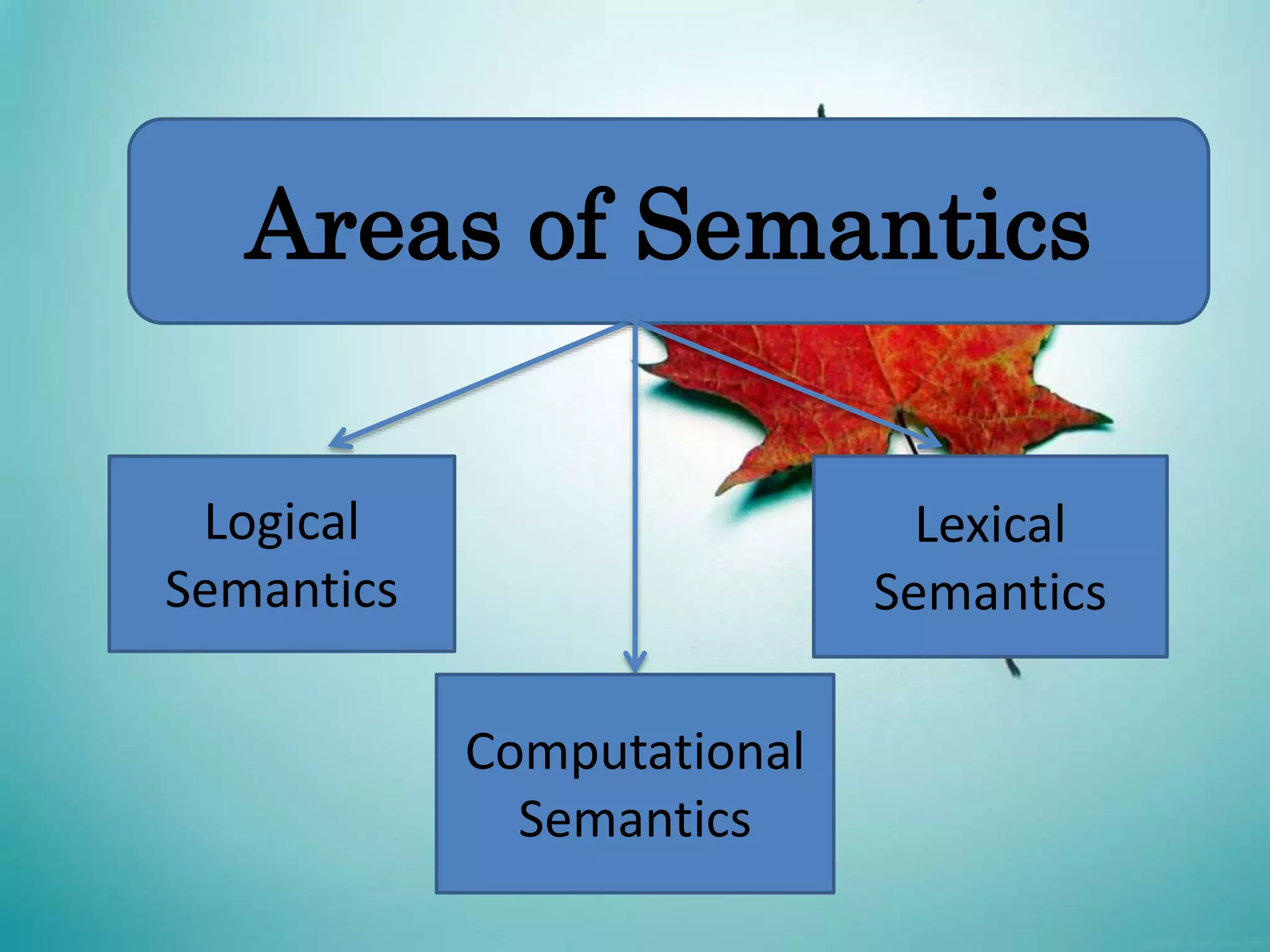
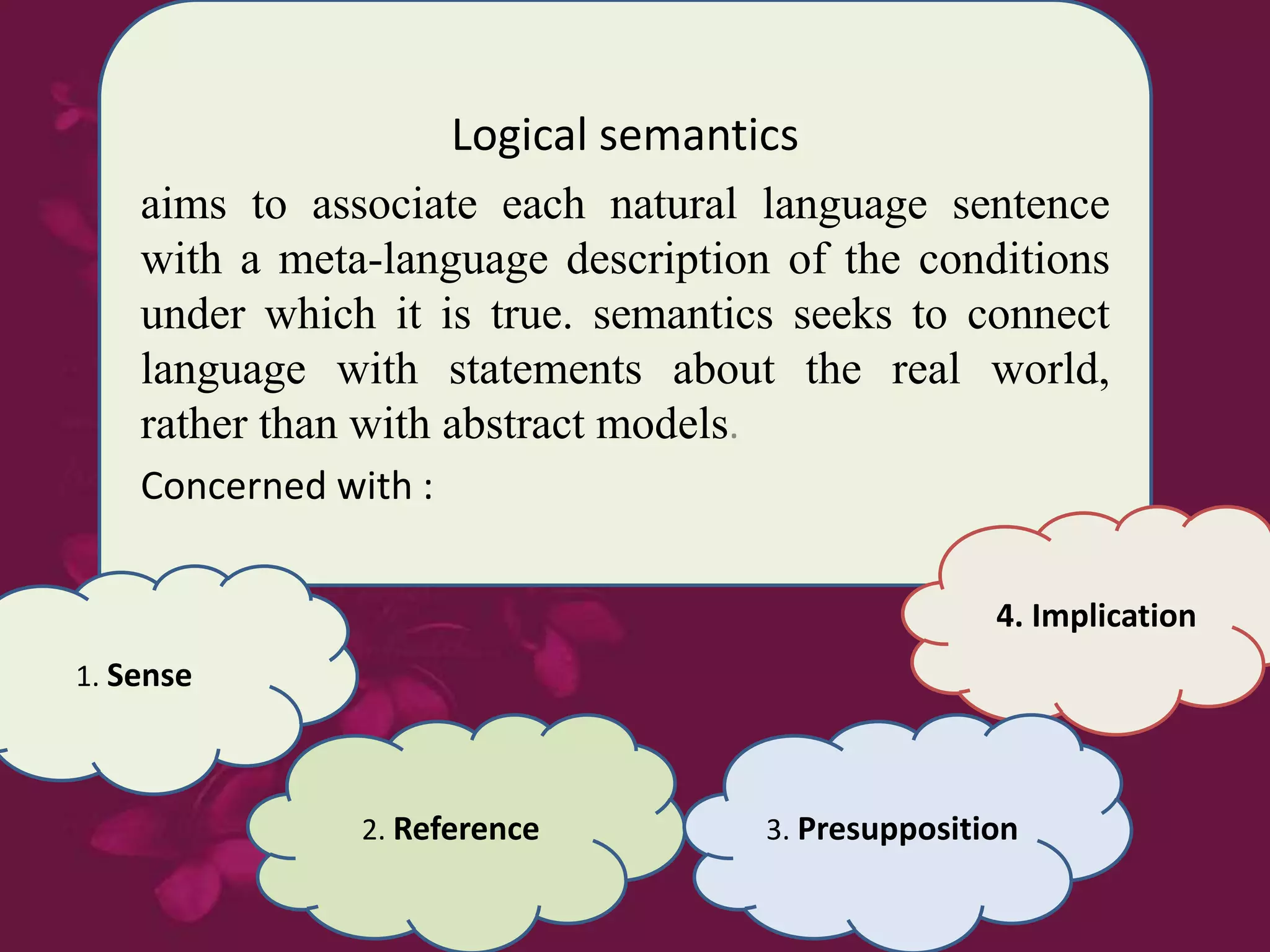
This document discusses semantics and provides an overview of key areas and researchers in the field. Semantics is defined as the study of meaning in language, focusing on the relationship between signs/words and their meaning for speakers. The key areas covered are logical semantics, which associates sentences with conditions of truth; lexical semantics, which studies word-level meaning; and computational semantics, which aims to automate meaning representation for natural language processing. Influential researchers mentioned include Donald Davidson, who developed truth-conditional semantics and questioned the notion of what a language is.