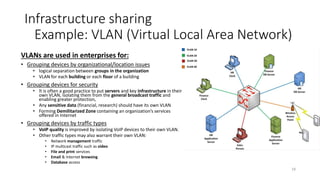
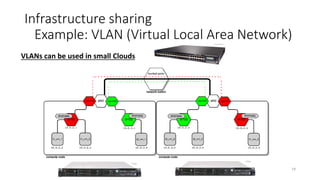
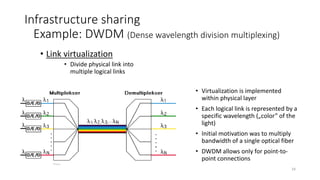
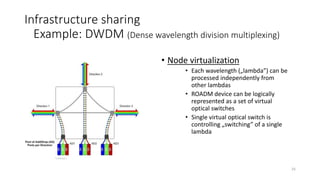
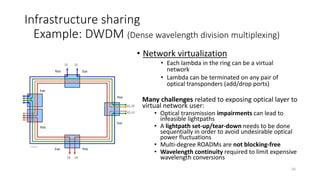
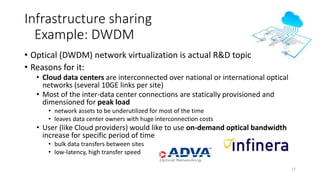
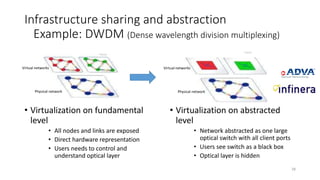
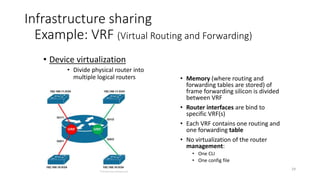
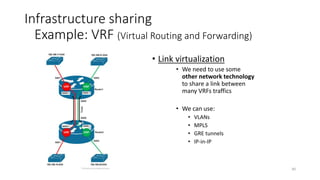
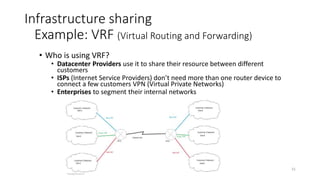
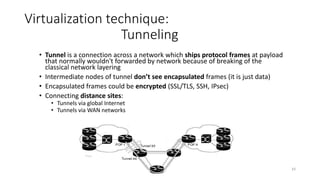
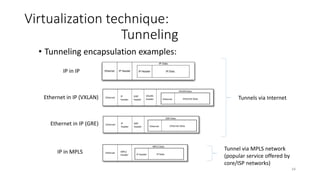
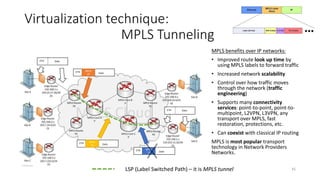
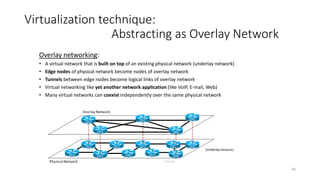
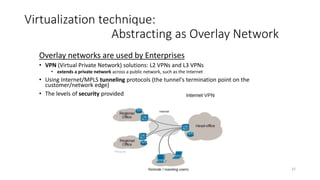
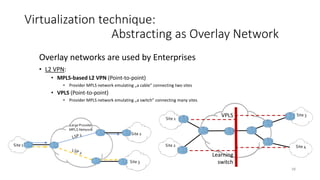
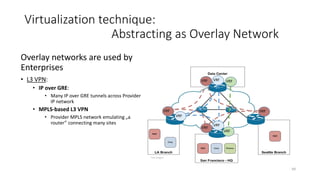
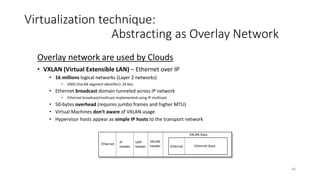
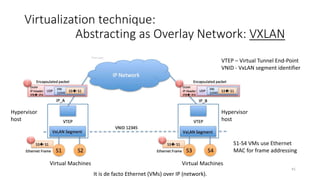
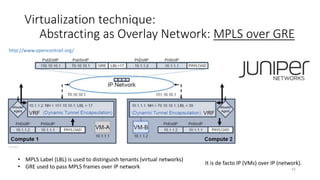
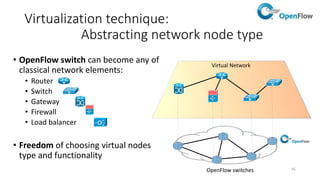
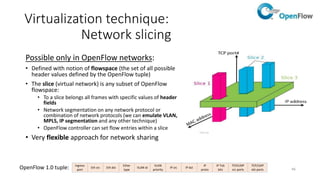
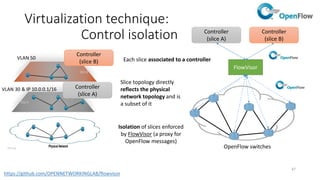
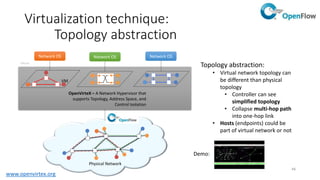
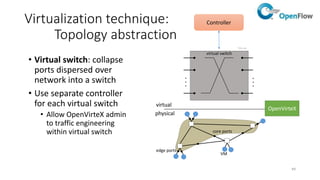
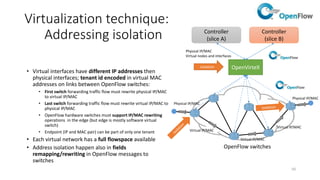
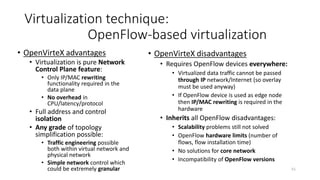
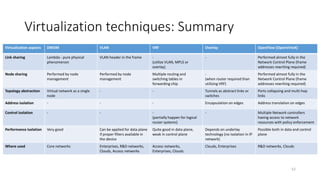
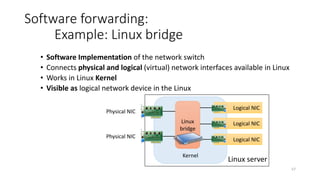
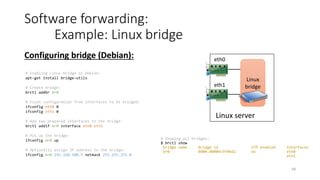
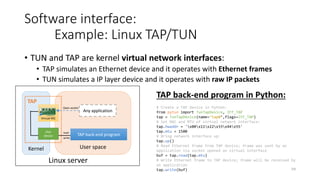
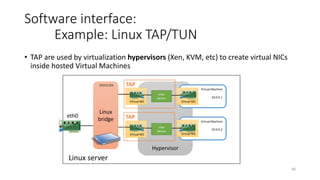
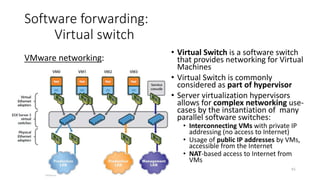
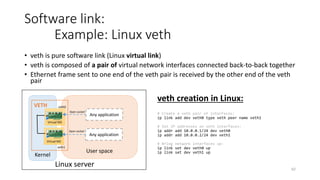
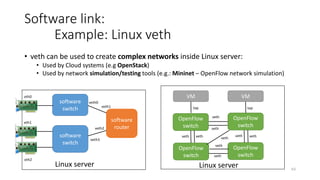
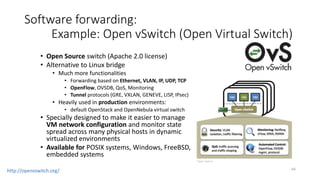
