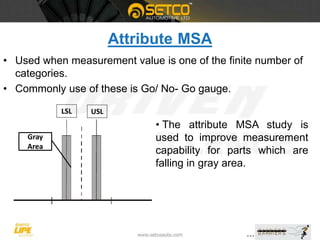
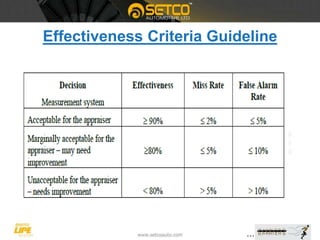
This document provides a detailed overview of Measurement System Analysis (MSA), explaining its purpose, types, and key terms. It outlines the steps to conduct an Attribute MSA, including selecting gauges, operators, and analyzing results such as kappa value, miss rate, and false rate. The document emphasizes the importance of MSA in ensuring accurate and reliable measurement systems in manufacturing processes.