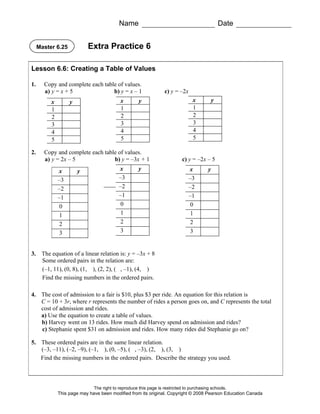
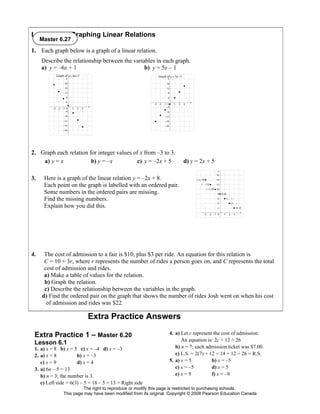
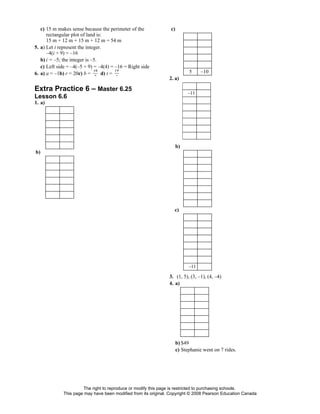
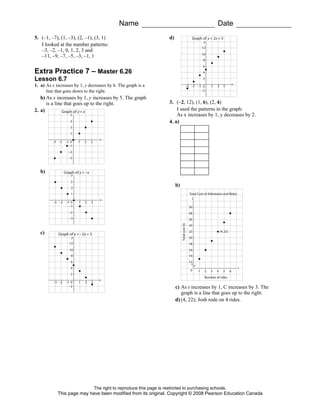
This document contains an extra practice worksheet for lesson 6.20 on solving equations using models. The worksheet contains 6 problems involving setting up and solving various equations to model word problems, finding unknown values, and verifying solutions. It provides students additional practice applying concepts of solving equations from the lesson.