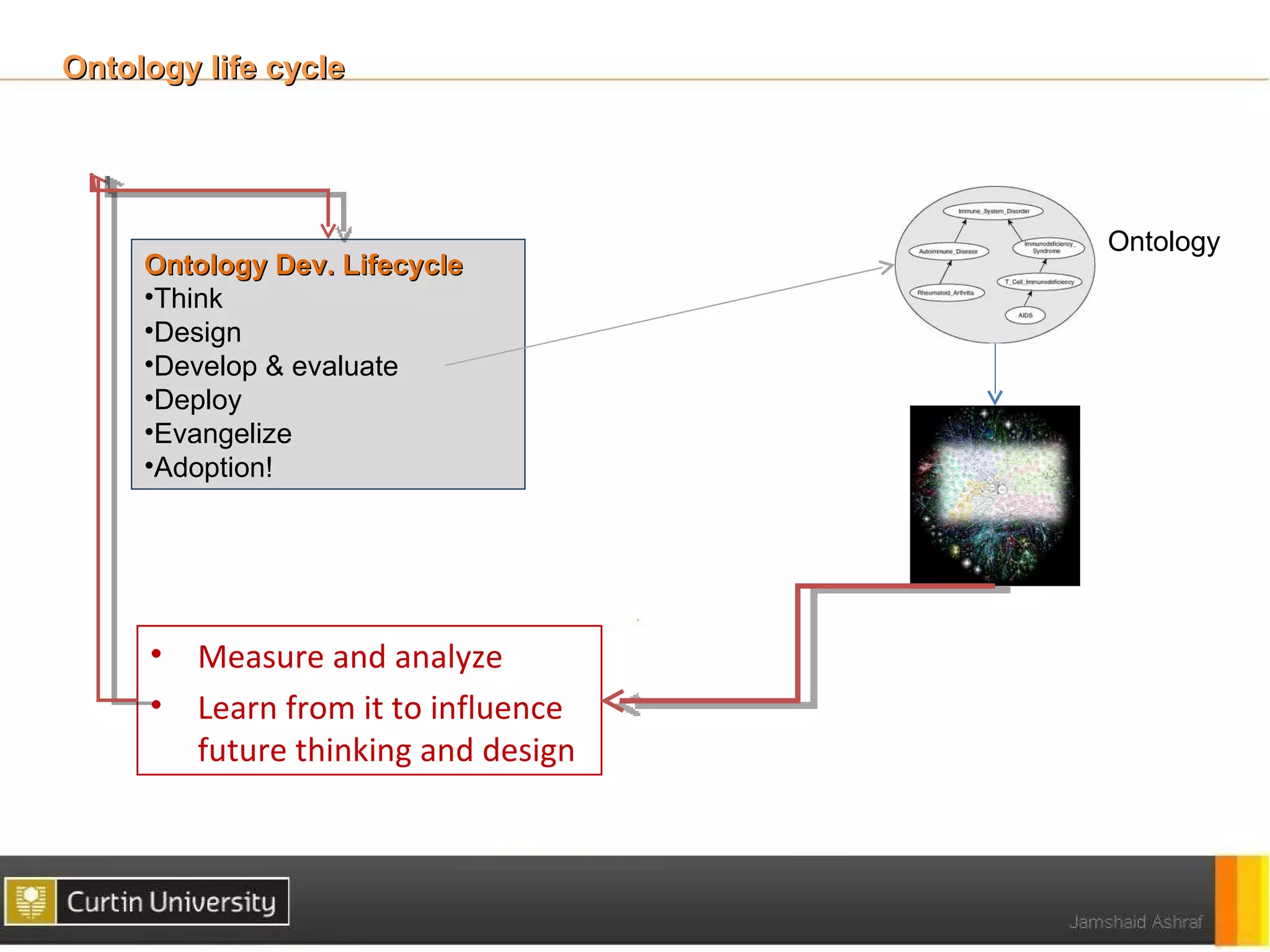
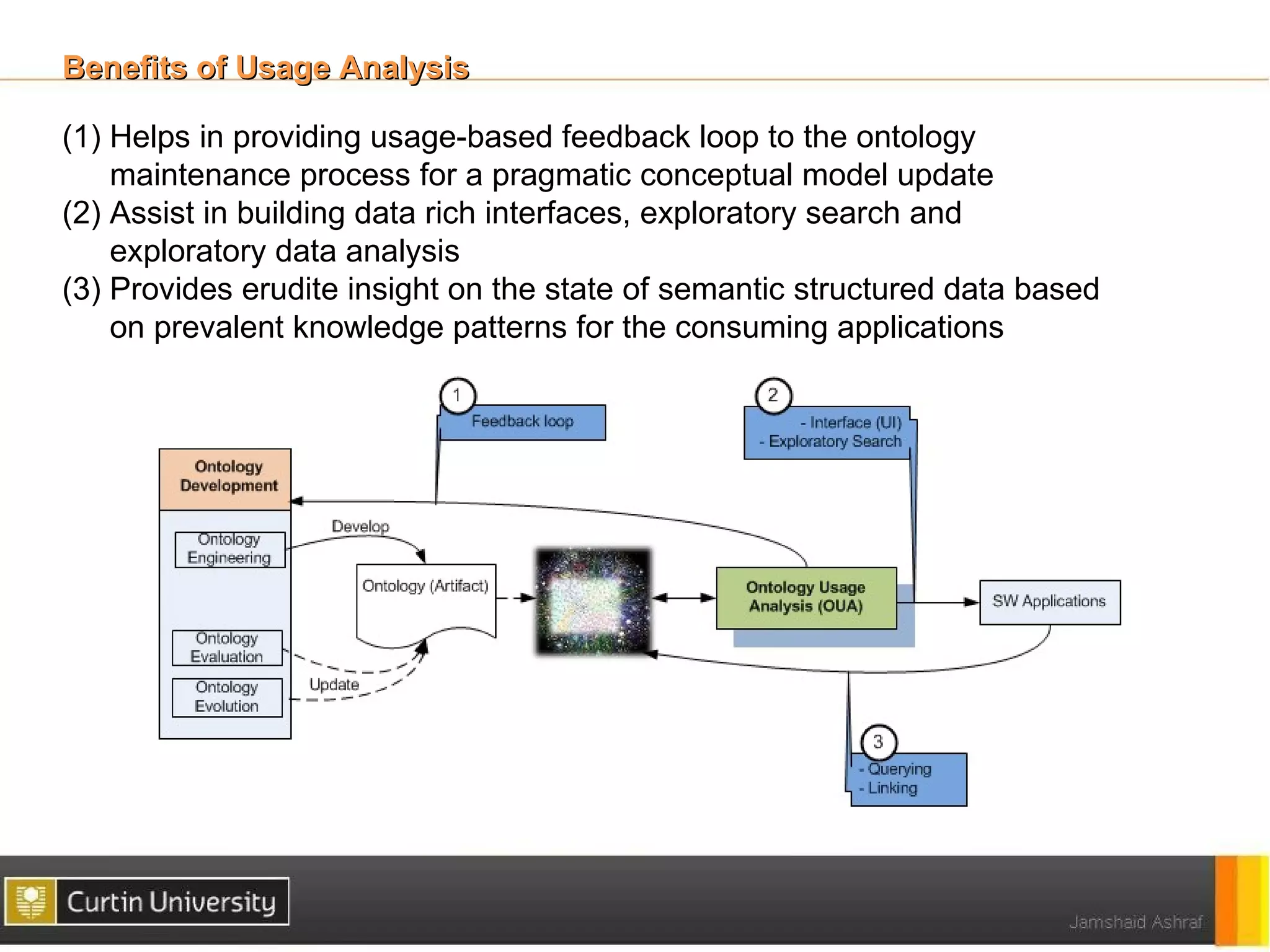
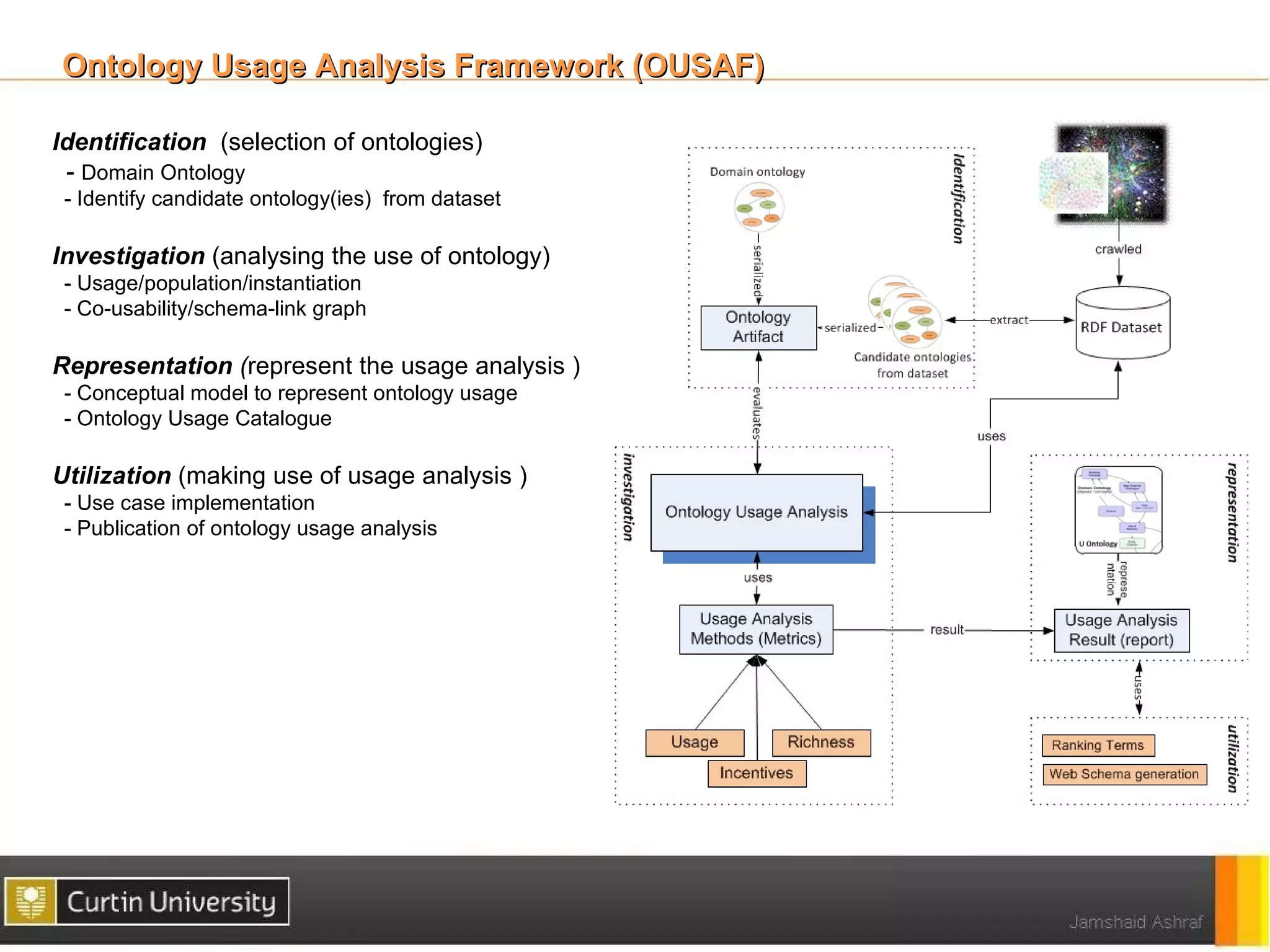
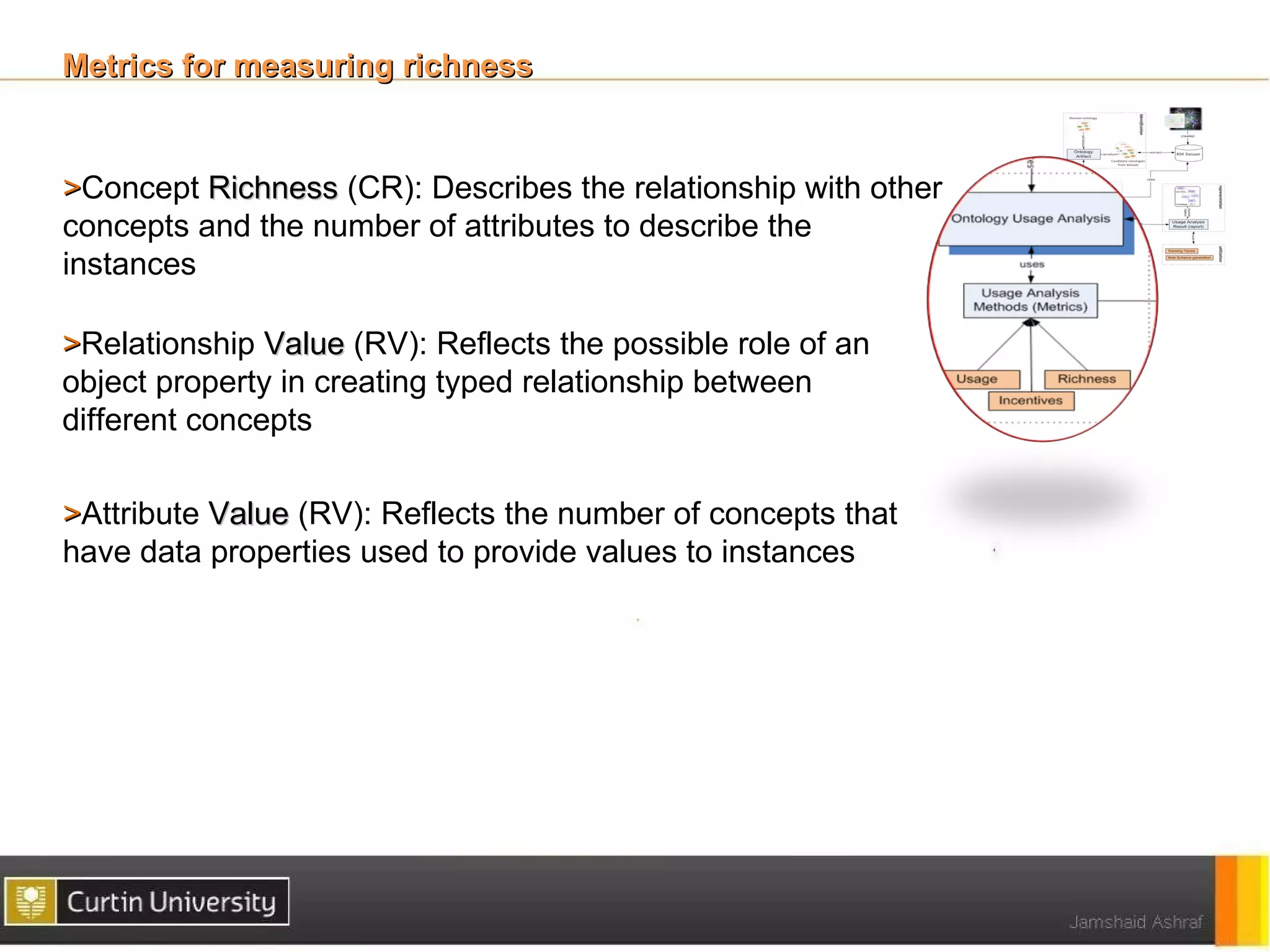
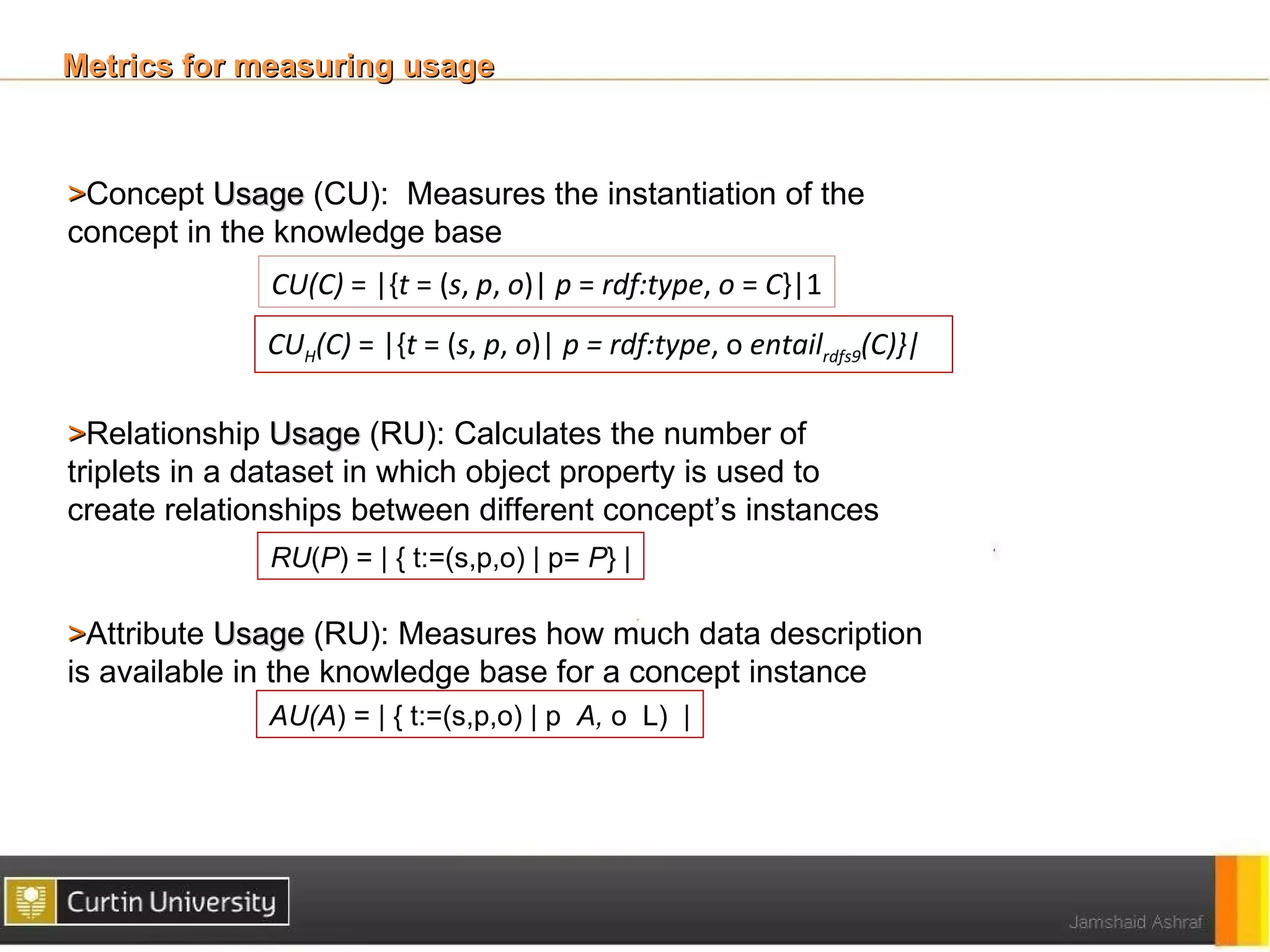
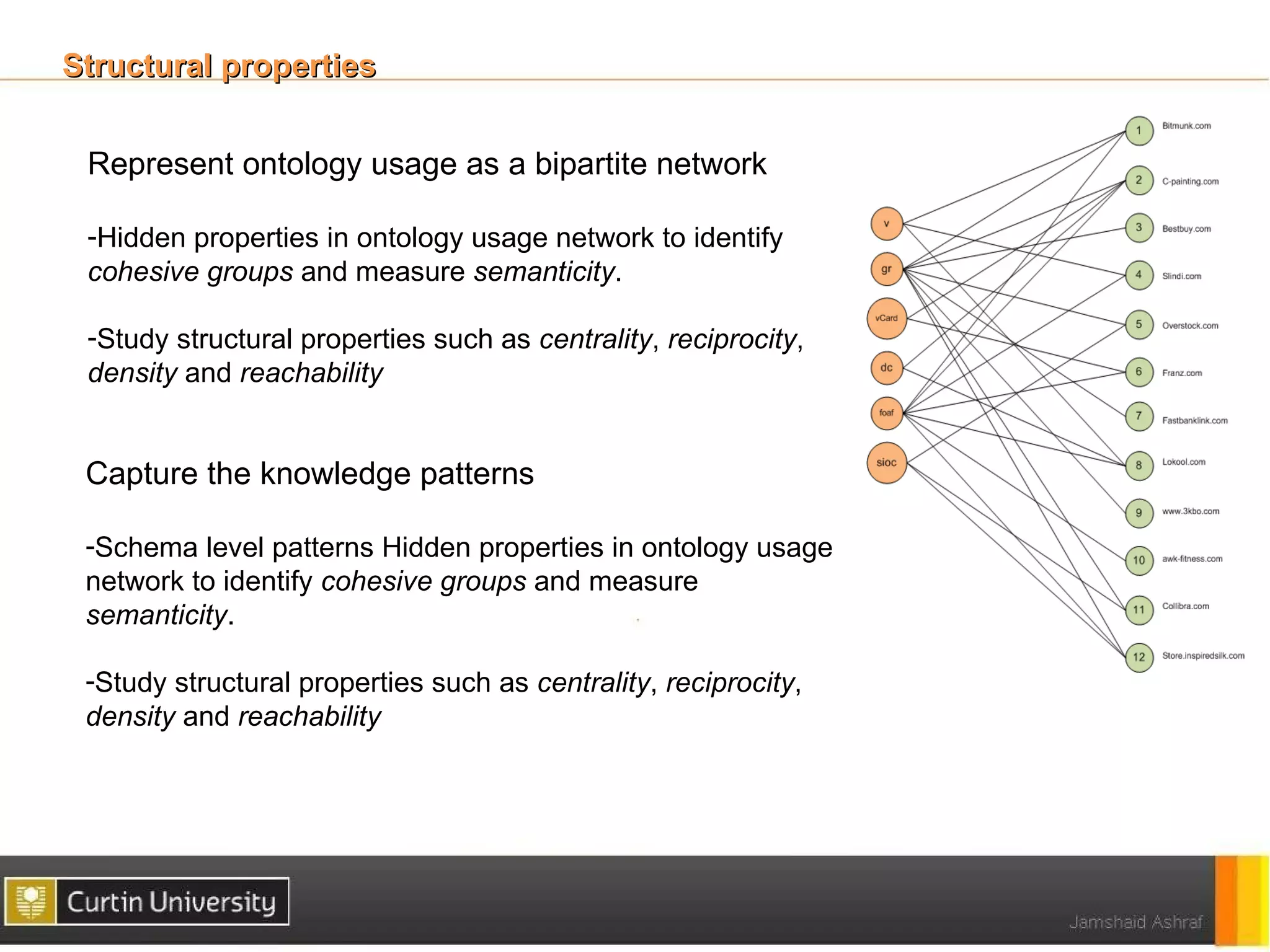
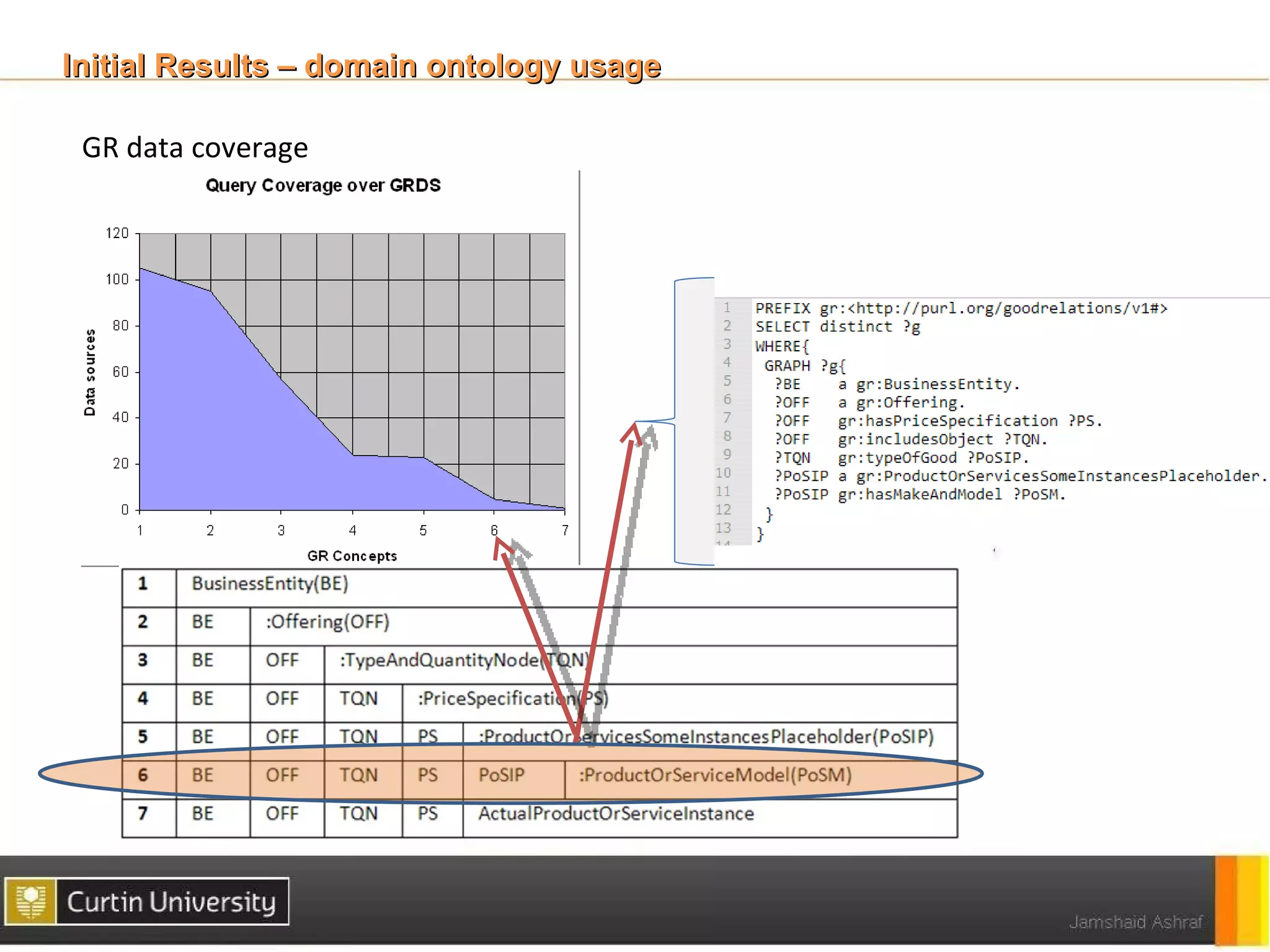
