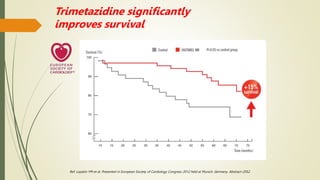
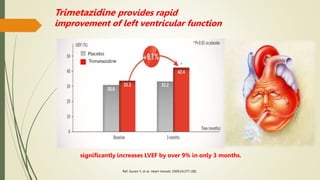
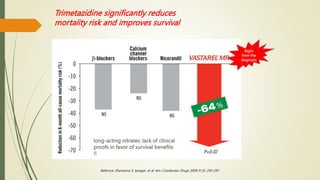
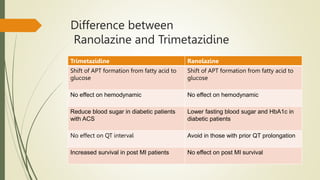
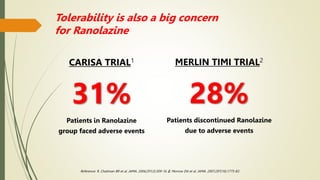
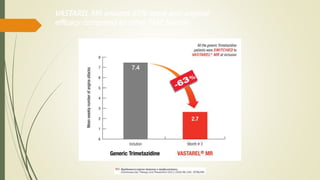
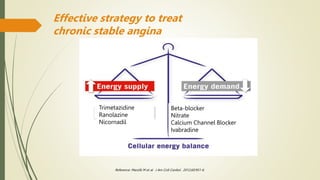
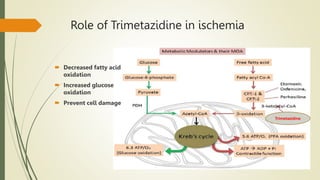
Trimetazidine is a newer anti-anginal drug that acts as a metabolic modulator. It works by shifting energy production in cardiac cells from fatty acid oxidation to glucose oxidation. This protects cells during ischemia. Trimetazidine reduces angina attacks, increases exercise tolerance, and improves outcomes like cardiac function and survival in patients with ischemic heart disease. It has fewer side effects than other anti-anginal drugs and is recommended as a second-line treatment option when first-line therapies are inadequate or not tolerated. However, not all trimetazidine formulations are equivalent, as generic copies may have reduced efficacy compared to the original research brand Vastarel MR.













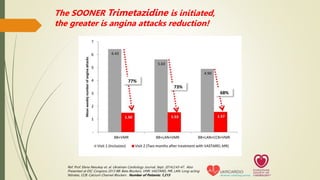

![Mean
weekly
number
of
angina
attacks
-31%
p < 0.00001
-80%
p < 0.00001
Reference: Glezer M et. al. Adv Ther. 2017 ;34(4):915-924. [CHOICE-2 Study]. Patients: 896 Stable angina patients. Medication: VASTAREL MR
was added to background antianginal therapy. In half of the patients (405), VASTAREL MR was added to beta-blocker. Treatment duration: 6
months; data recorded at baseline, followed-up after 2 weeks, 2 months, 4 months and 6 months.
Published
APRIL
2017
Trimetazidine ensures QUICK, STRONG &
SUSTAINED relief from angina](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronicstableangina-230212101444-a6e8cb1f/85/Chronic-Stable-Angina-pptx-28-320.jpg)