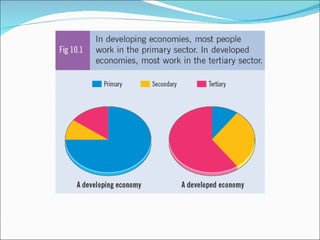
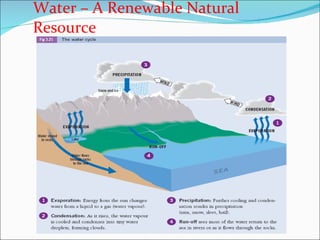
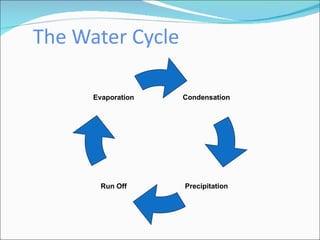
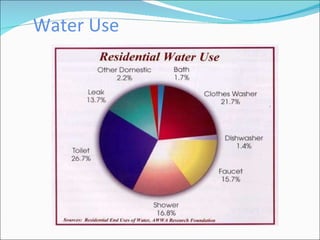
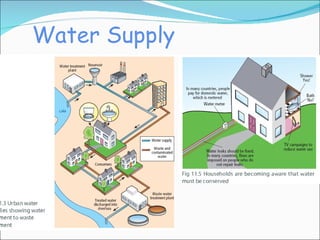
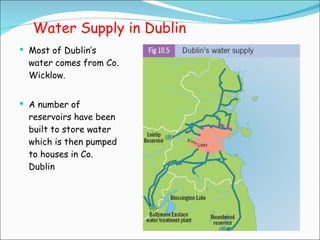
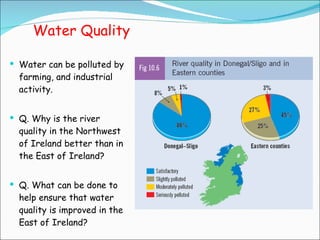
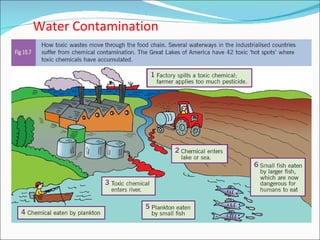
Primary economic activity involves extracting natural resources from the land and sea, such as through farming, fishing, forestry, mining, and quarrying. Natural resources are things provided by nature that are useful to people, and can be renewable like water, fish, plants and crops; or non-renewable like coal, oil and gas. Most people in developing countries work in primary economic activities compared to developed countries due to the types of resources available.