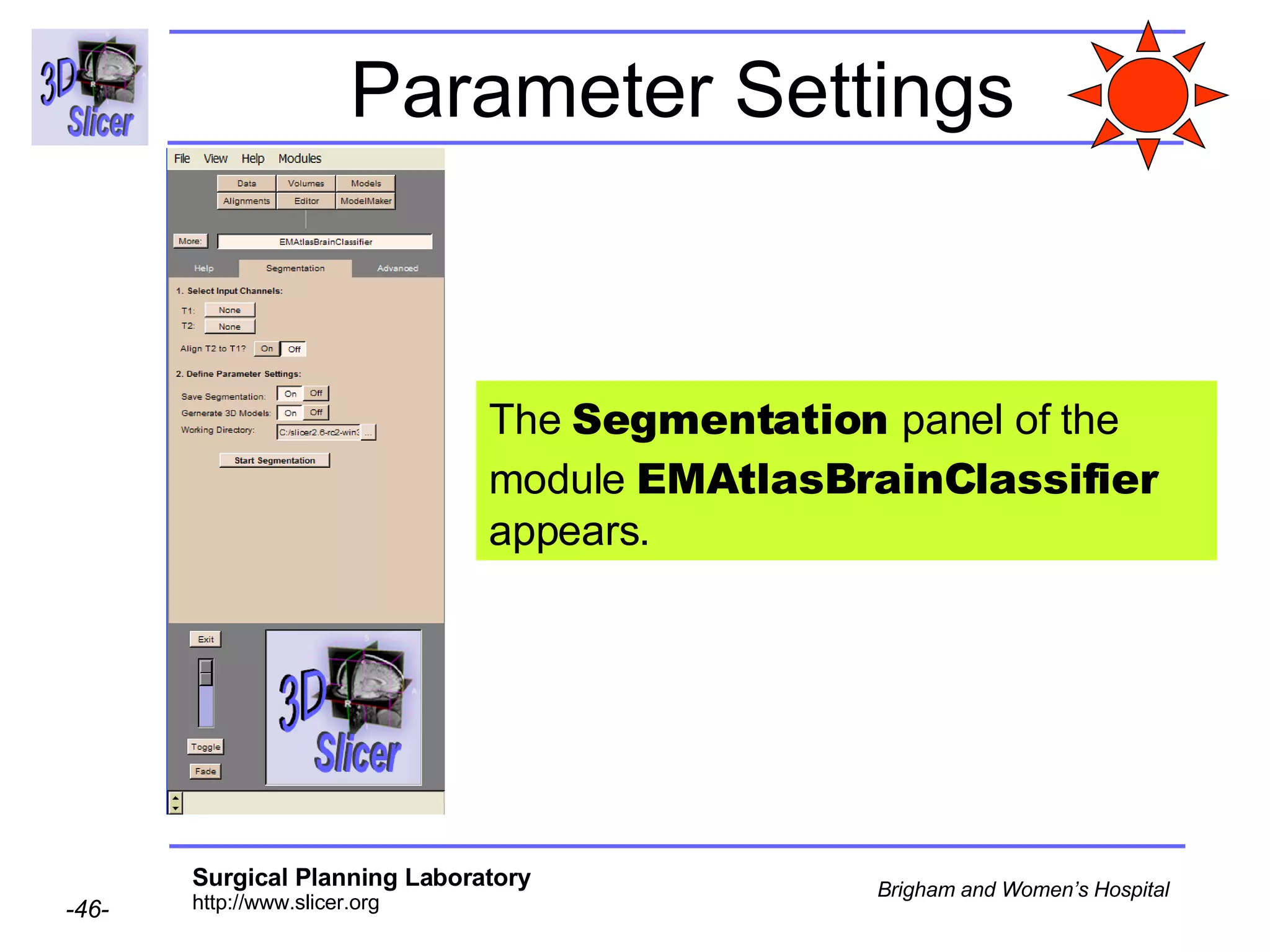
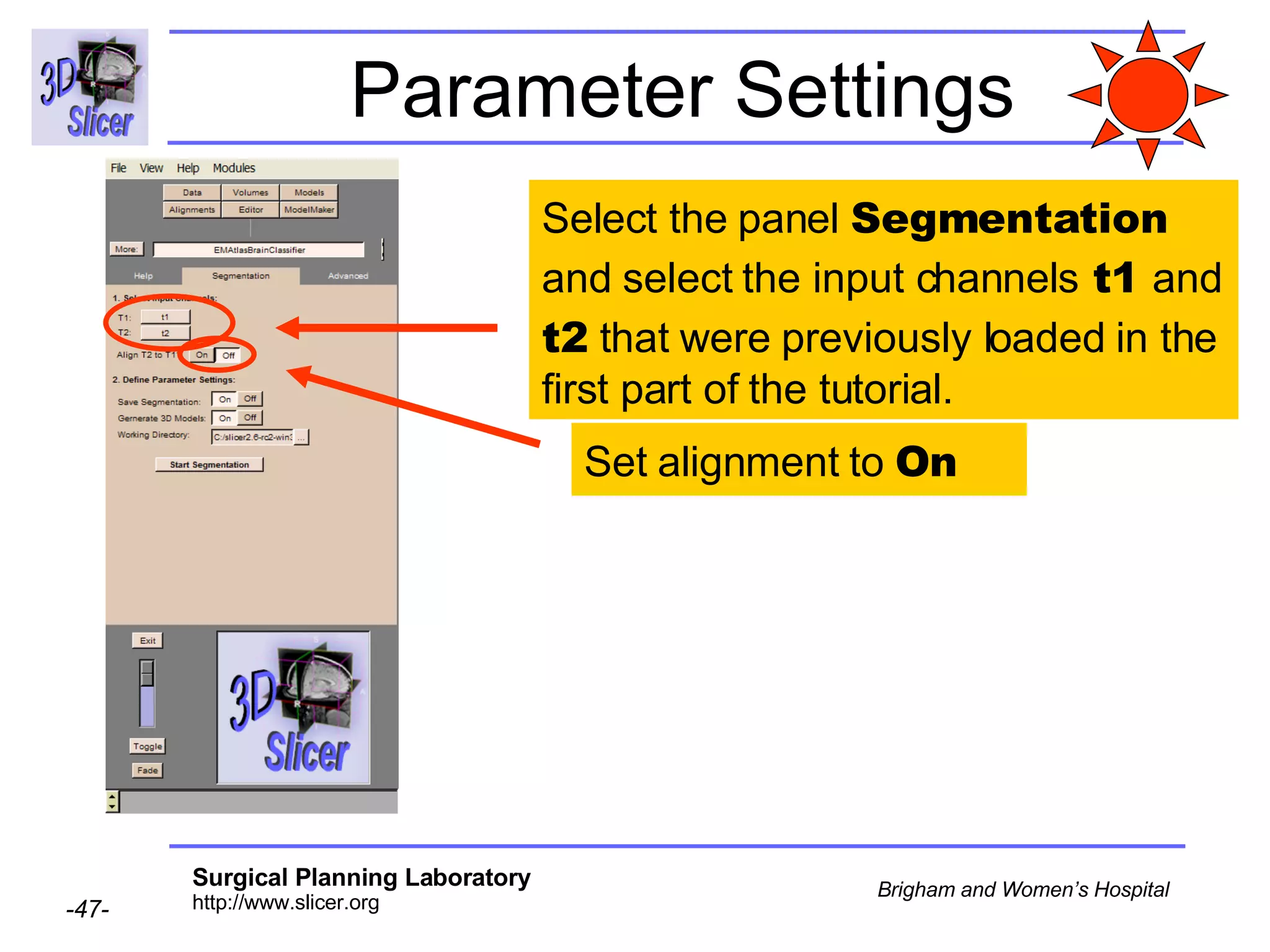
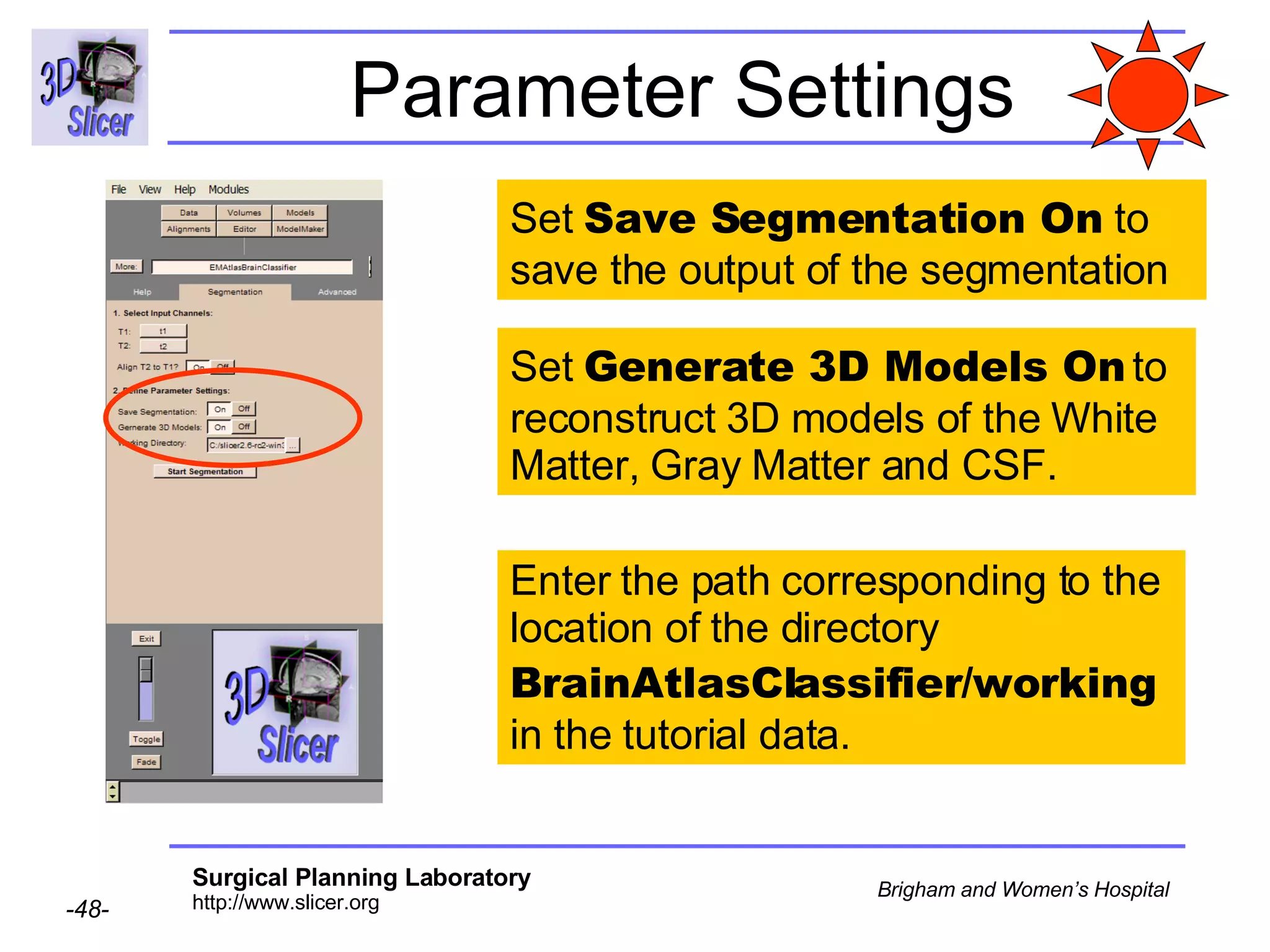