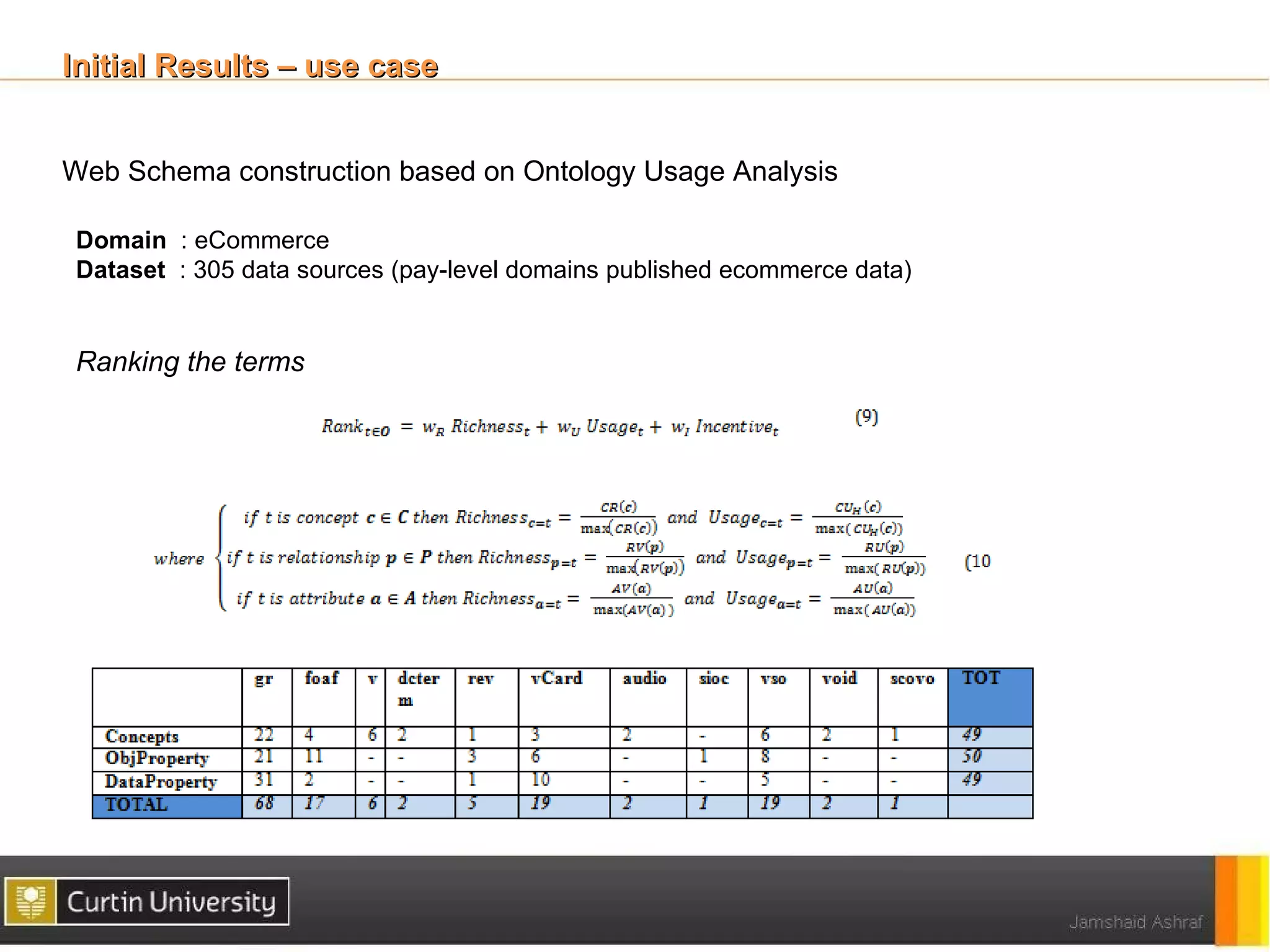
The document discusses a framework for ontology usage analysis, addressing the increase in ontology use and the need for better visibility into how they are utilized in the semantic web. It presents the Ontology Usage Analysis Framework (OUSAF), which includes methods for identifying