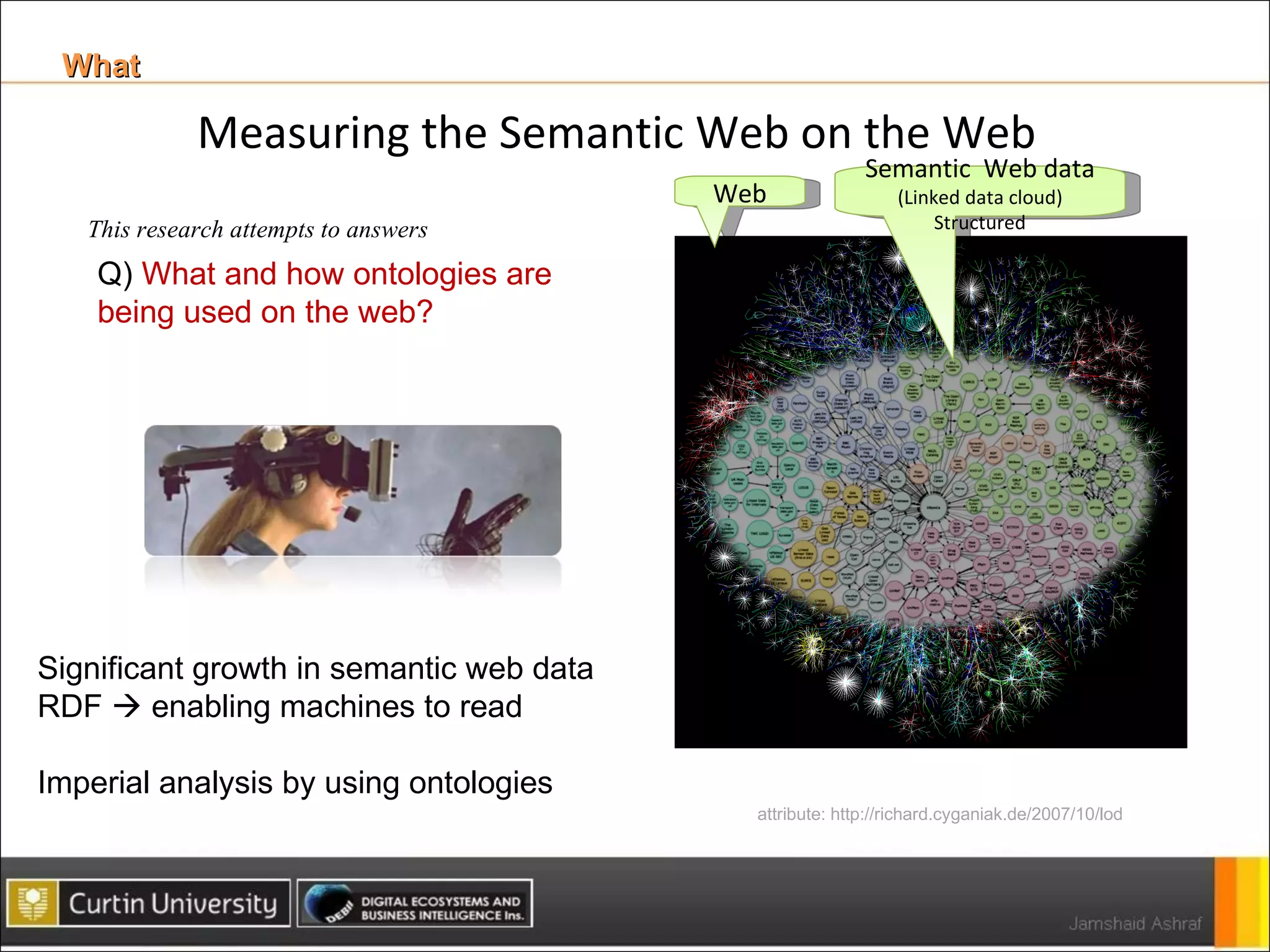
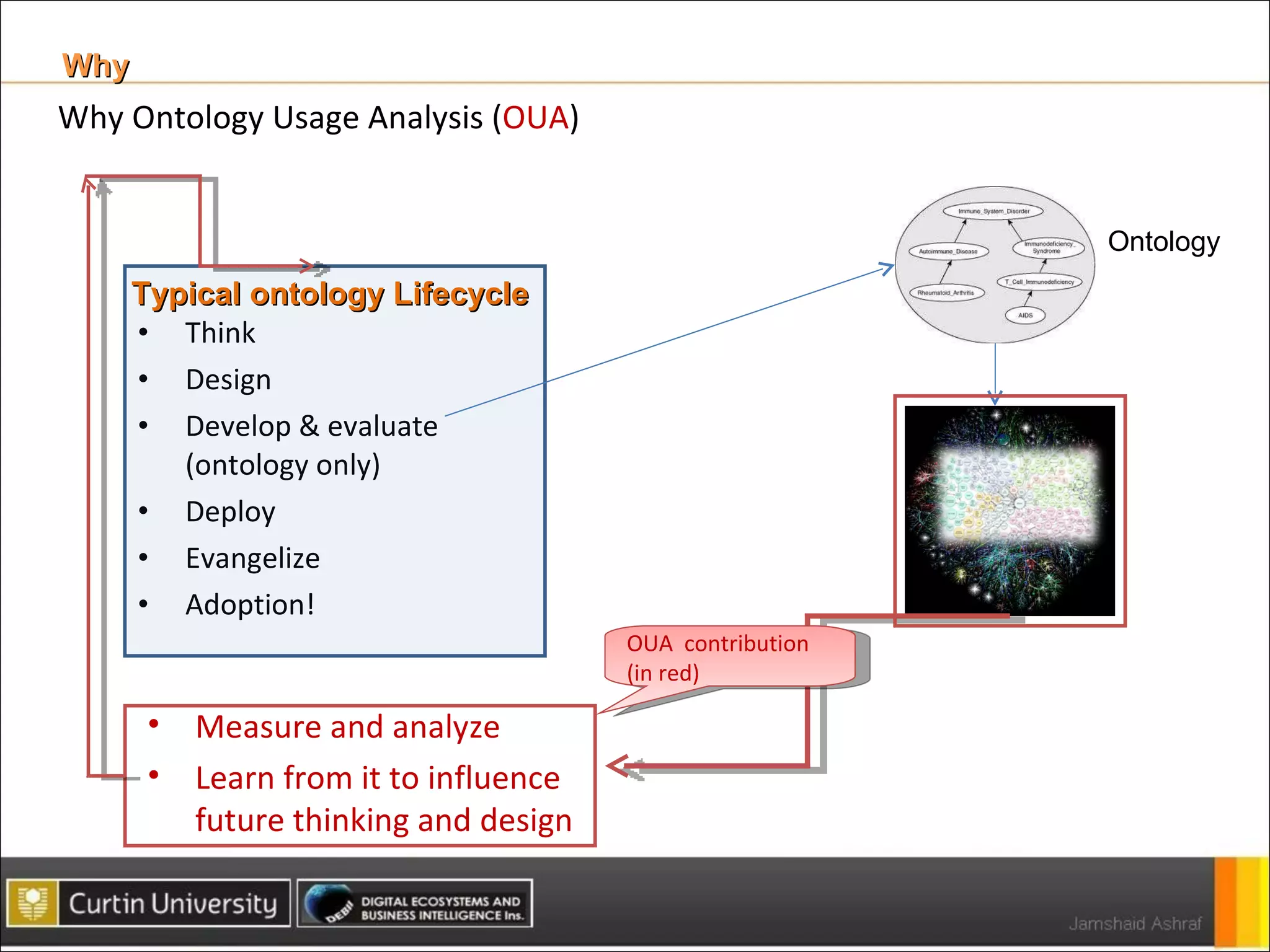
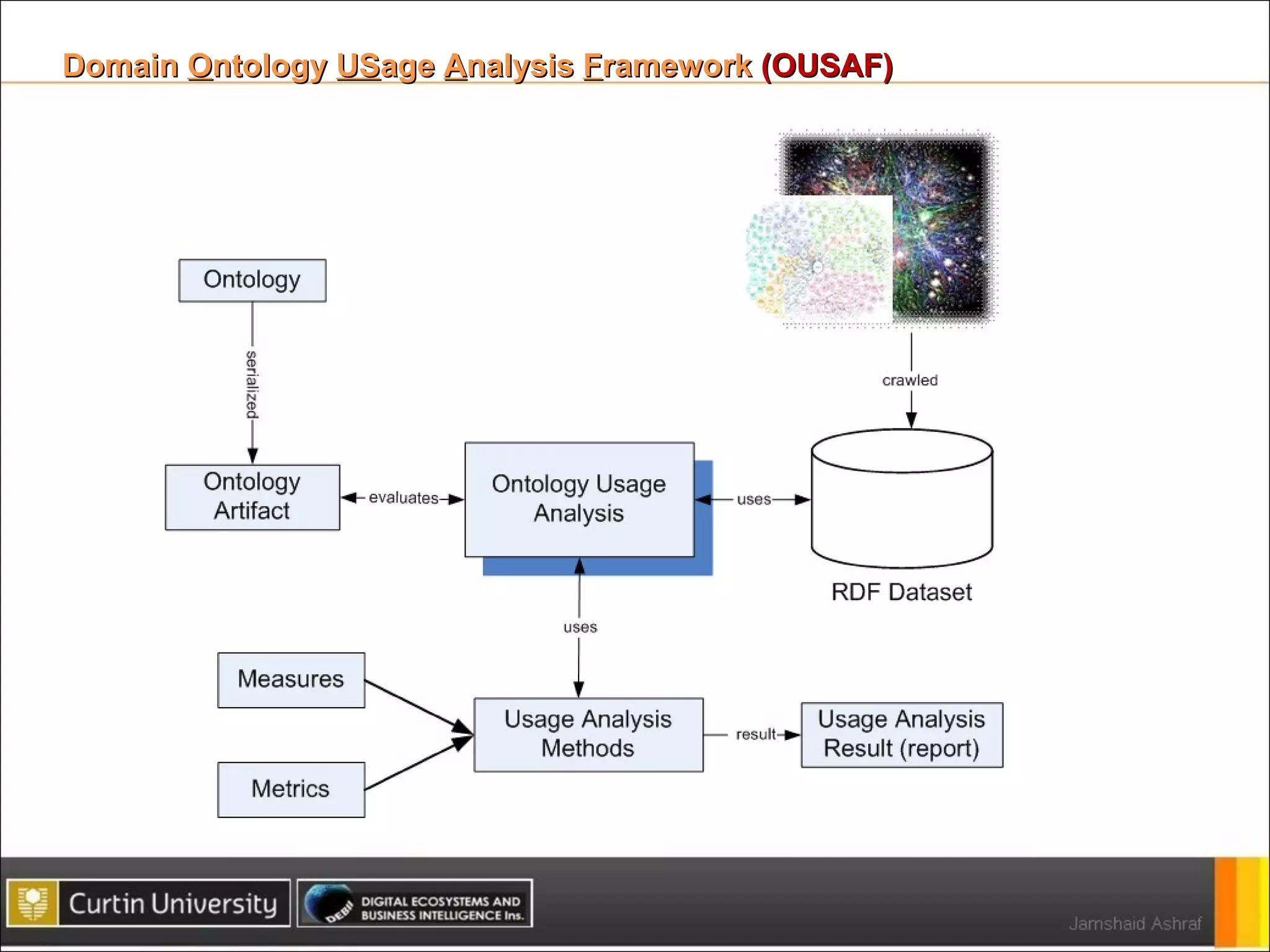
