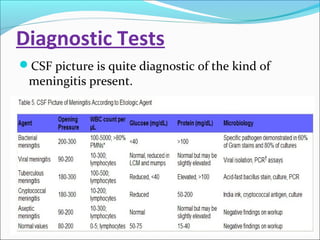
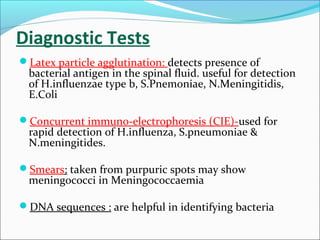
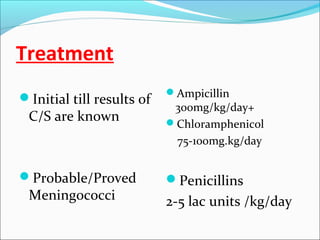
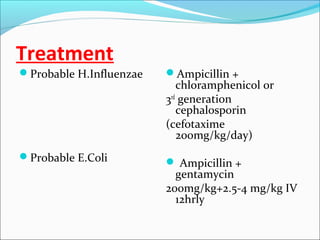
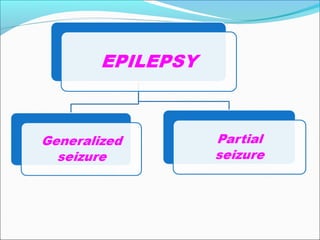
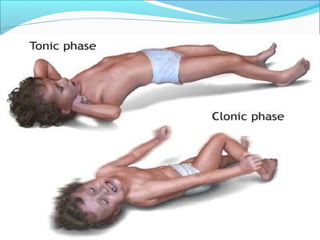
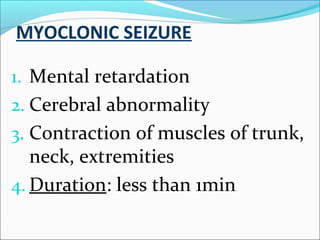
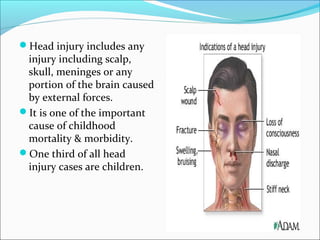
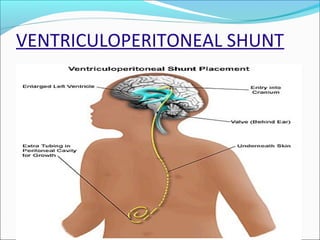
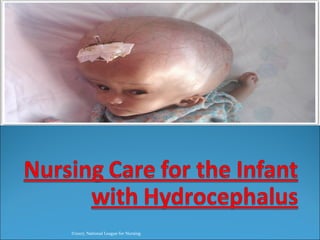
The document discusses hydrocephalus in children, defining it as a condition characterized by excessive cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. It covers the etiology, pathophysiology, clinical features, imaging studies, and treatment of hydrocephalus, noting that the mainstay of treatment is surgical placement of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid from the brain to the abdomen. Complications of hydrocephalus and hydrocephalus treatment are also reviewed.




















![Ketan Thummar-Hydrochephalus in children
Complications: Infection
Two days after the insertion of the VP shunt,
the patient develops signs of a shunt infection.
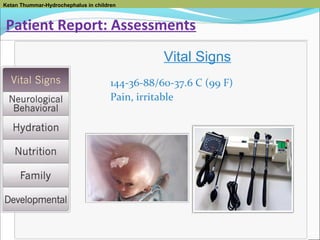
Temperature at 1600 39.4 C (103 F).
Child demonstrating behaviors consistent with IICP.
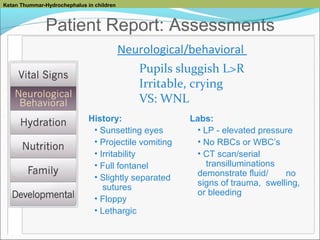
Monitor for Symptoms:
• Temperature
• Pain and tenderness
• Irritability
• Incisional changes,
abdominal distension/ pain
assess for meningitis
(nuchal pain, etc.)
Nursing Actions:
• Culture wound (+S. Aureus)
• CSF (from LP)
• Provide antipyretics
acetaminophen [Tylenol]or
ibuprofen [Advil]
• Administer antibiotics
cefuroxine [Ceftin])
• Comfort](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meningitis-in-children-131124053524-phpapp01/85/Pediatric-Nursing-Neurology-29-320.jpg)