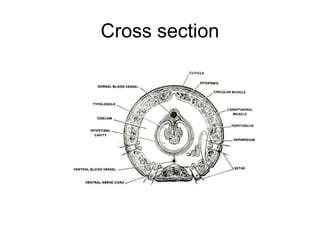
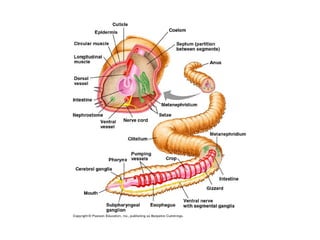
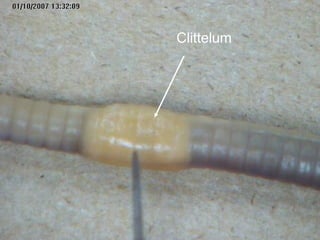
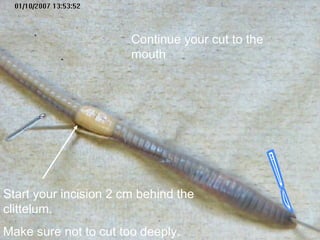
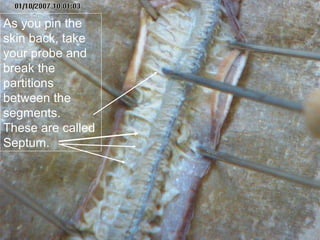
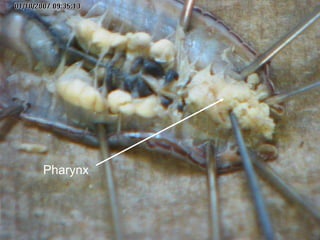
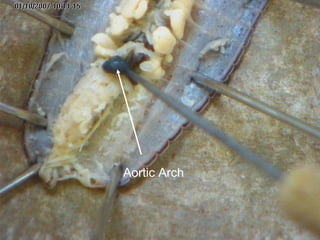
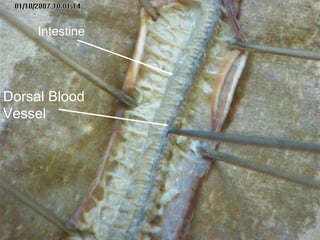
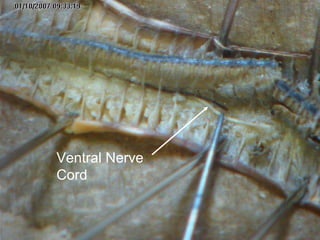
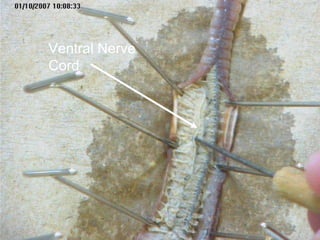
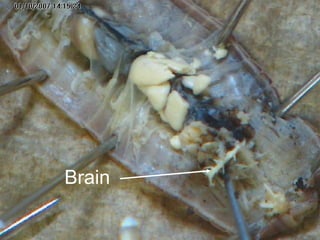
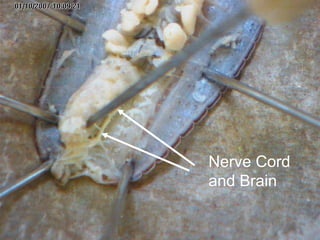
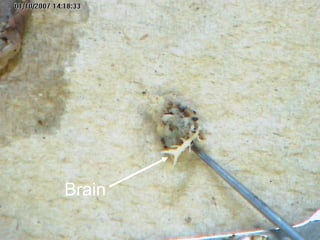
The document provides instructions for students to dissect an earthworm and identify its internal and external structures. It lists the key terms students should know and the tools needed. Students are instructed to identify segments, septum, setae, the pharynx, esophagus, crop, gizzard, intestine, aortic arches, ventral nerve cord, dorsal blood vessel, clittelum, seminal vesicles, and seminal receptacles. The dissection procedure involves pinning the worm, making an incision behind the clittelum, separating the skin using pins, and using a probe to break partitions between segments. Key structures to locate include the mouth, setae, sperm duct, and clittelum.