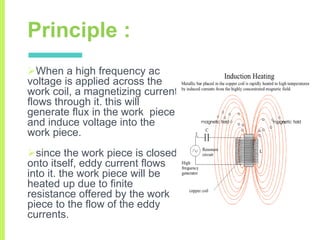
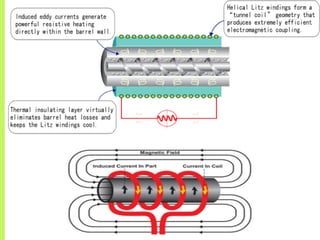
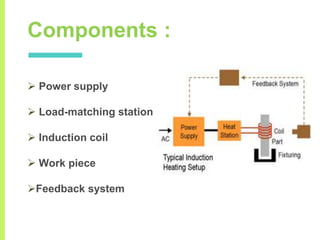
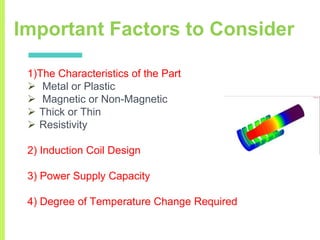
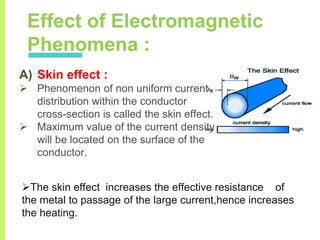
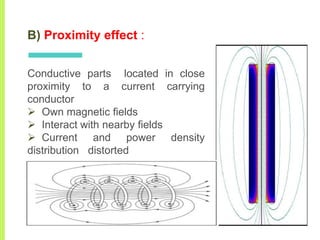
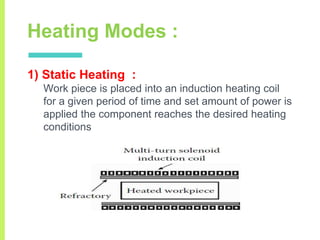
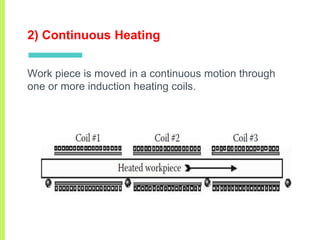
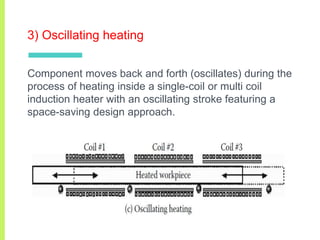
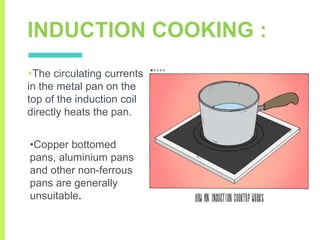
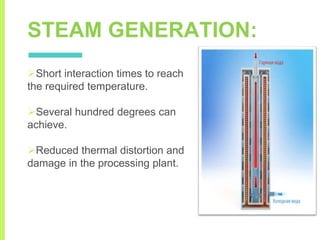
The document summarizes a seminar on induction heating. It describes induction heating as a process of heating an electrically conducting object by electromagnetic induction through heat generated in the object by eddy currents. It discusses the principle, components, effects of electromagnetic phenomena like skin effect and proximity effect, different heating modes, applications in areas like cooking, sealing, pasteurization, and advantages like precise localized heating and speed while also noting limitations like high costs.