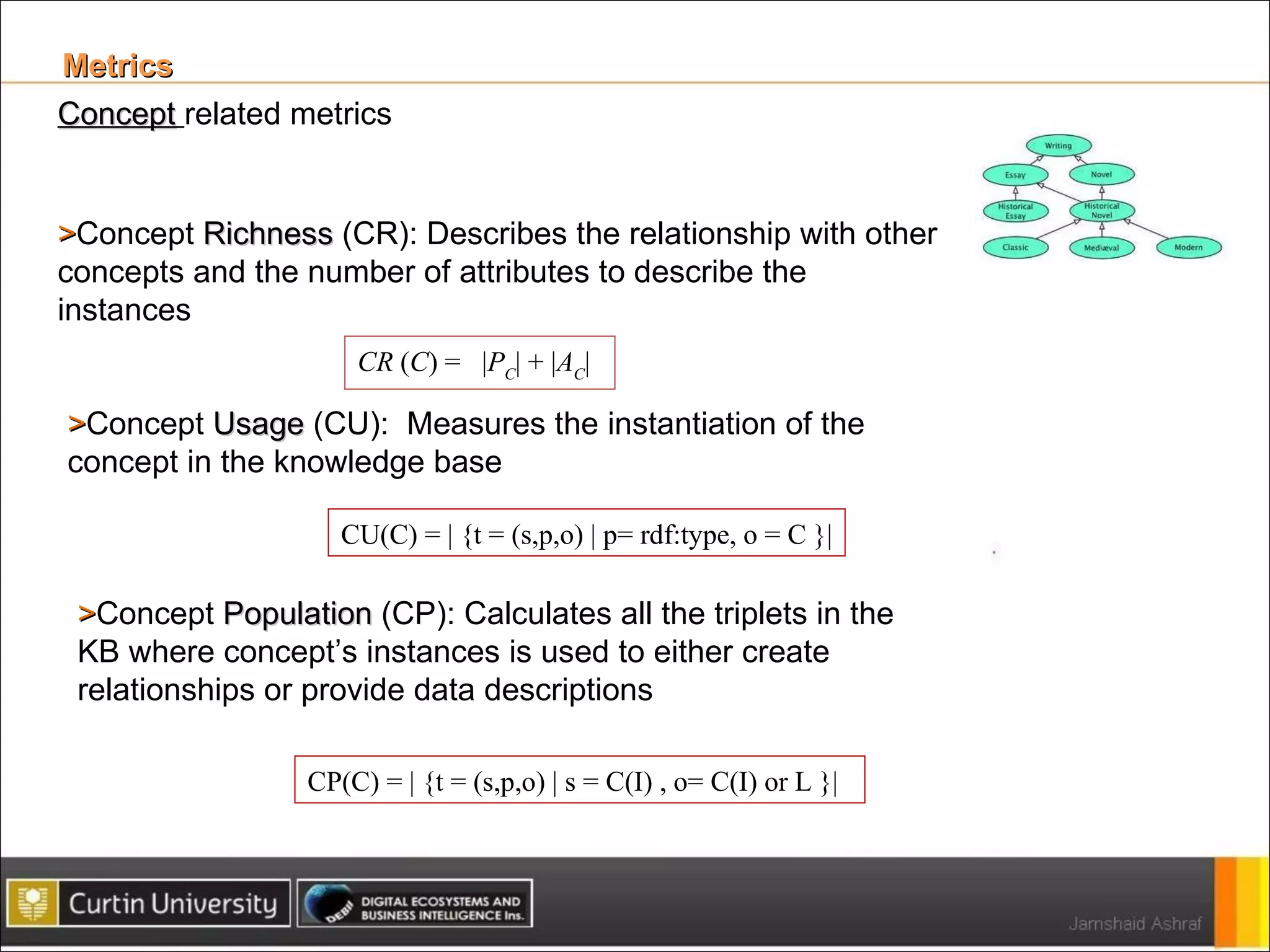
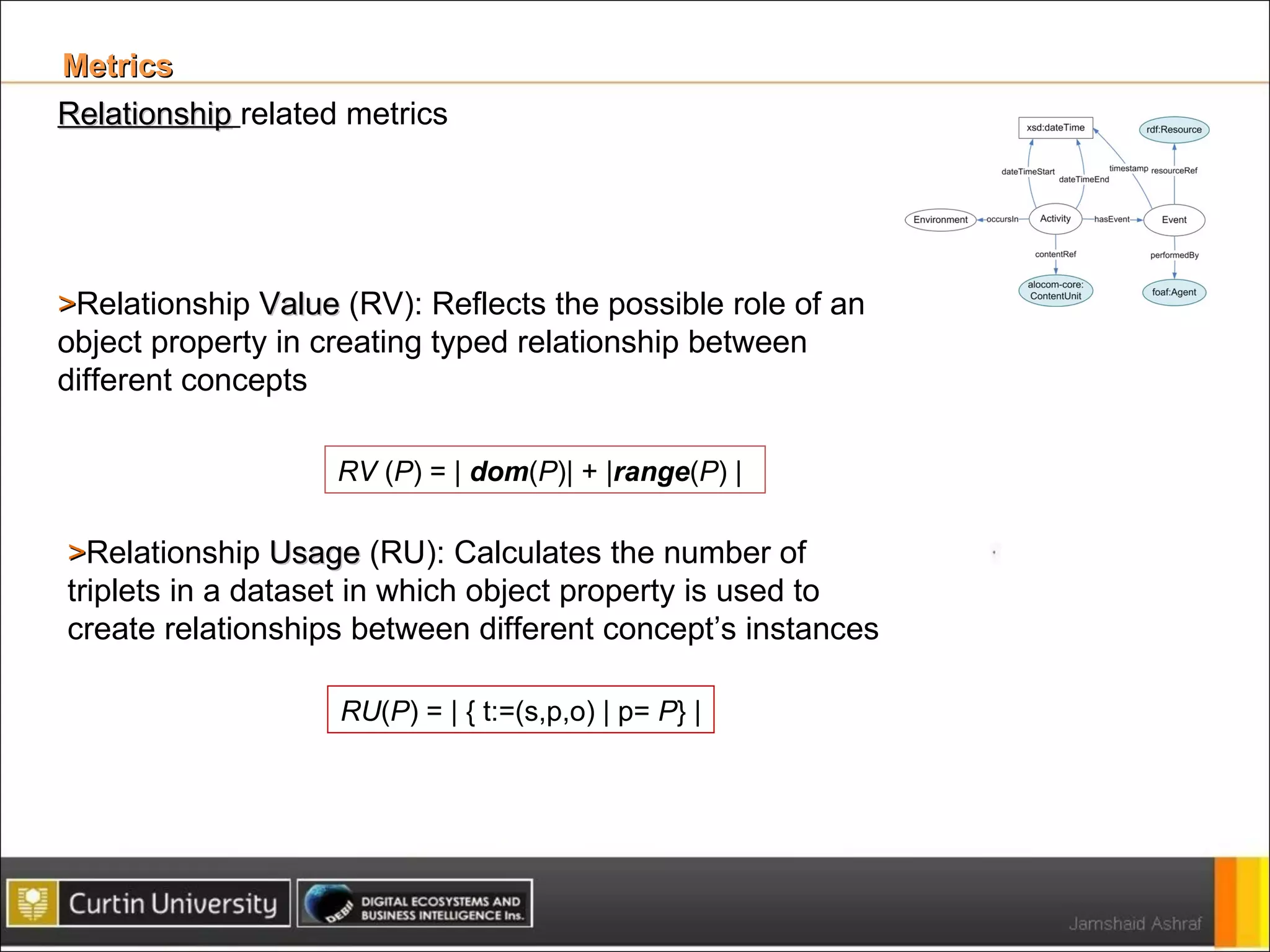
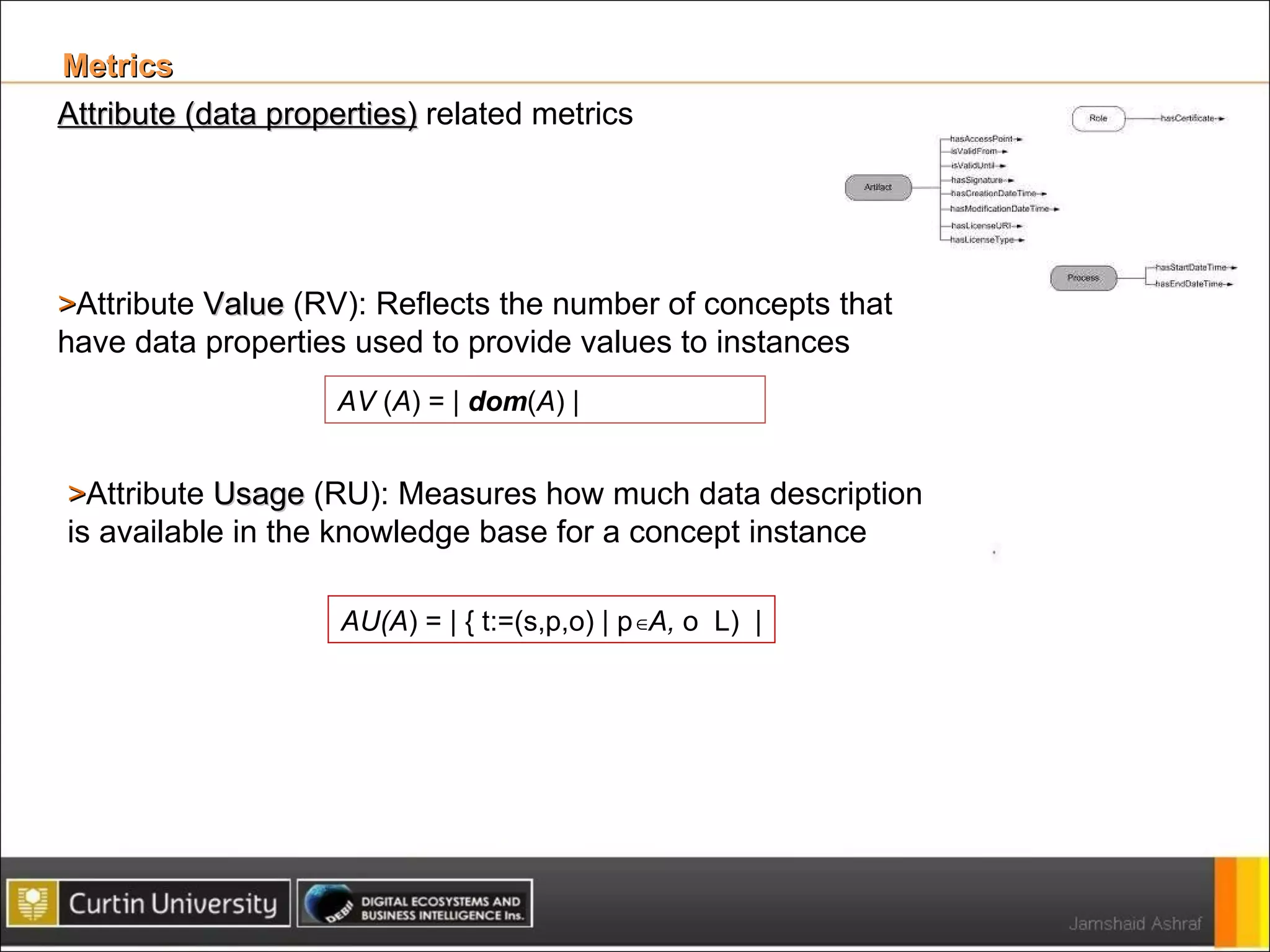
