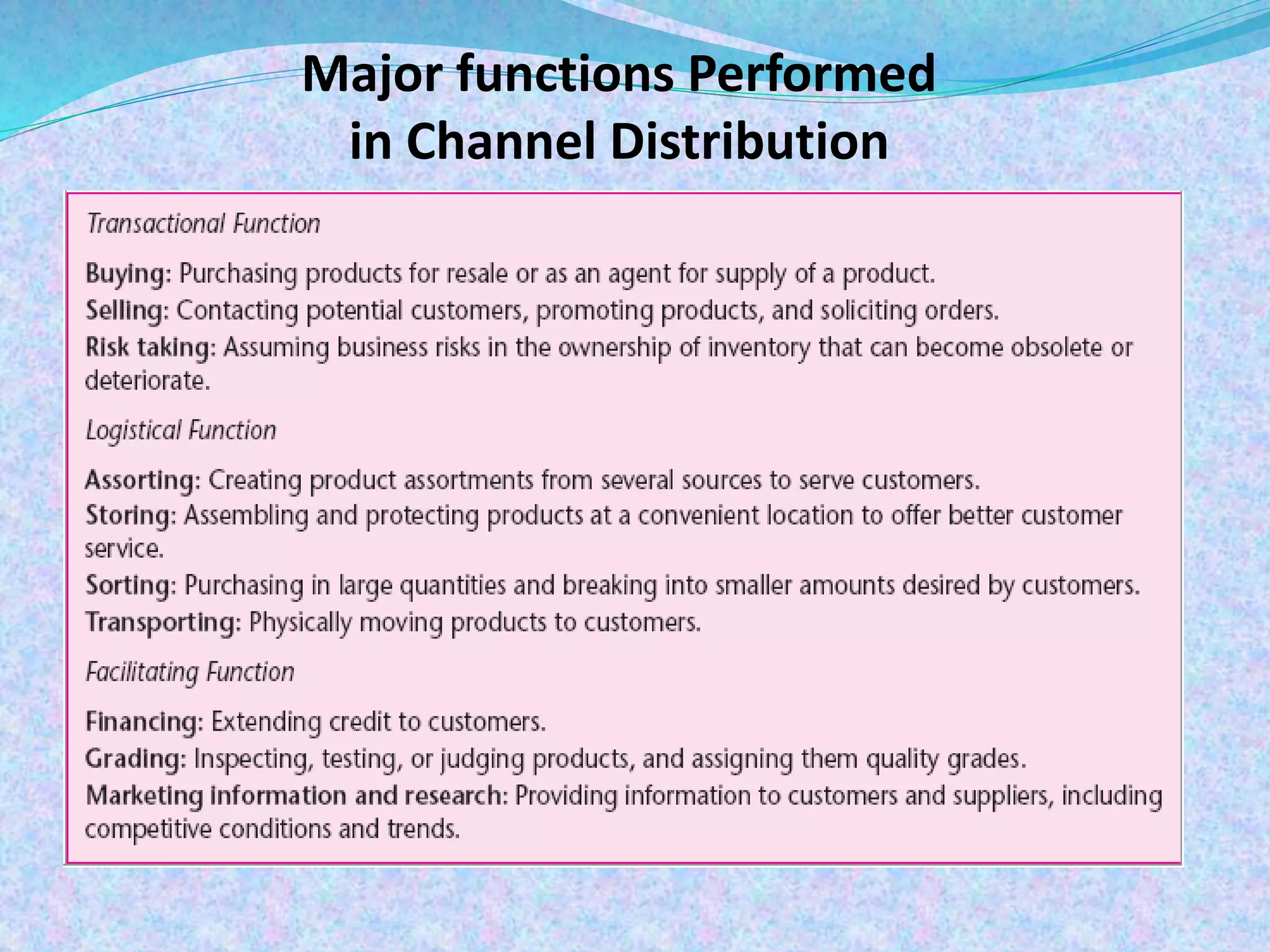
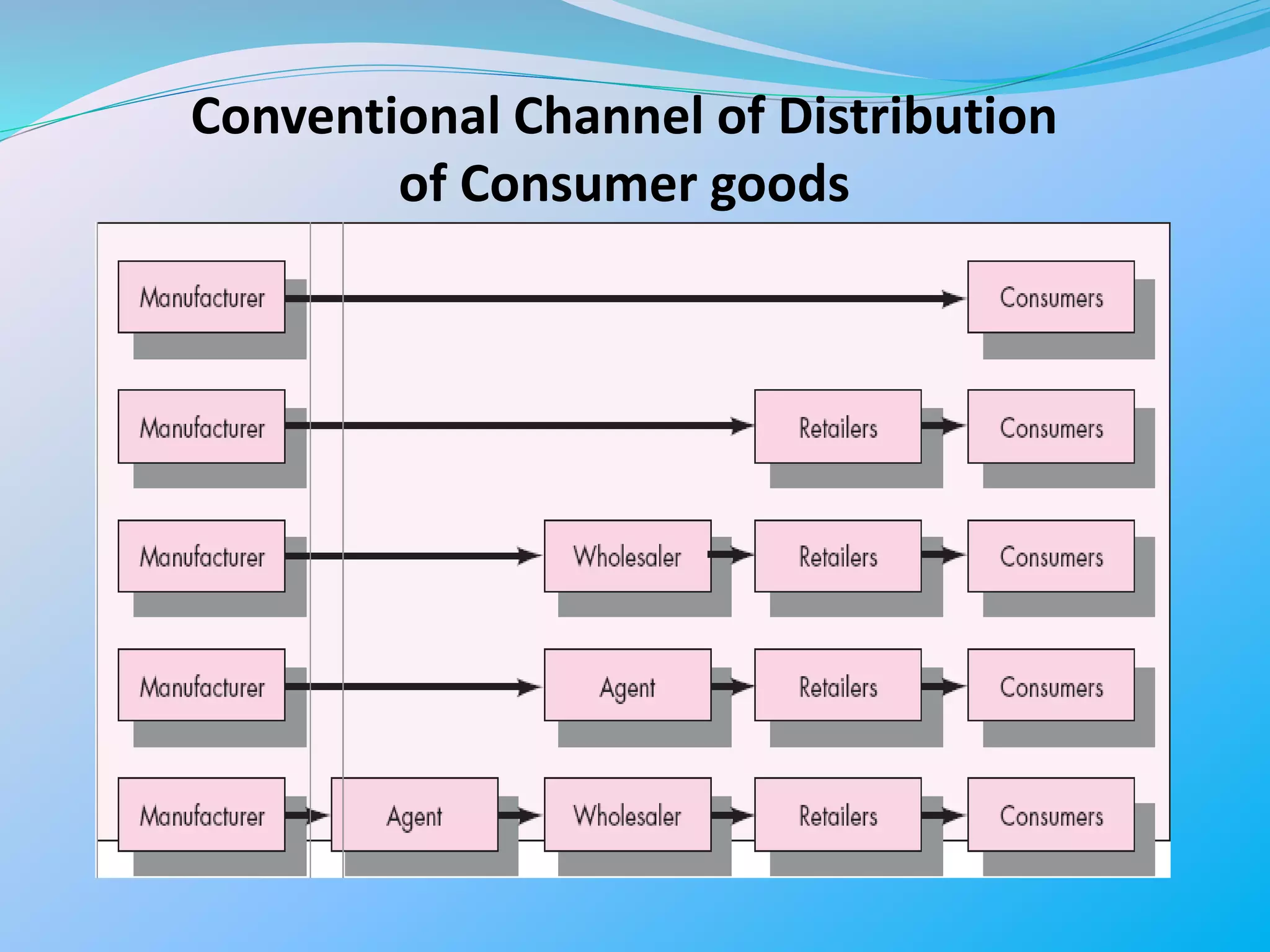
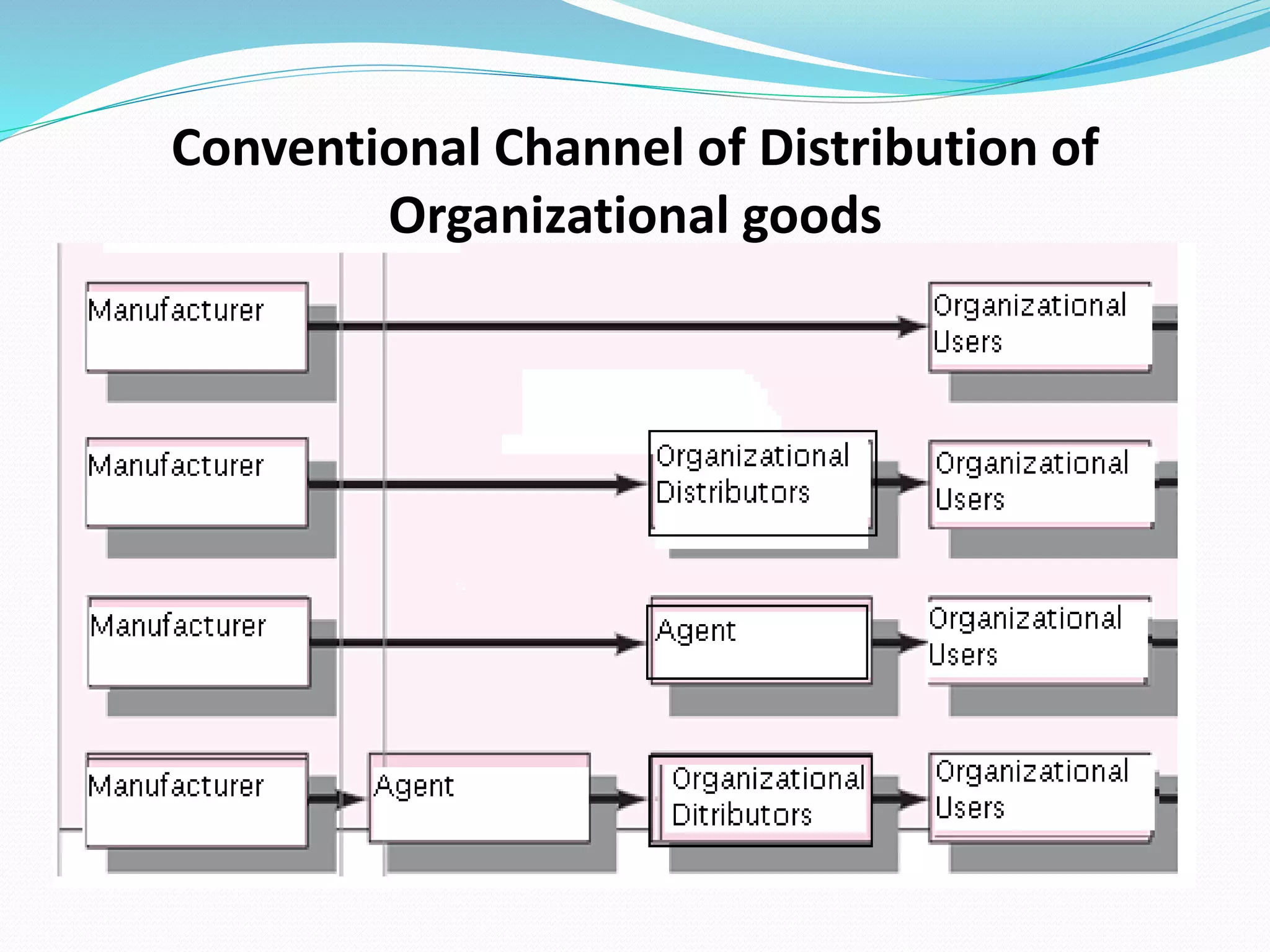
The document outlines distribution strategies, highlighting various marketing intermediaries such as middlemen, wholesalers, retailers, and agents that facilitate the journey of goods from producers to consumers. It categorizes distribution channels into intensive, selective, and exclusive strategies while discussing considerations for channel planning and total distribution costs. Additionally, it provides an overview of wholesaling and different retail formats, including specialty stores, department stores, warehouse stores, grocery stores, resale stores, online stores, and non-store retailing methods.