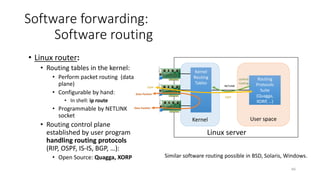
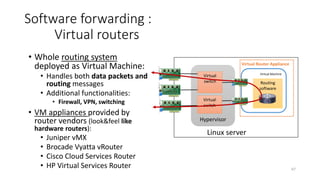
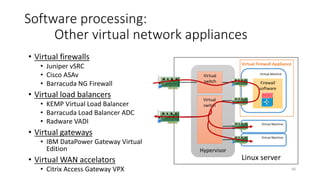
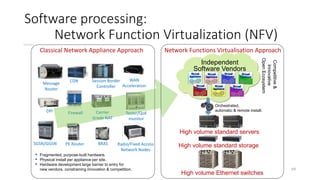
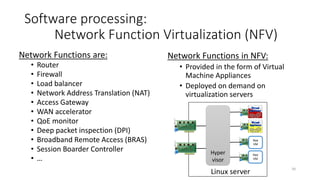
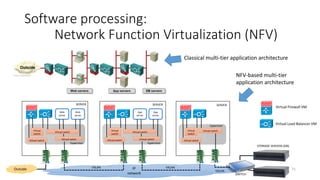
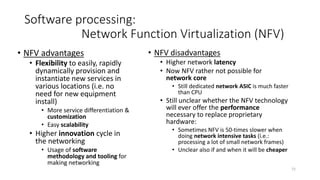
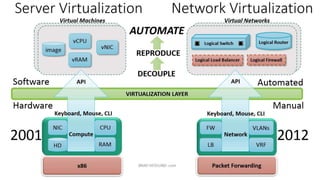
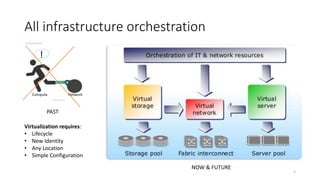
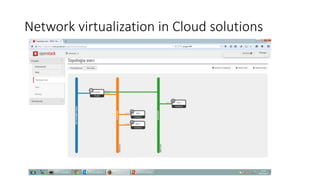
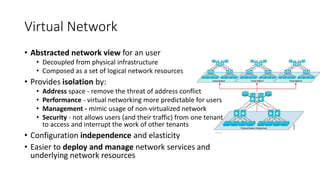
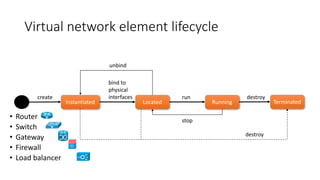
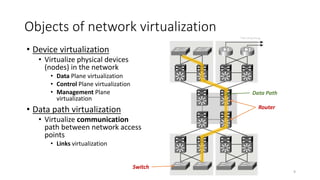
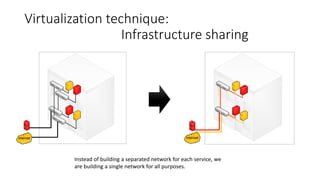
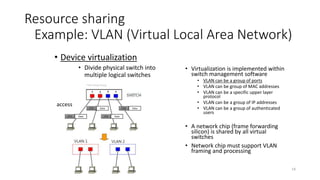
Network virtualization allows sharing of physical network infrastructure between multiple virtual networks through abstraction and tunneling techniques. It provides benefits like increased infrastructure utilization, scalability, agility, and security. Common virtualization techniques include VLANs to divide switches into logical segments, DWDM to multiply fiber bandwidth, VRFs to partition routers, and tunneling protocols like GRE, VXLAN, and MPLS to encapsulate and transport traffic across physical networks. Overlay networks further abstract the physical underlay into virtual topologies to support multiple isolated tenant networks on shared infrastructure.





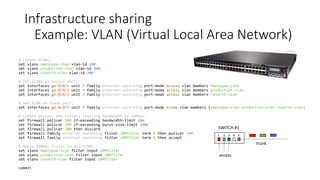
![Infrastructure sharing
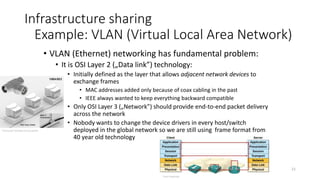
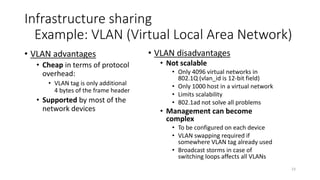
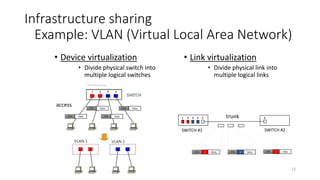
