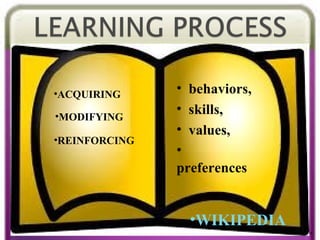
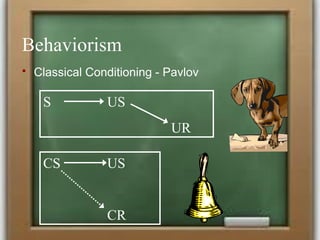
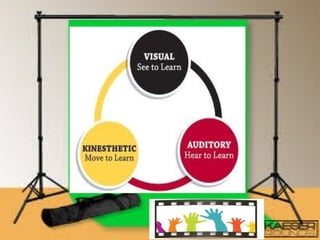
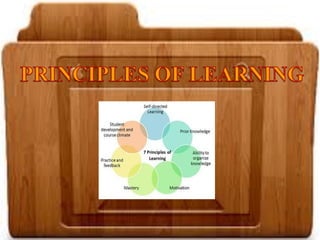
The document discusses several theories of learning including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. It provides an overview of key aspects of each theory such as major contributors, core concepts, and implications for teaching practices. Learning is described as a complex process influenced by both internal cognitive and external social factors.