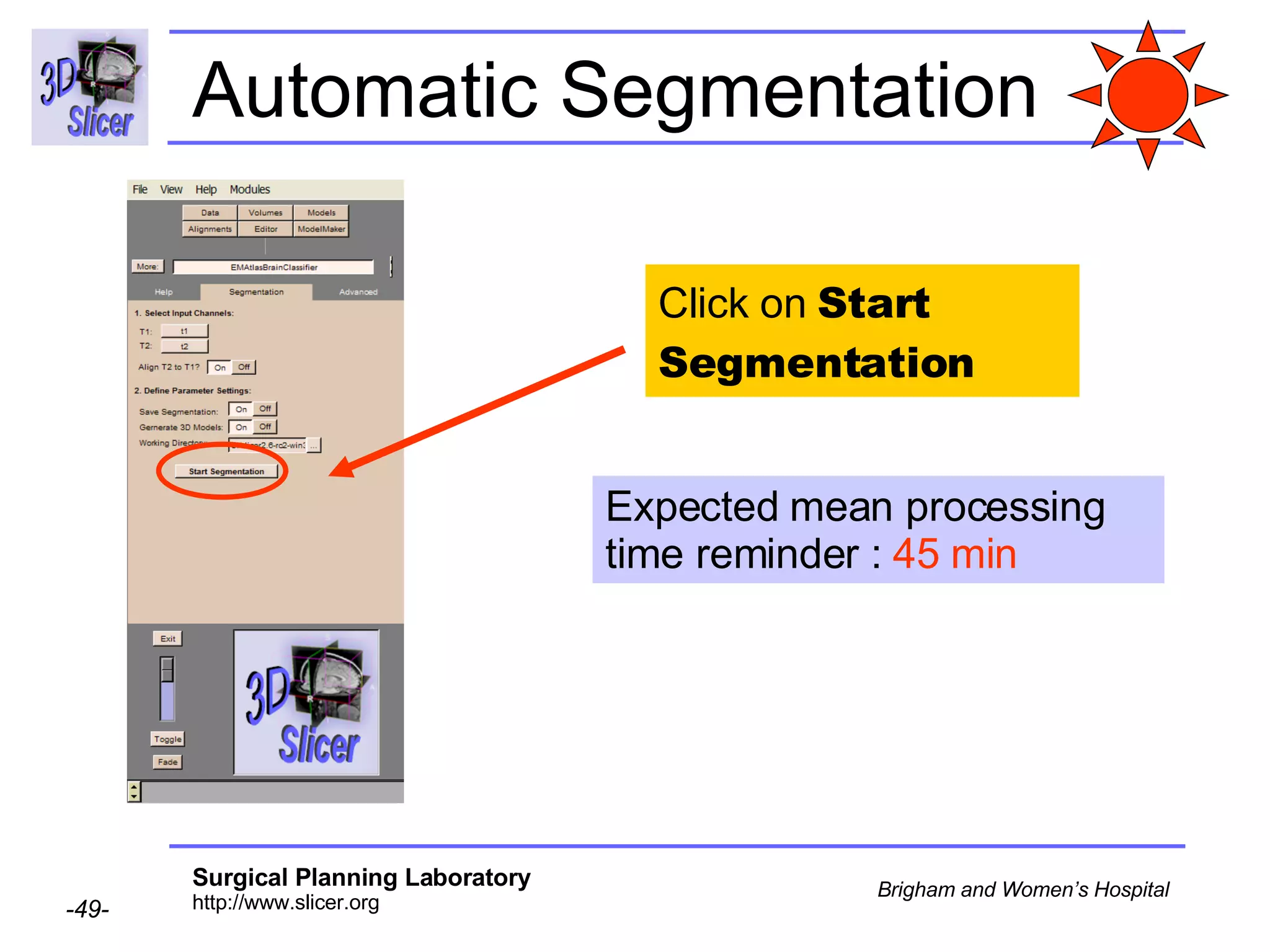
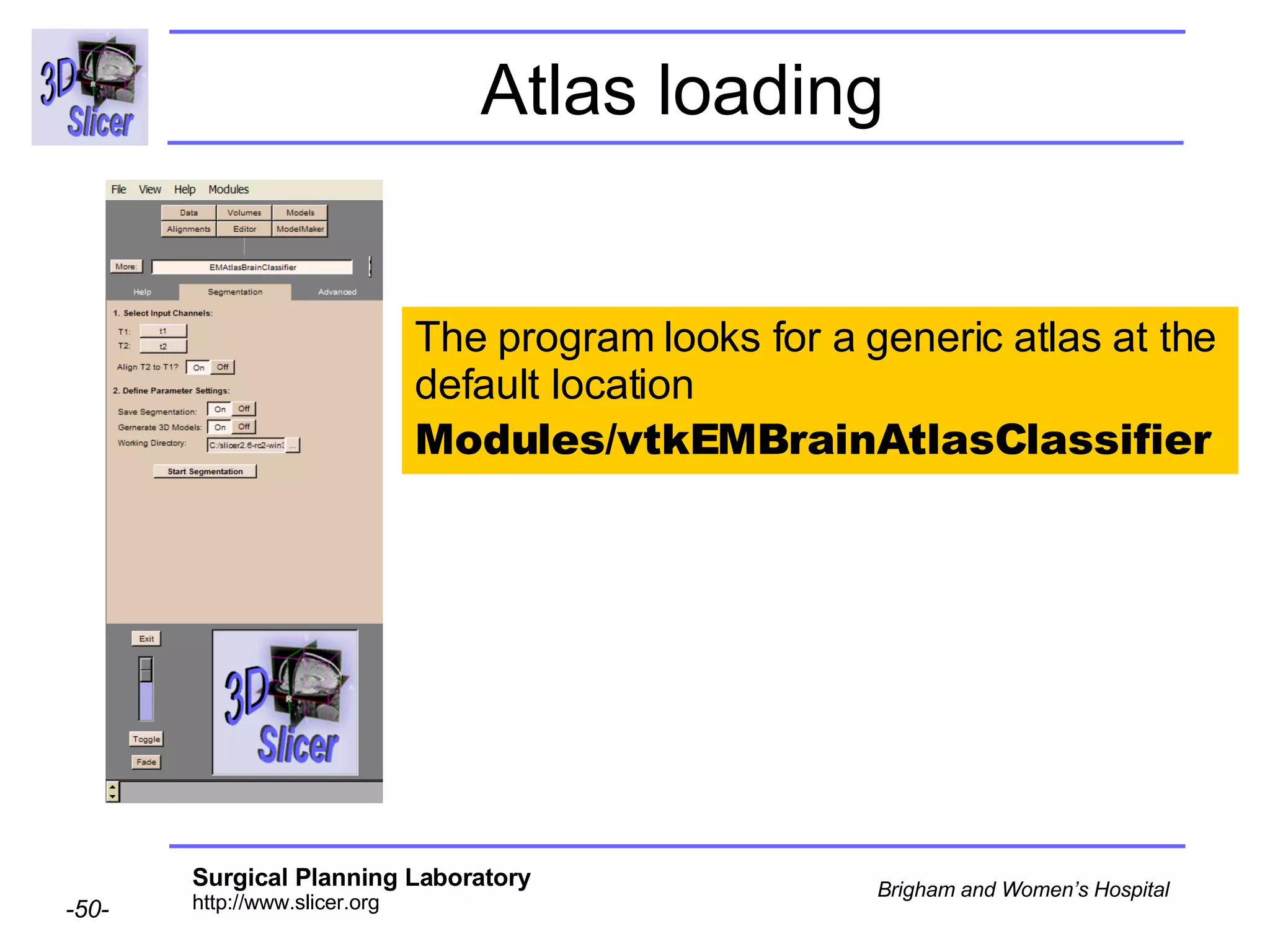
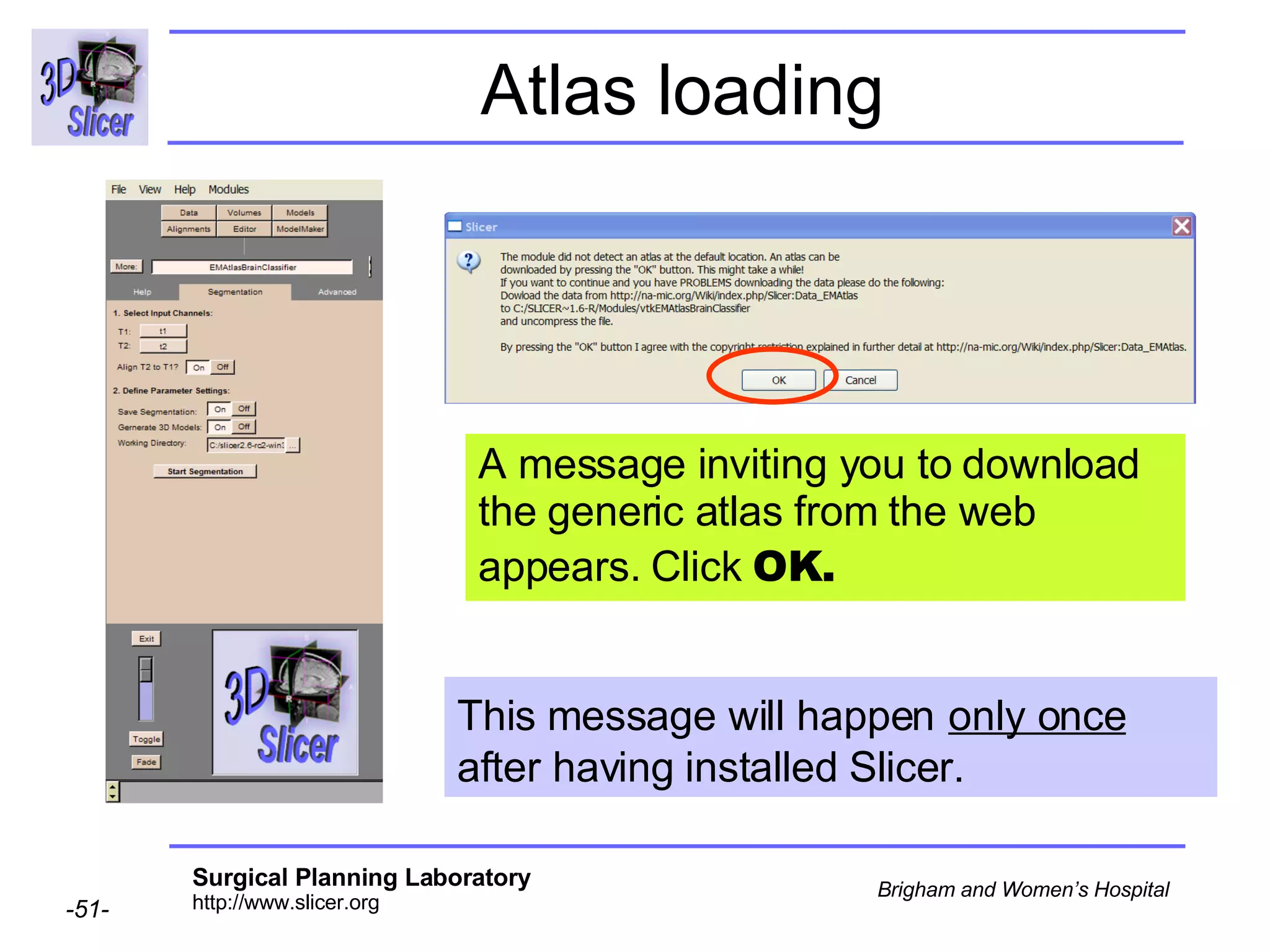
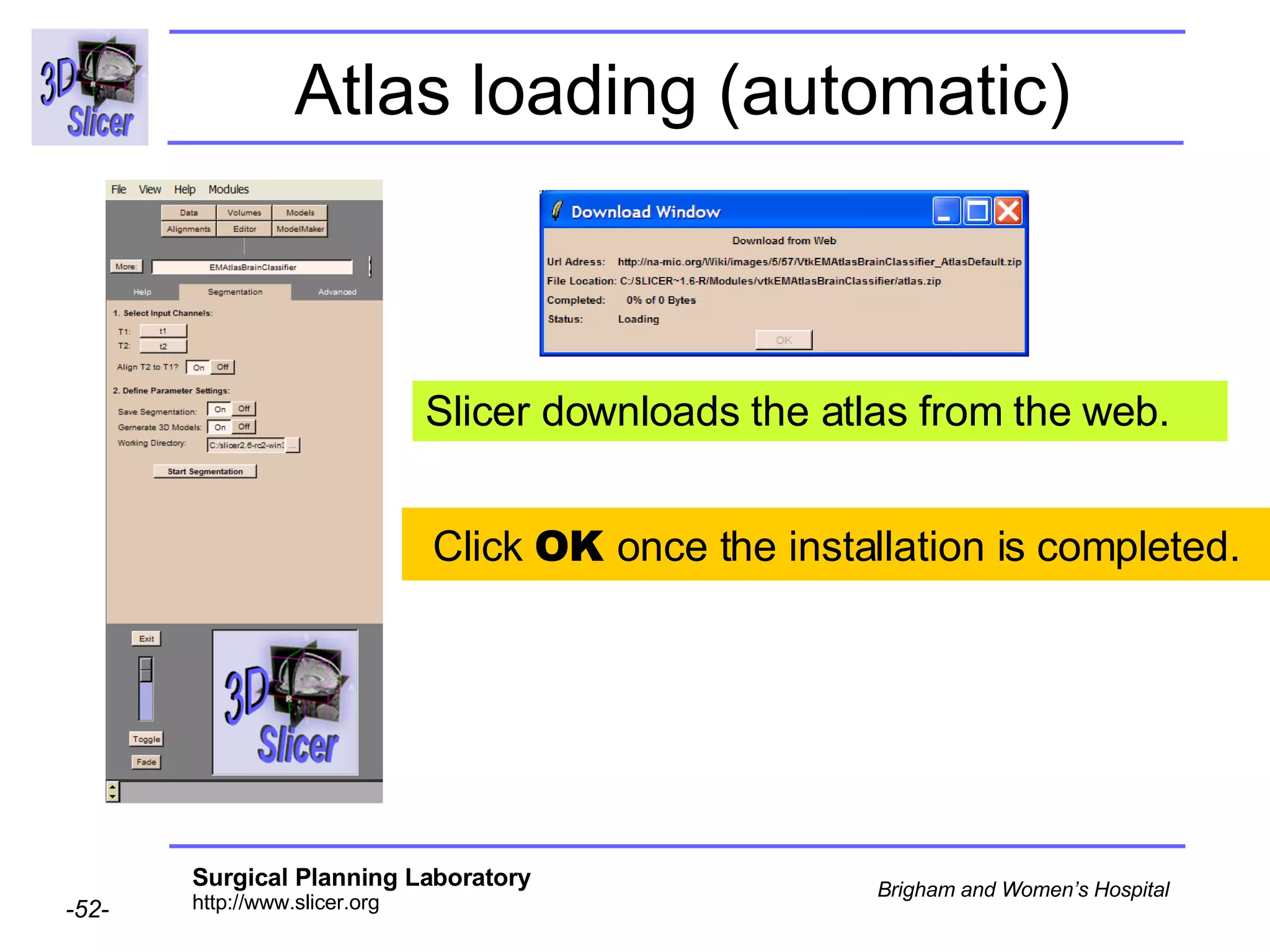