ontologies, analyzing their usage, and implementing metrics to evaluate concept, relationship, and attribute usage. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of understanding ontologies' roles in the linked data cloud and suggests future work to enhance datasets and automate the ontology usage catalog publication.

![Knowledge focused
[1999 – 2006] - ONTOLOGY
Instance data
Ontologies
Knowledge Focused
•Ontology Languages
•Ontology authoring tools
•Reasoning
•Ontology evaluation
•Ontology evolution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ouaphdsymjamshaideswc2012v0-2-120614231558-phpapp02/75/A-Framework-for-Ontology-Usage-Analysis-2-2048.jpg)
![(Structured) Data focused
Ontologies
[2006 – to data] - LINKED DATA
Linked Data
Data Focused
•Linked Data principles
•Linked Open Data project
•LOD cloud
•RDFa
•RDF data analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ouaphdsymjamshaideswc2012v0-2-120614231558-phpapp02/75/A-Framework-for-Ontology-Usage-Analysis-3-2048.jpg)


![U Ontology
Ontology Usage Ontology (U Ontology)
Goal : Capture the detail of ontologies and their usage
Use cases :
- publish the ontology usage details on the web.
- generate prototypical SPARQL queries
Reusing existing ontologies
-Ontology Metadata Vocabulary (OMV) [1]
-Ontology Application Framework (OAF) [2]
-FOAF, DC
[1] Hartmann, J., Palma, R., Sure, Y., Suárez-Figueroa, M.C., Haase P.: OMV– Ontology Metadata Vocabulary. In: The
Ontology Patterns for the Semantic Web (OPSW) Workshop at ISWC 2005, Galway, Ireland (2005)
[2] http://ontolog.cim3.net/file/work/OntologySummit2011/ApplicationFramework/OWL-Ontology/BenefitsAndTechniques-
WithDocumentation.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ouaphdsymjamshaideswc2012v0-2-120614231558-phpapp02/75/A-Framework-for-Ontology-Usage-Analysis-16-2048.jpg)