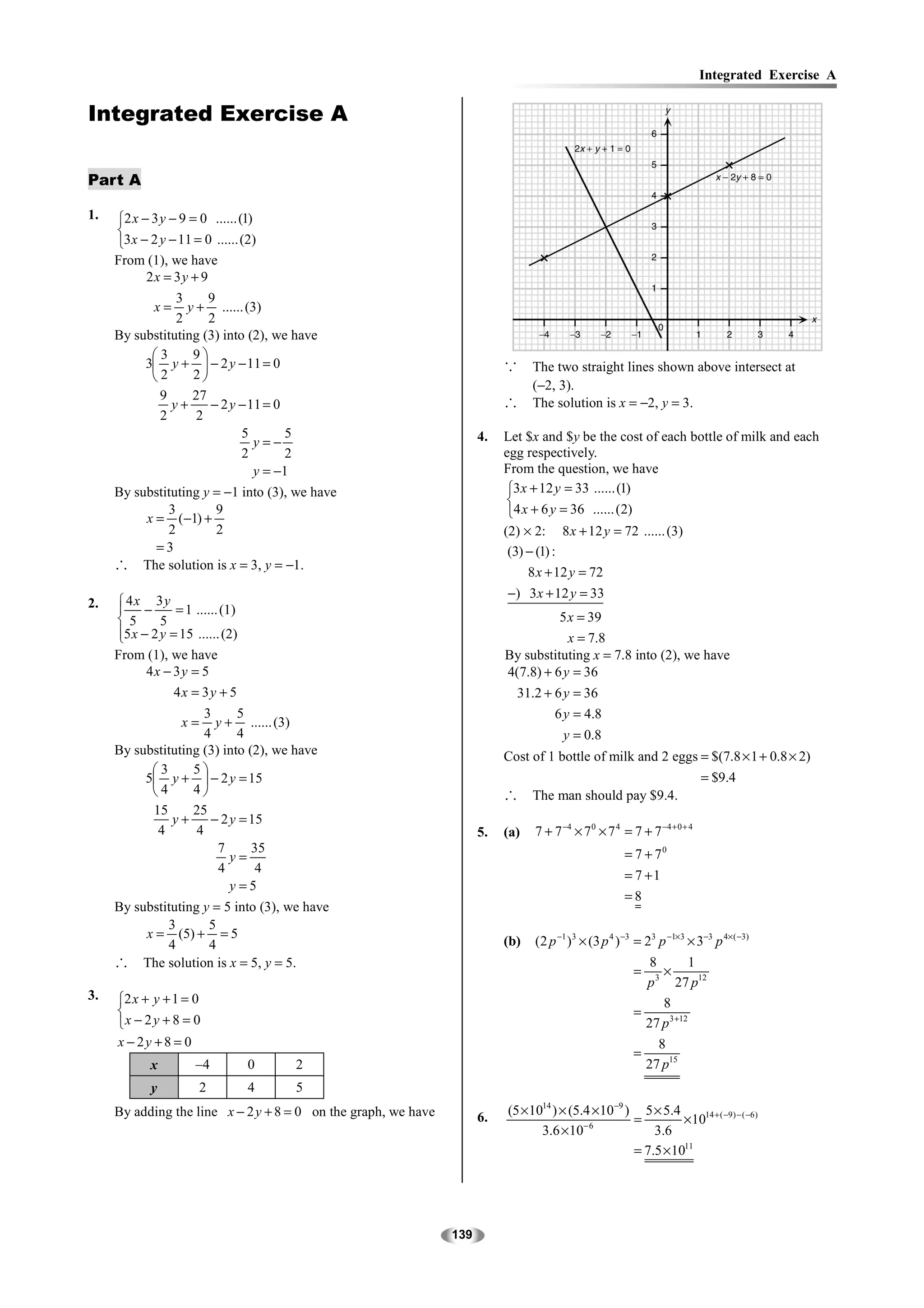
1. The document contains examples solving systems of linear equations and linear inequalities arising from word problems about mixtures, costs, graphs of lines, and similar contexts.
