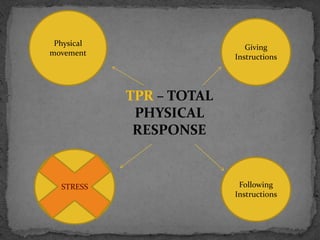
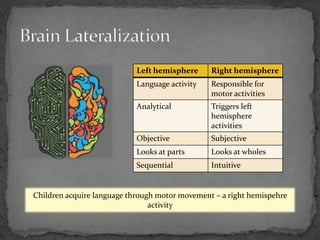
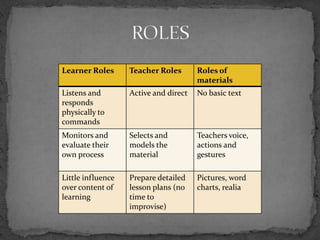
TPR, or Total Physical Response, is a language teaching method that uses physical movement in response to verbal commands to help reduce stress associated with language learning. It is based on how infants acquire their first language through comprehending and then producing responses. Using TPR, students first focus on comprehending commands and responding physically before being asked to respond verbally. The method encourages students to perform physical activities in response to commands given by the teacher in the target language to help students internalize vocabulary and grammar structures in a stress-free, comprehensible way similar to first language acquisition.