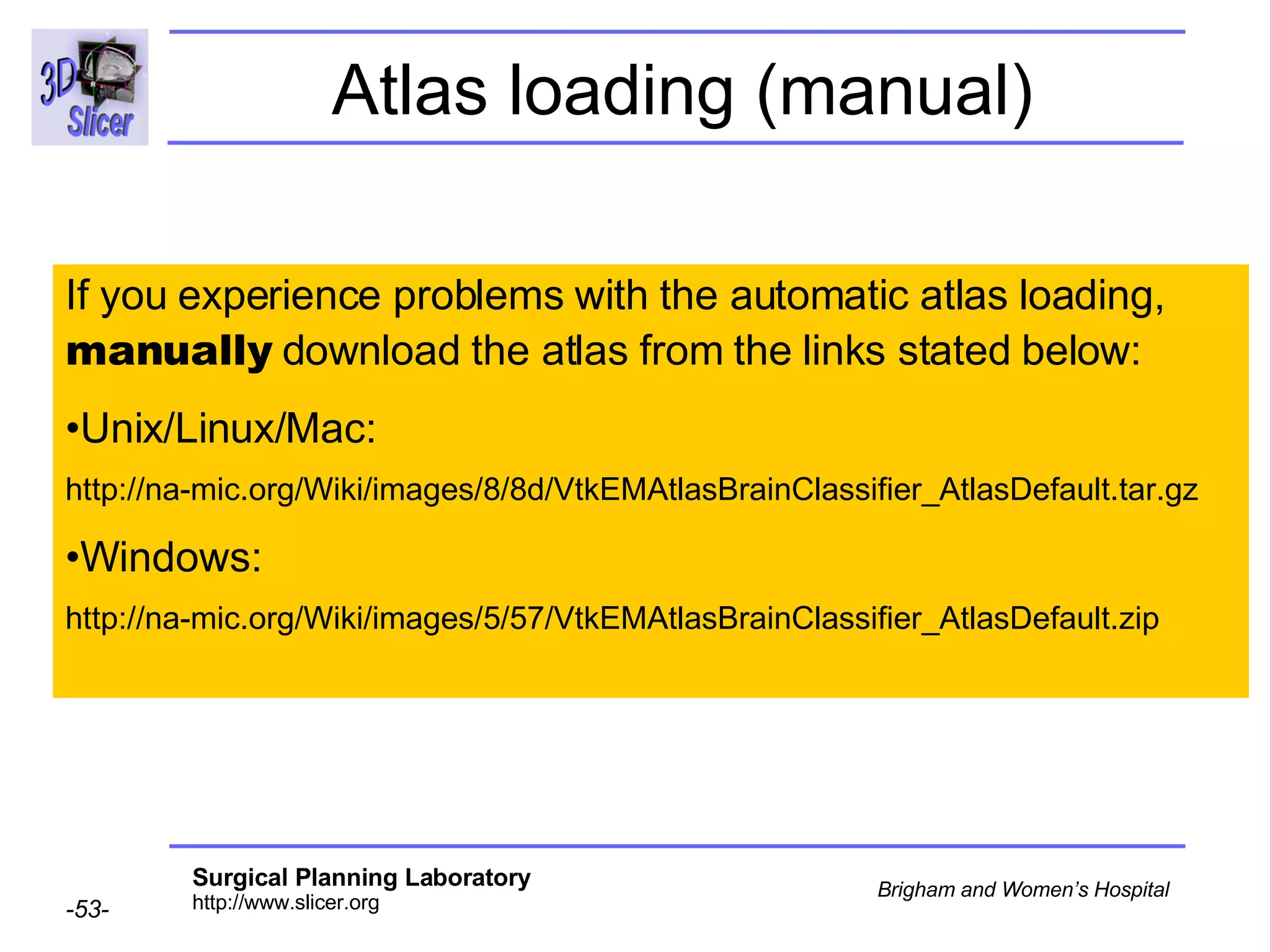
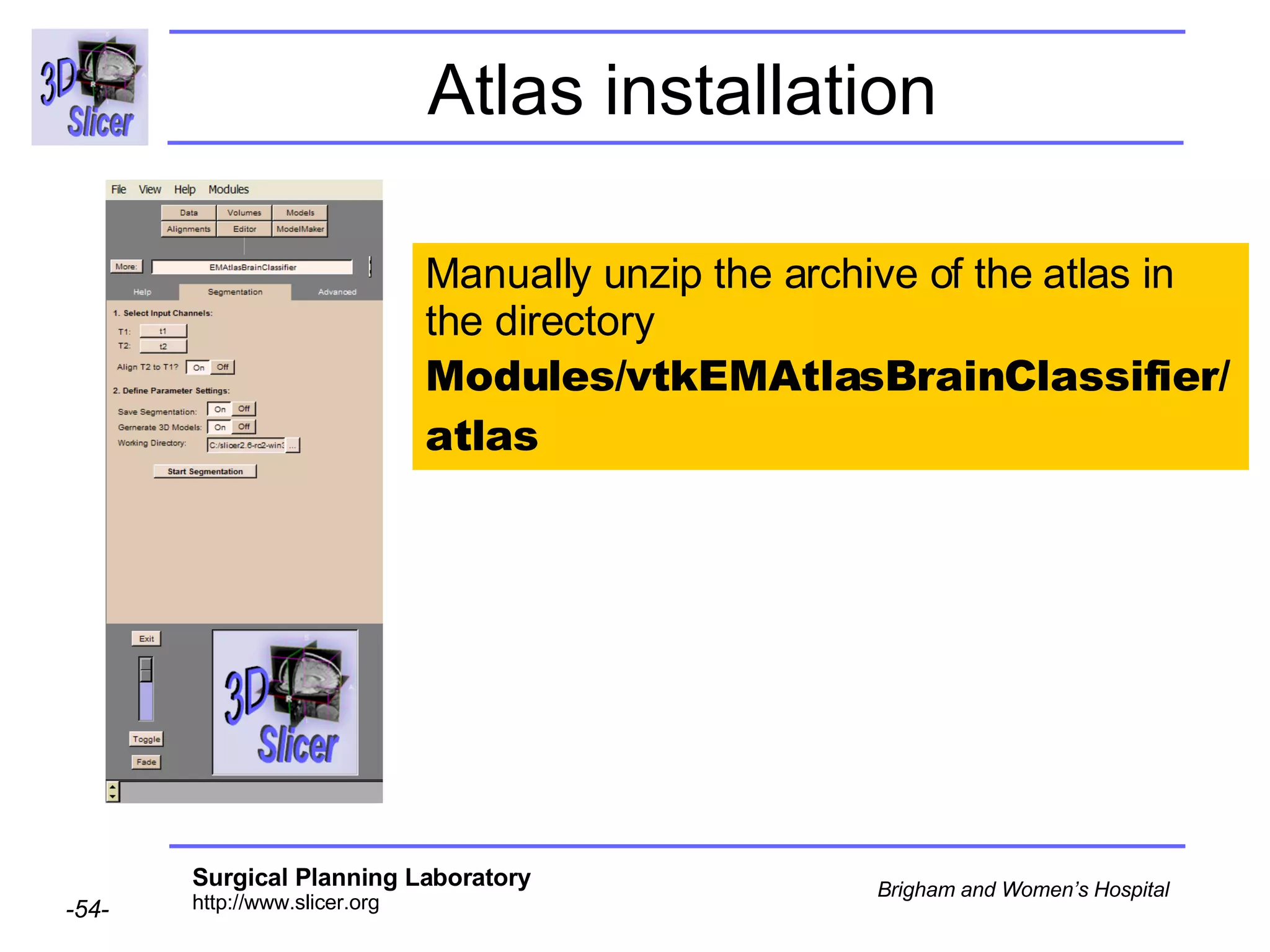
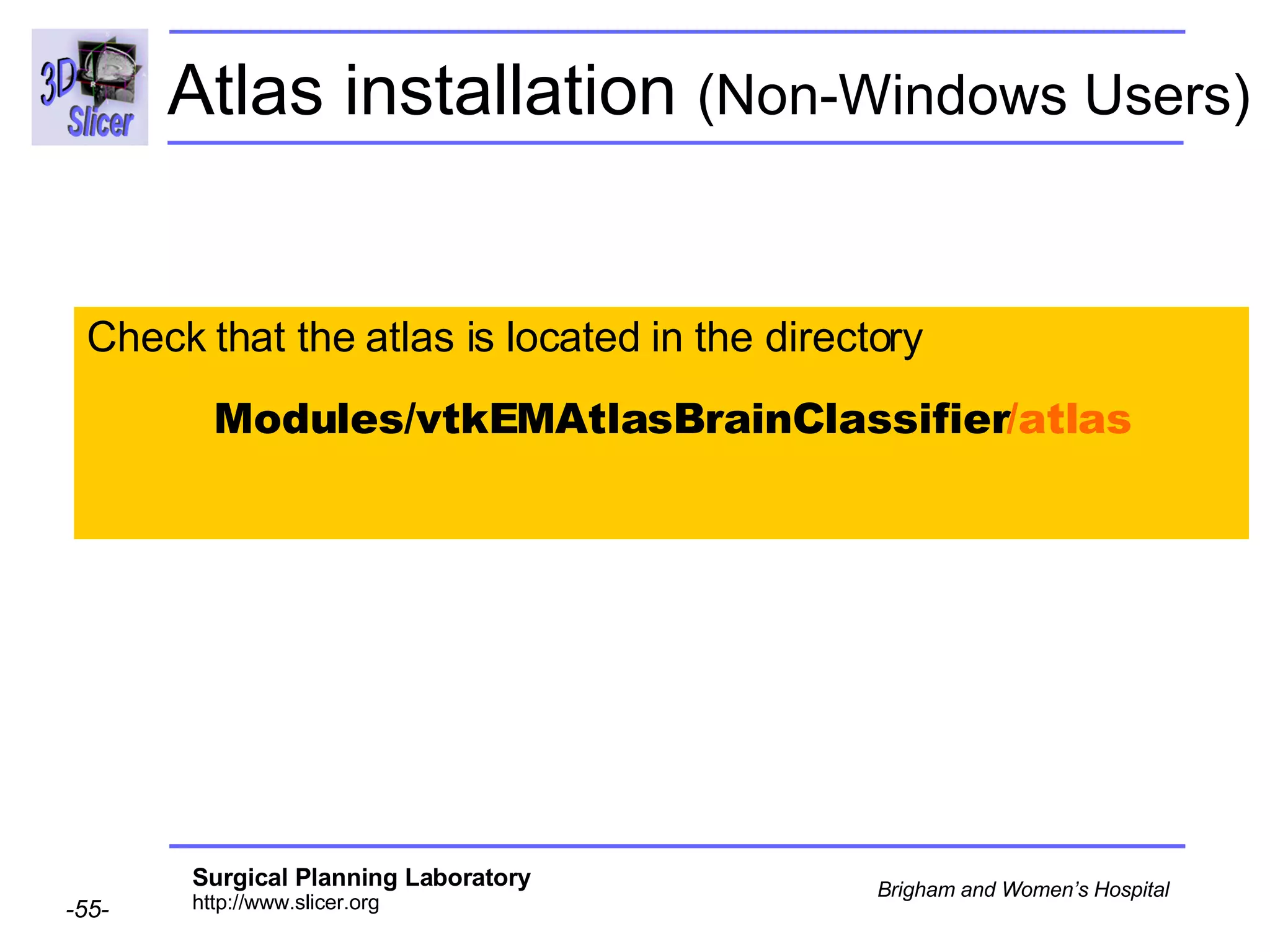
