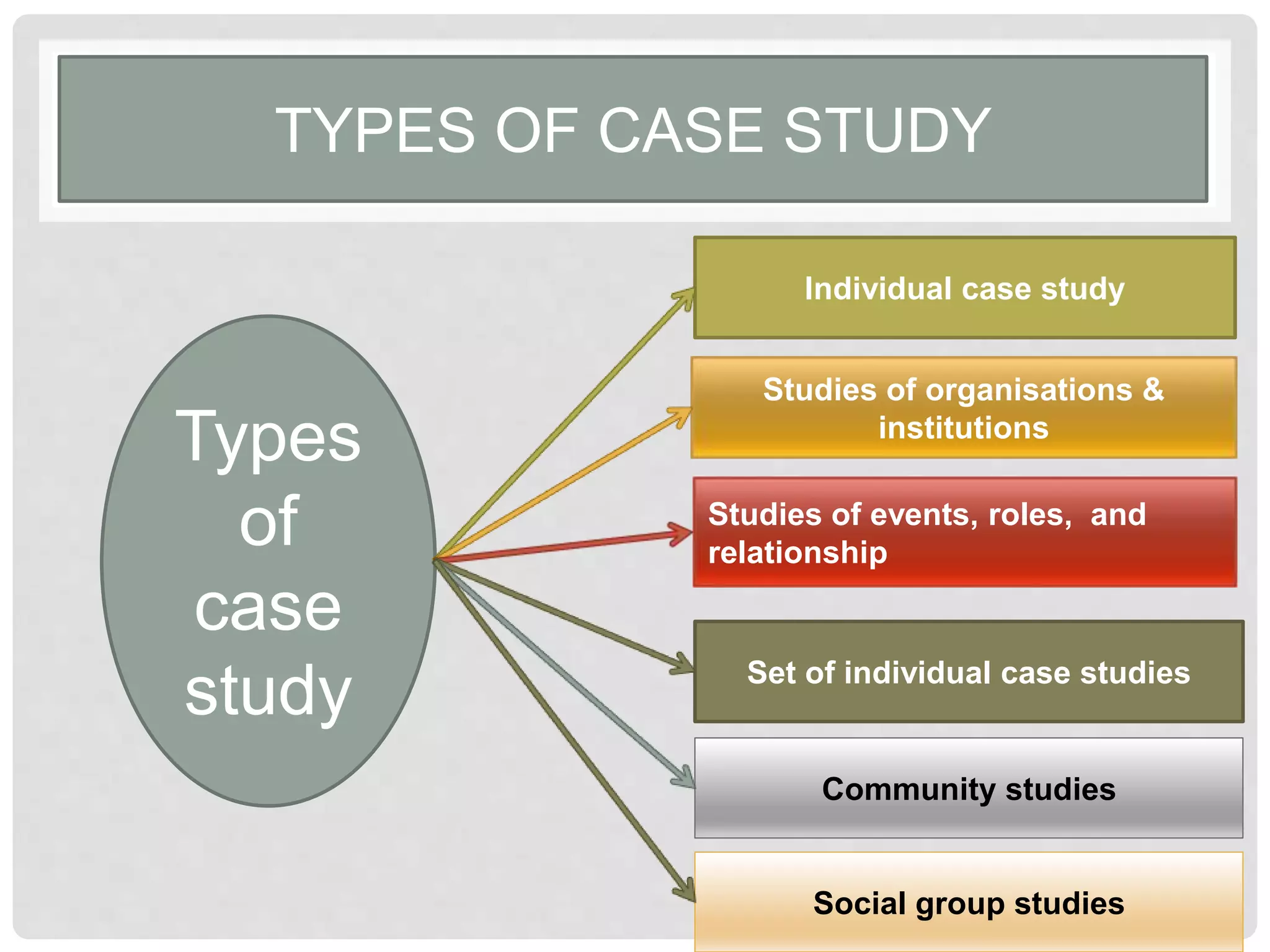
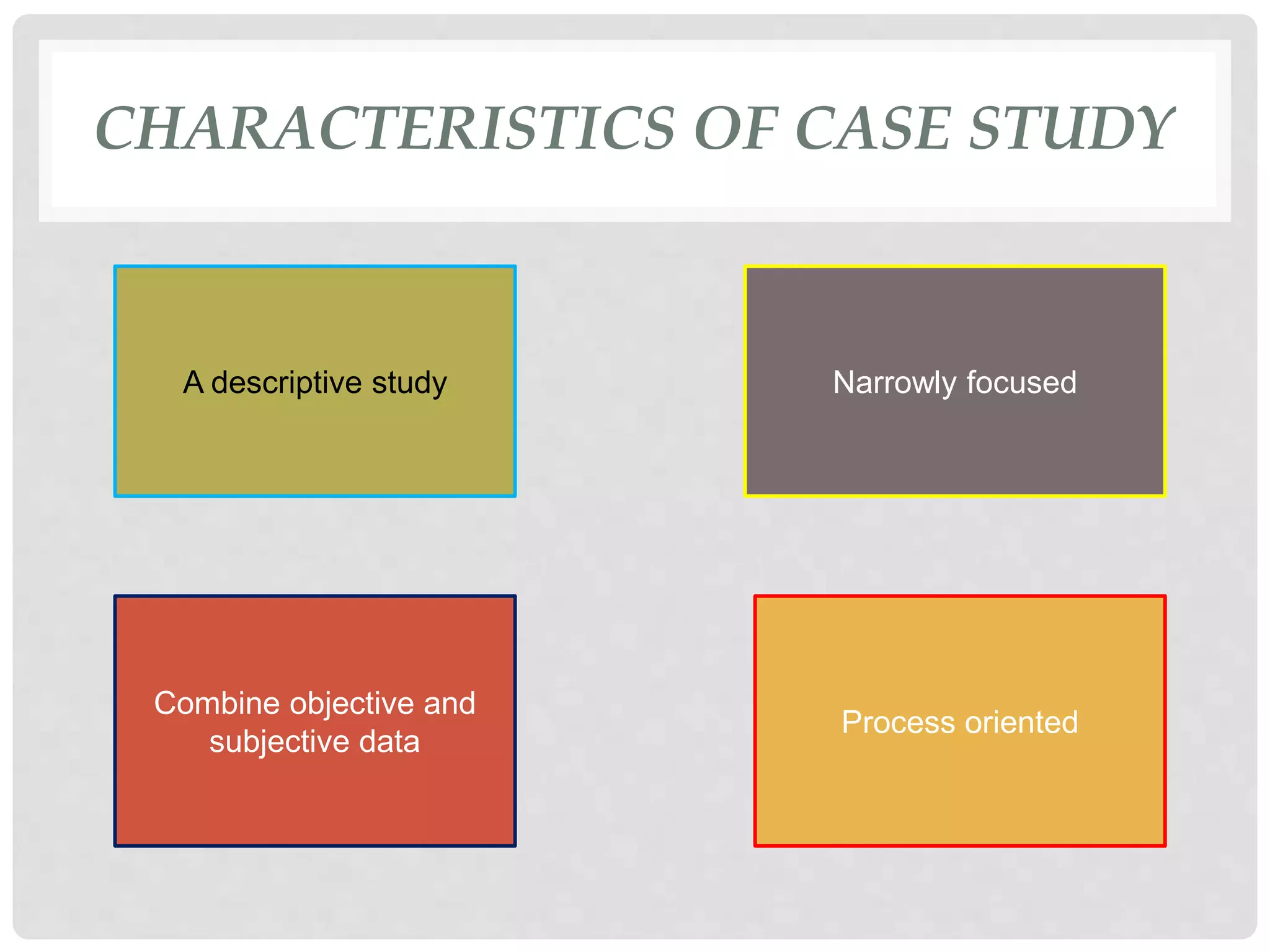
This document discusses the case study research method. It defines case study as an in-depth investigation of a social unit or event that provides deep insights. The document outlines various types of case studies including individual, community, and organizational. It also discusses characteristics such as being descriptive and process-oriented. The document reviews definitions from several scholars and describes techniques used in case studies like observation, interviews, documents and records. It outlines advantages like developing an in-depth understanding and hypotheses, and disadvantages such as lack of generalization and being time-consuming.