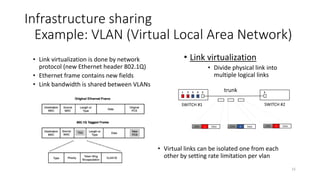
Example: VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
SWITCH #1
1 2 3 4 5
trunk
access
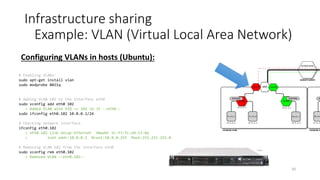
# Create VLANs:
set vlans employee-vlan vlan-id 100
set vlans production-vlan vlan-id 200
set vlans research-vlan vlan-id 300
# Set VLANs on access ports (1GbE):
set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access vlan members employee-vlan
set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access vlan members production-vlan
set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode access vlan members research-vlan
# Set VLAN on trunk port (10GbE):
set interfaces xe-0/0/5 unit 0 family ethernet-switching port-mode trunk vlan members [employee-vlan production-vlan research-vlan]
# Create policer and filters limiting bandwidth to 1Gbps:
set firewall policer 1G if-exceeding bandwidth-limit 1g
set firewall policer 1G if-exceeding burst-size-limit 10m
set firewall policer 1G then discard
set firewall family ethernet-switching filter 1Gfilter term 1 then policer 1G
set firewall family ethernet-switching filter 1Gfilter term 1 then accept
# Apply 1Gbps filter to all VLANs:
set vlans employee-vlan filter input 1Gfilter
set vlans production-vlan filter input 1Gfilter
set vlans research-vlan filter input 1Gfilter
commit
®JuniperJuniper JUNOS commands:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkvirtualization-150420162242-conversion-gate02/85/Network-virtualization-16-320.jpg)