The document summarizes the performance management system used by Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL), a large Indian public sector manufacturing company. The key points are:
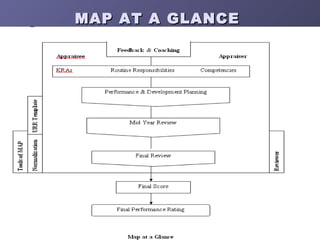
1. BHEL uses an electronic performance management system called e-MAP that establishes annual performance plans with key result areas, routine responsibilities, and development goals for executives and middle managers.
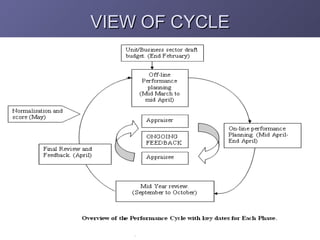
2. The e-MAP cycle includes performance planning, mid-year reviews, final reviews, and normalization to align individual scores based on company, unit, and department performance.
3. Normalization means high and low performers in different departments may receive different ratings even with the same final score, to account for variation in department performance against targets.