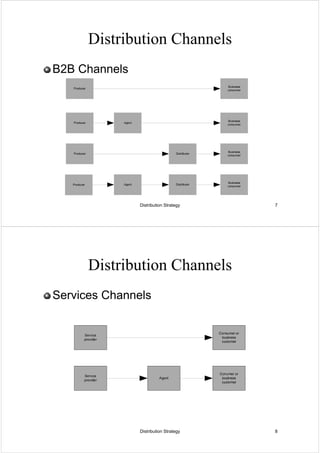
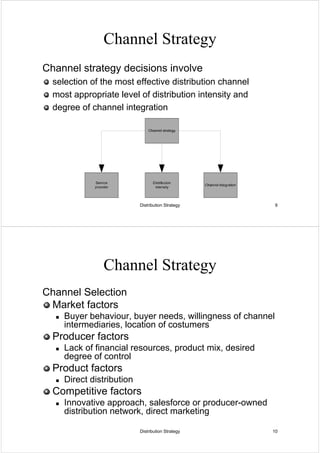
This document discusses distribution strategy. It defines distribution as one of the four aspects of marketing, with distributors acting as middlemen between manufacturers and retailers. It then discusses distribution channels and how they are used to reconcile producer and consumer needs. The document outlines different channel strategies involving selection, intensity, and integration of channels. It also discusses channel management, physical distribution systems, and some ethical issues related to distribution.