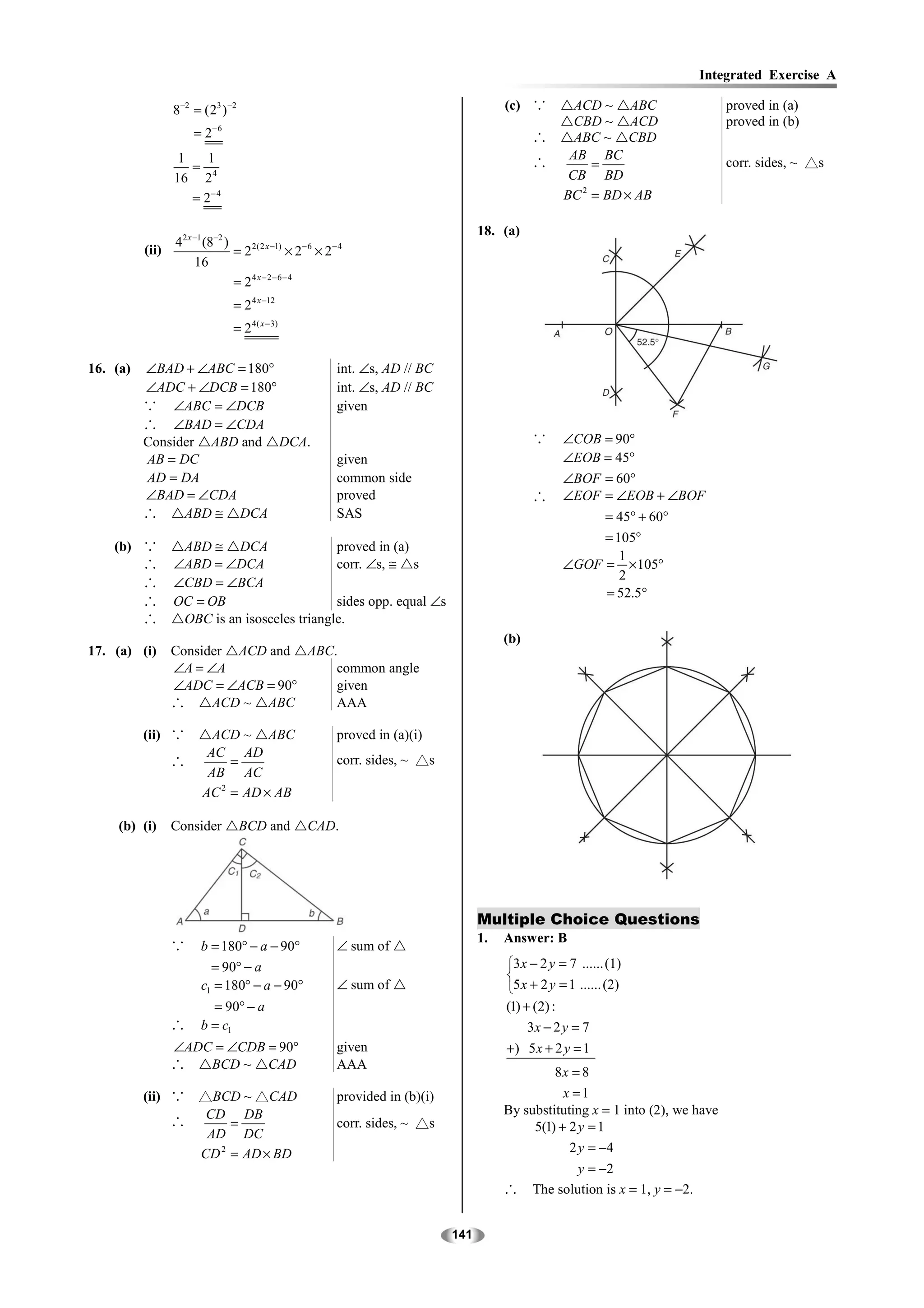
2. Similar figures and corresponding parts of congruent triangles are used to solve for missing lengths and angle measures.
3. Place value and binary and hexadecimal number systems are explained.