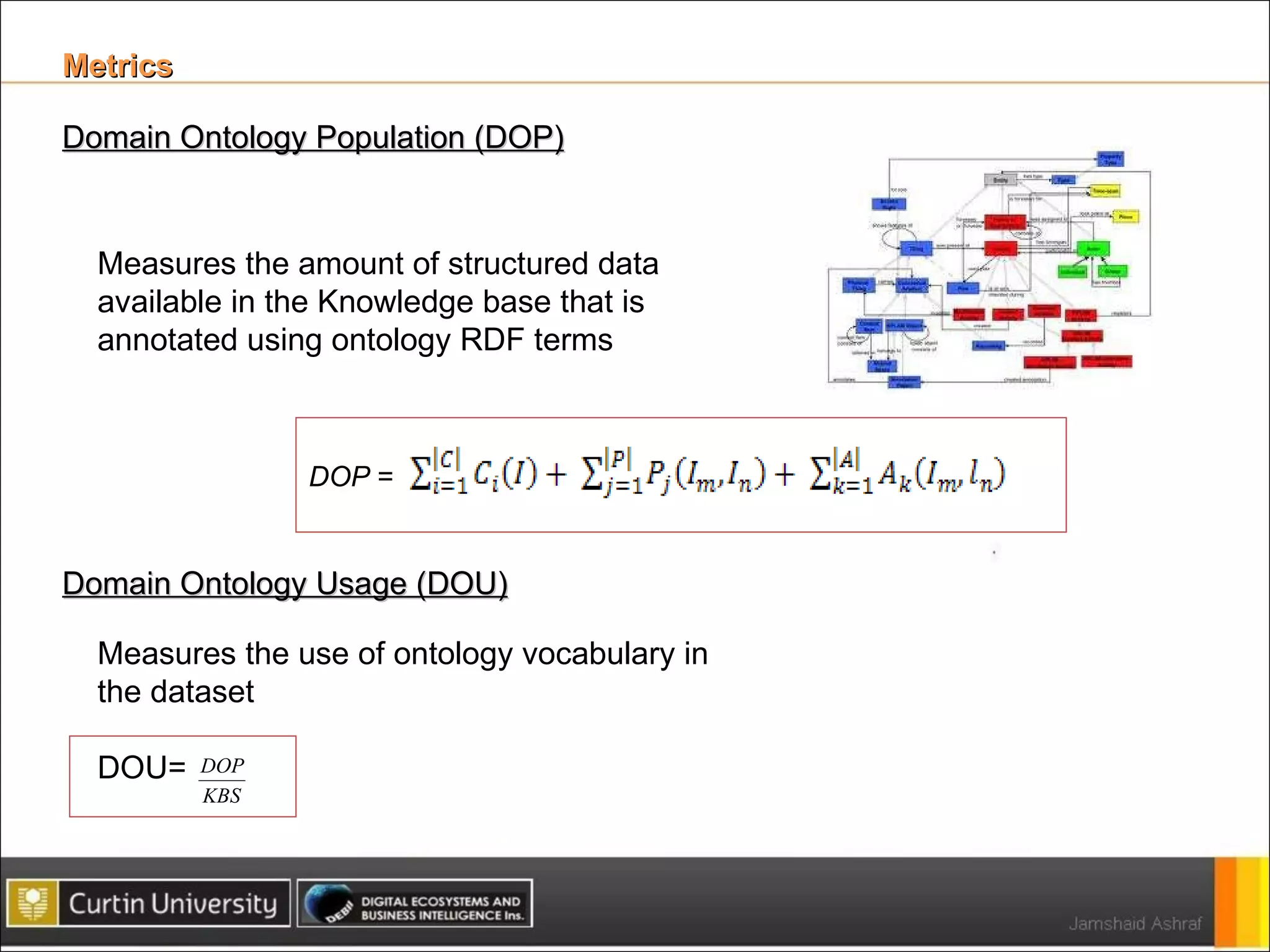
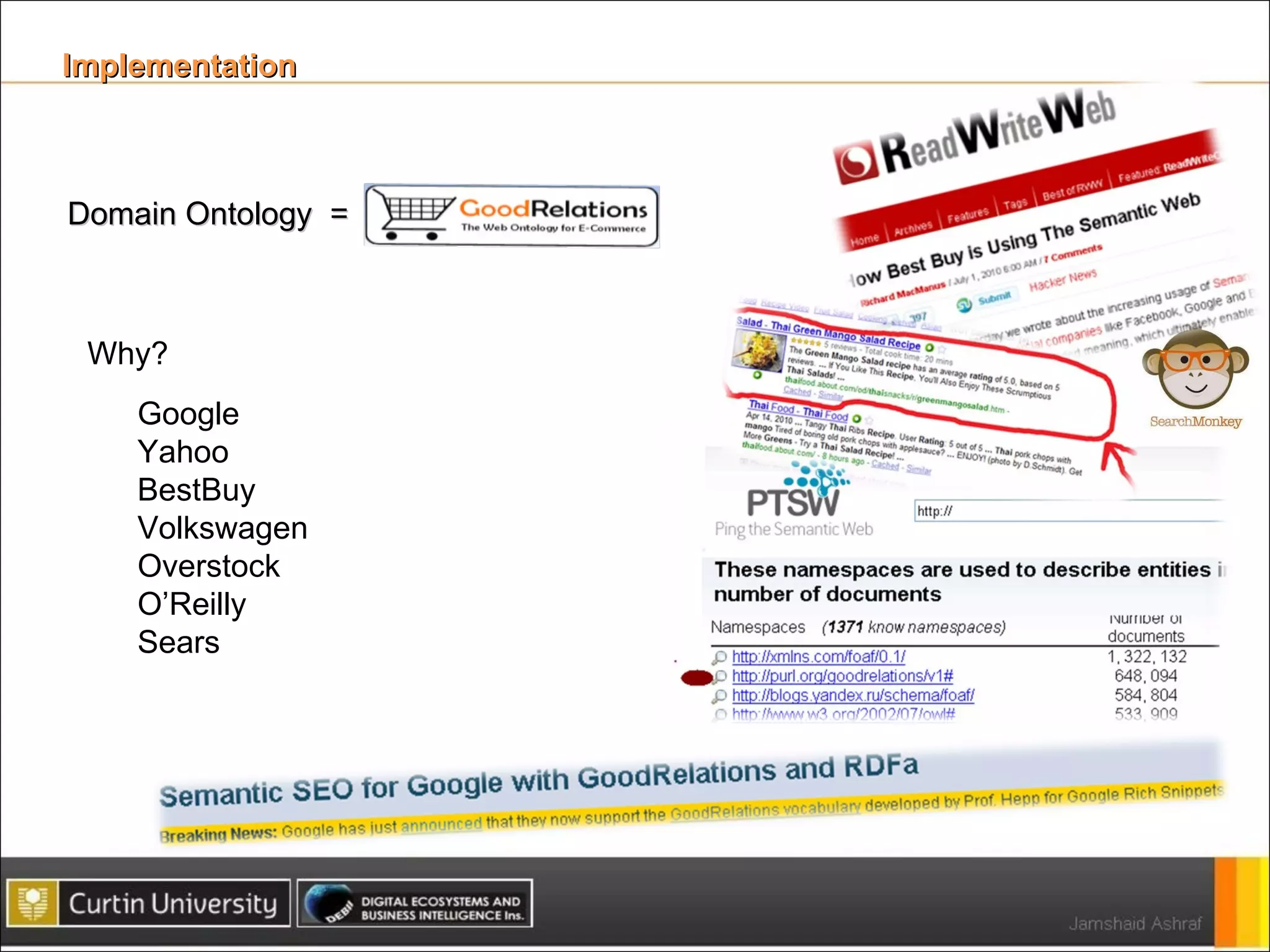
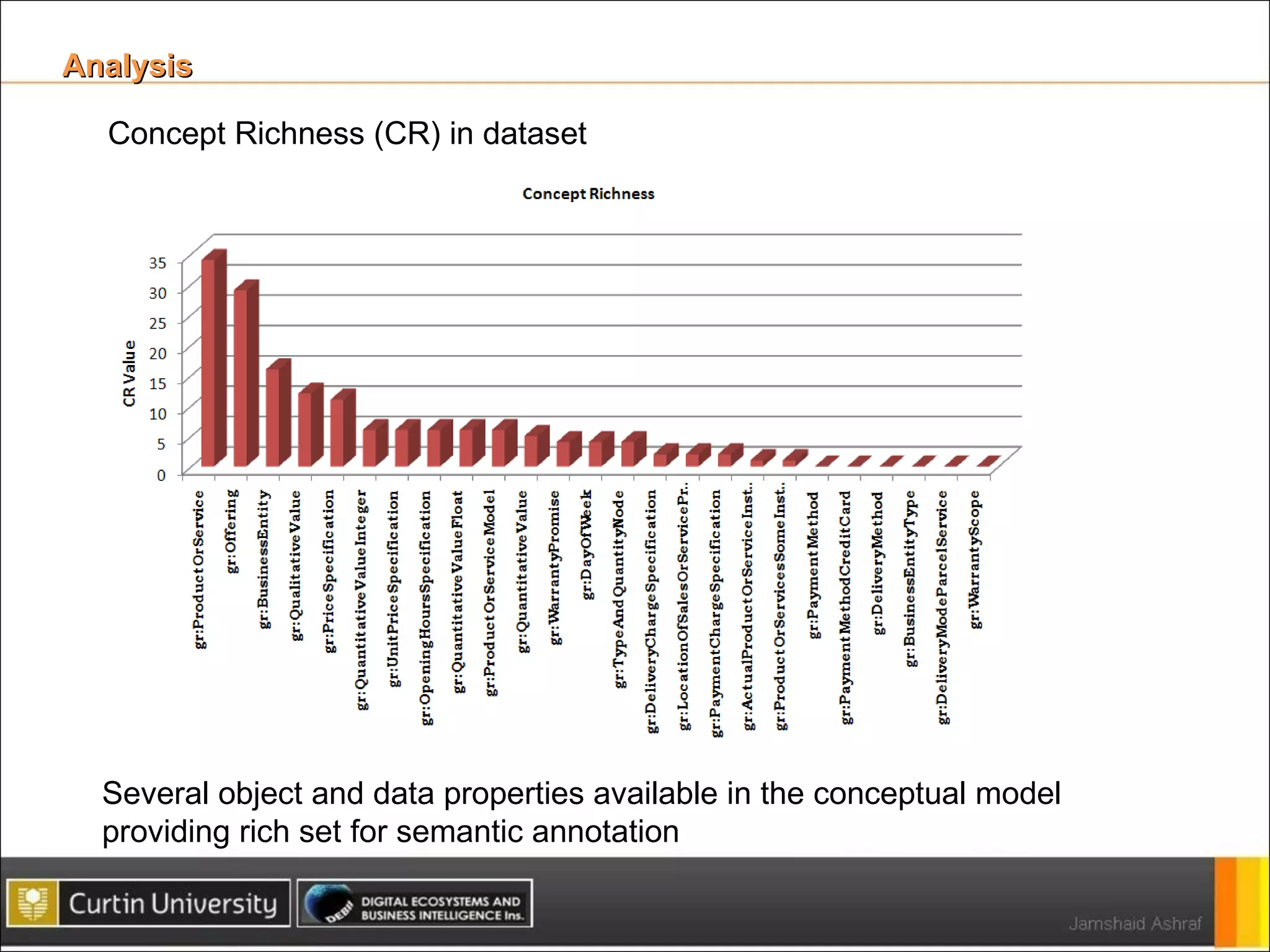
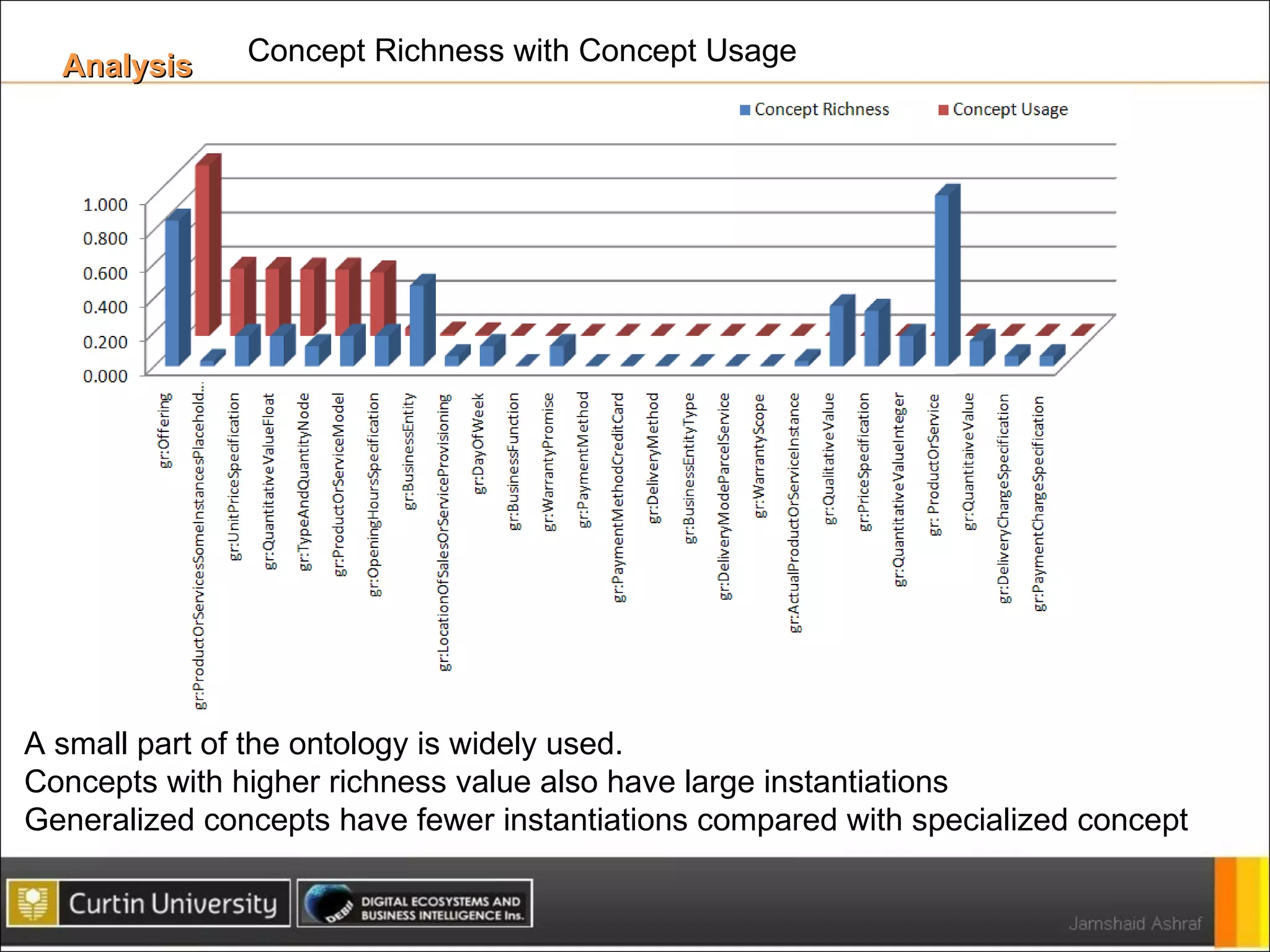
