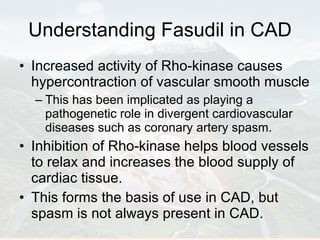
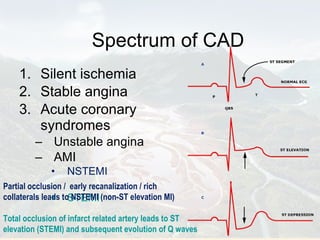
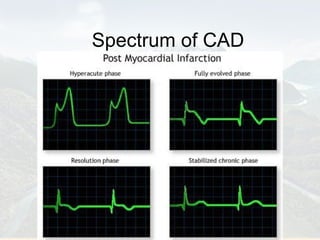
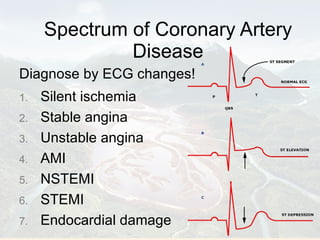
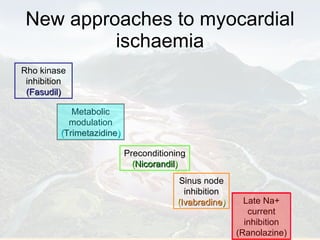
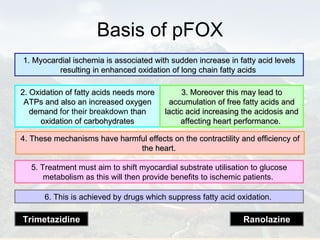
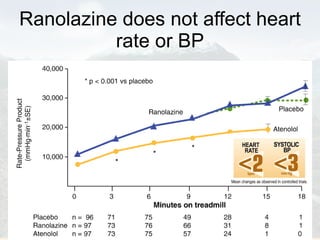
Ranolazine is a new antianginal drug that represents a new class of drugs. It partially inhibits fatty acid oxidation and shifts energy production to a more efficient carbohydrate oxidation during ischemia. It also inhibits late inward sodium currents, reducing calcium overload and improving diastolic function and myocardial perfusion. Ranolazine has been shown to reduce angina frequency and improve exercise ability with no effects on blood pressure or heart rate. Its benefits and mechanisms of action were discussed along with its indications, studies, and potential role in other conditions such as diabetes and cardioplegia.




![Ranolazine Ranolazine represents a new class of antianginal drugs. It is a compound with a structure similar to trimetazidine. Ranolazine is a partial inhibitor of fatty acid oxidation [ pFOX ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ranolazine-091126103039-phpapp02/85/Ranolazine-14-320.jpg)



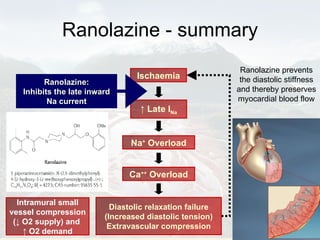
![Ranolazine – the background In the ischaemic myocardium, late inward Na+ currents occur. This contributes to an ↑ in intracellular Na+, This leads to an increase in intracellular Ca++ [ through the sodium-calcium exchanger] ?? Calcium overload in ischaemic cells leads to impaired relaxation. This is called diastolic stiffness.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ranolazine-091126103039-phpapp02/85/Ranolazine-19-320.jpg)




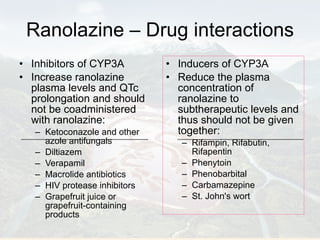
![Ranolazine – Drug interactions Reduce doses of the following drugs: Simvastatin Digoxin [Coadministration of Ranolazine and digoxin increases the plasma concentrations of digoxin by approx. 1.5-fold]; Tricyclic antidepressants & some antipsychotics Ranolazine prolongs the QT-interval. Hence, it is contradicted in patients with prolonged QT-intervals.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ranolazine-091126103039-phpapp02/85/Ranolazine-26-320.jpg)









![New indication for ranolazine In the European Union, the drug remains indicated for stable angina as an add-on therapy when symptoms aren't controlled with first-line agents. Basis for such change As seen in the MERLIN-TIMI 36 trial and in clinical practice, patients with ischemia and angina can be at increased risk for arrhythmias and also often have diabetes. Considering its mechanism of action, established cardiovascular safety, and observed reductions in arrhythmias and [glycosylated hemoglobin], ranolazine now becomes an even more important drug in the treatment of chronic angina.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ranolazine-091126103039-phpapp02/85/Ranolazine-38-320.jpg)