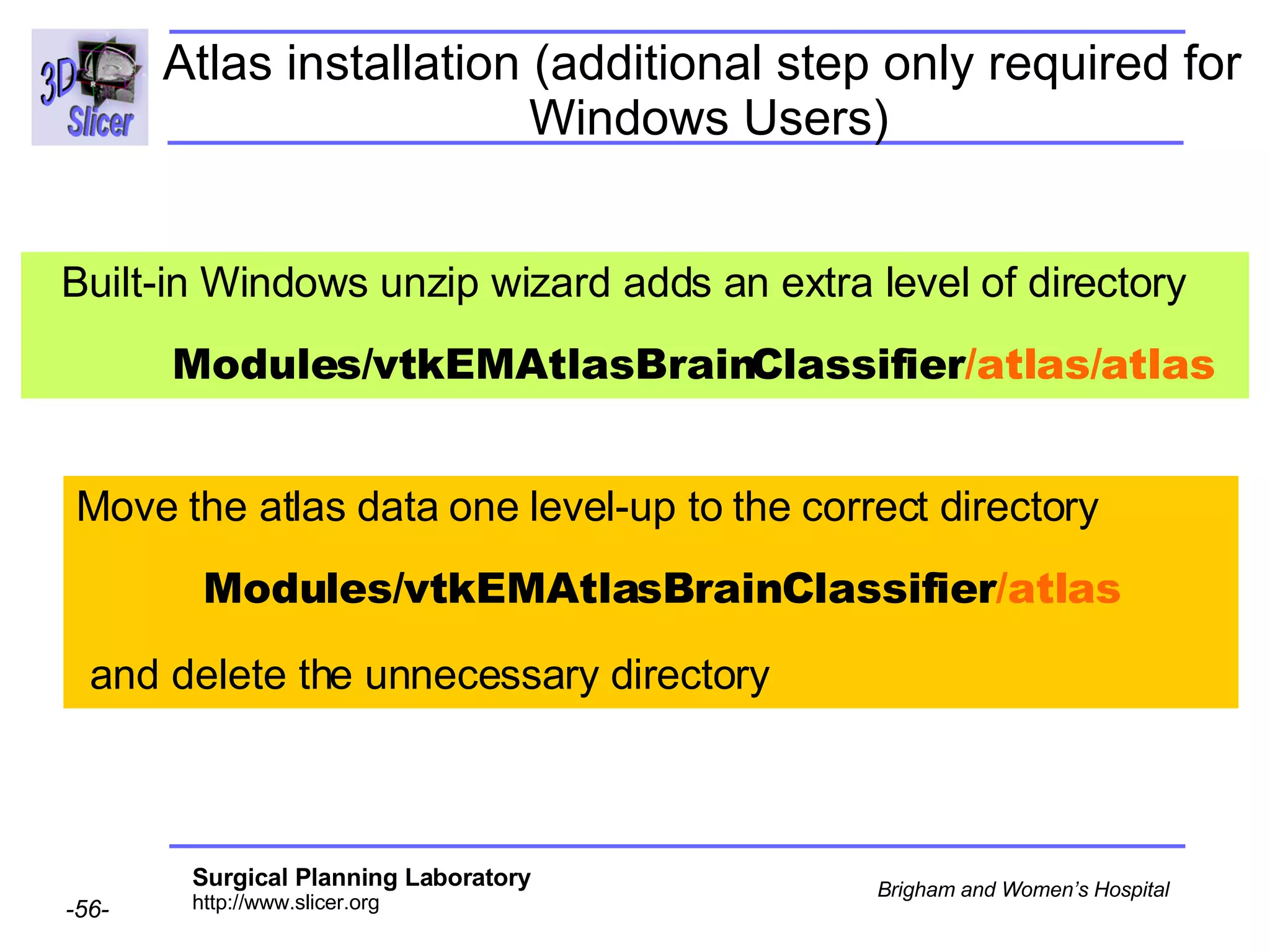
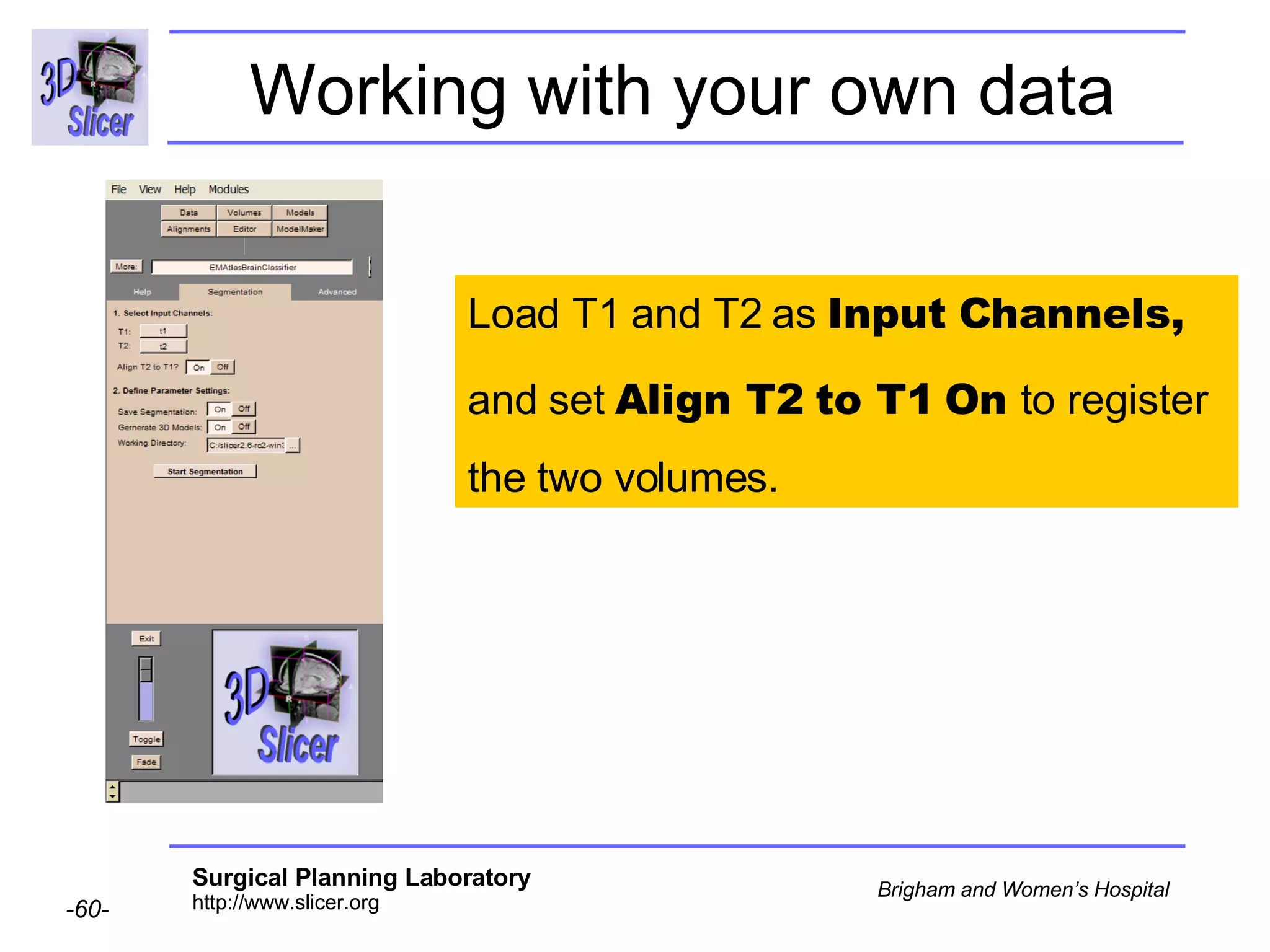
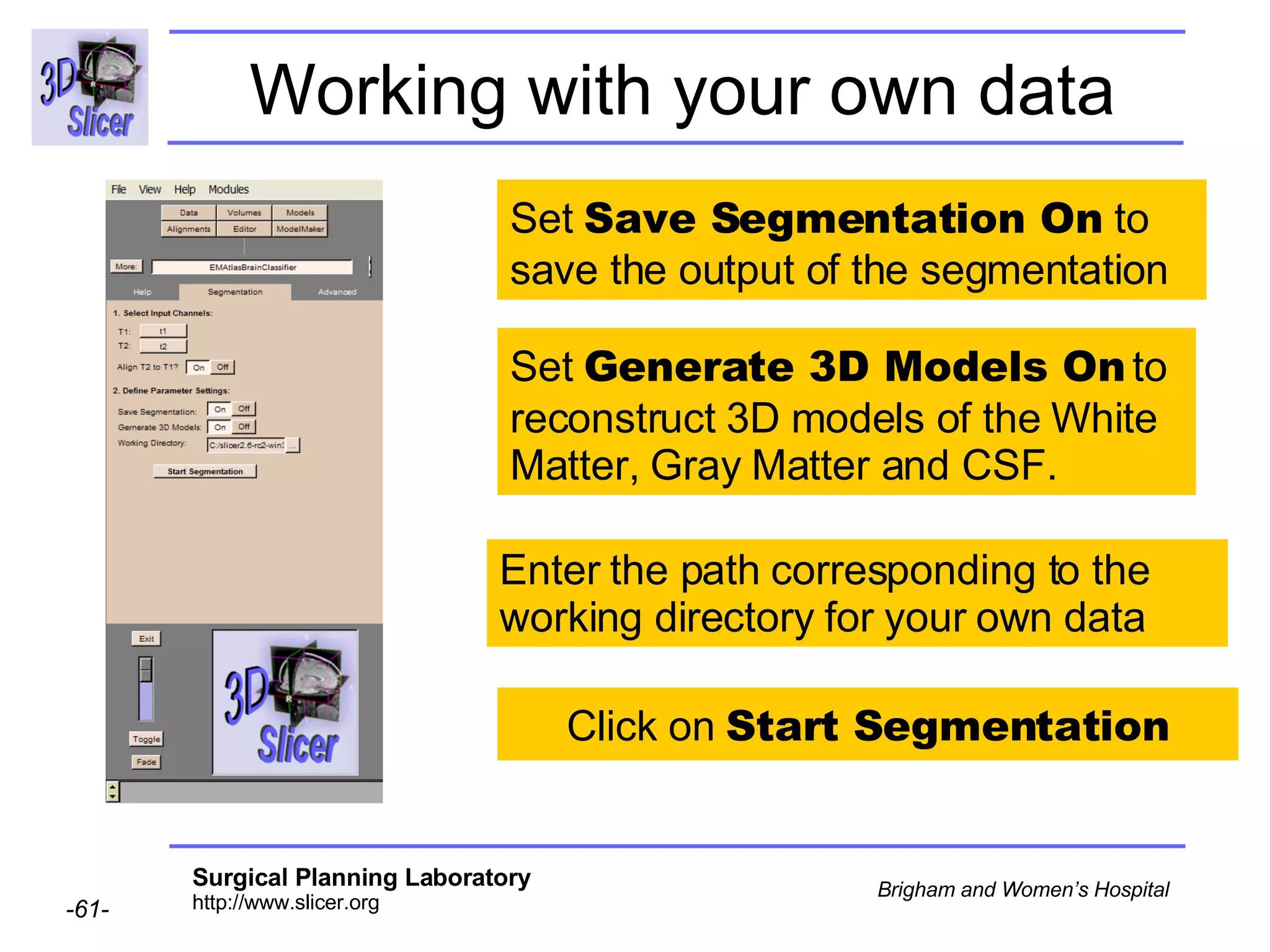
This document provides instructions for using the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm within the 3D Slicer software to automatically segment brain structures from MRI data. It outlines a 5-part tutorial: 1) an overview of the generic atlas and EM pipeline, 2) loading tutorial data, 3) hardware requirements, 4) segmenting the tutorial data, and 5) segmenting your own data. The EM algorithm relies on a previously computed generic atlas to generate a patient-specific atlas and segment brain structures into white matter, gray matter, CSF and background.