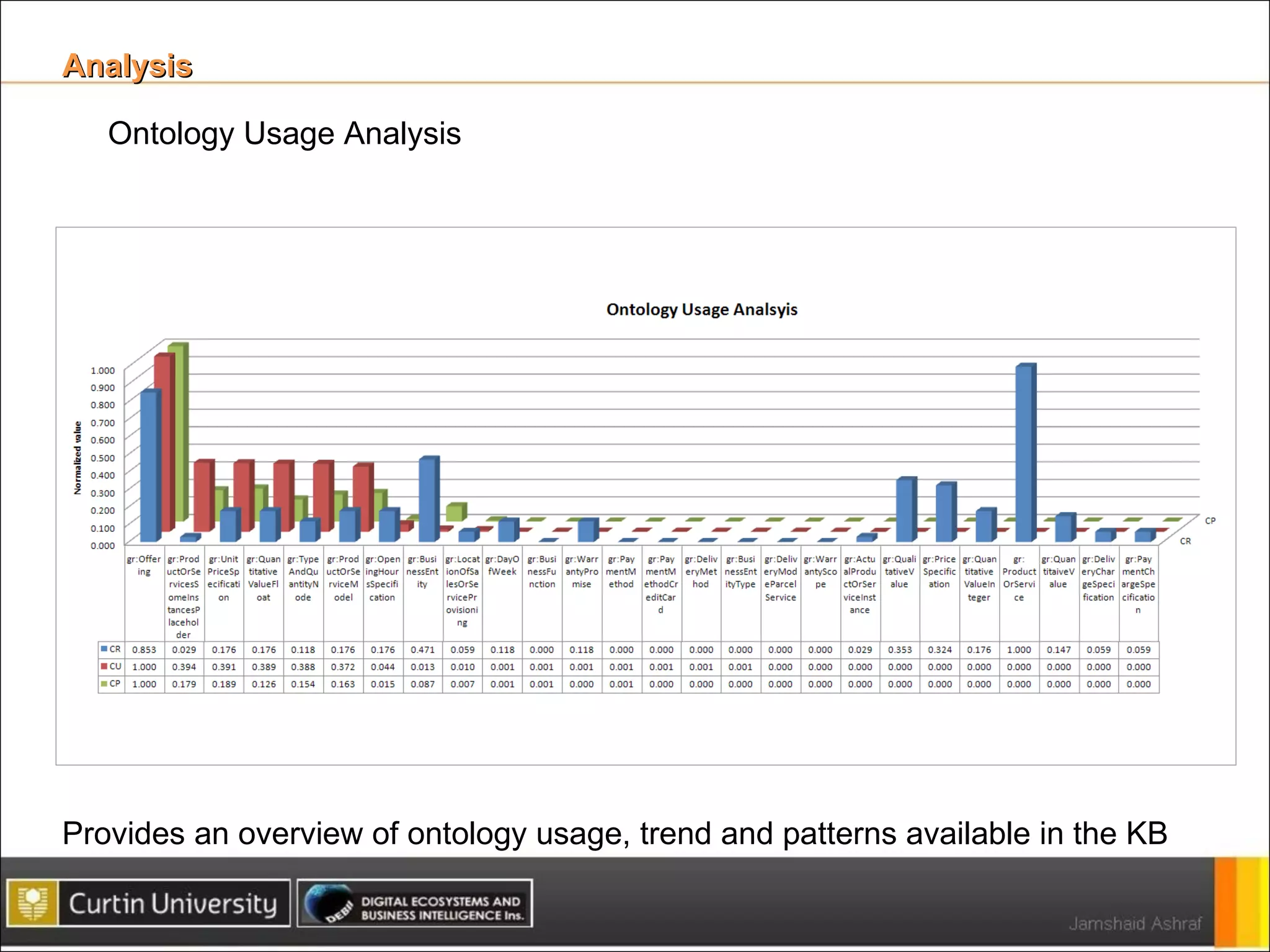
The document presents a framework for analyzing usage of domain ontologies on the semantic web. It proposes metrics to measure ontology usage, including concept richness, concept usage, and relationship and attribute values. The framework was implemented to analyze usage of ontologies in datasets from companies like Google and Yahoo. The analysis provided insights into ontology usage trends and patterns in the knowledge bases. Ontology usage analysis can help ontology engineers understand usage and evolve ontologies, as well as anticipate available knowledge when developing applications.