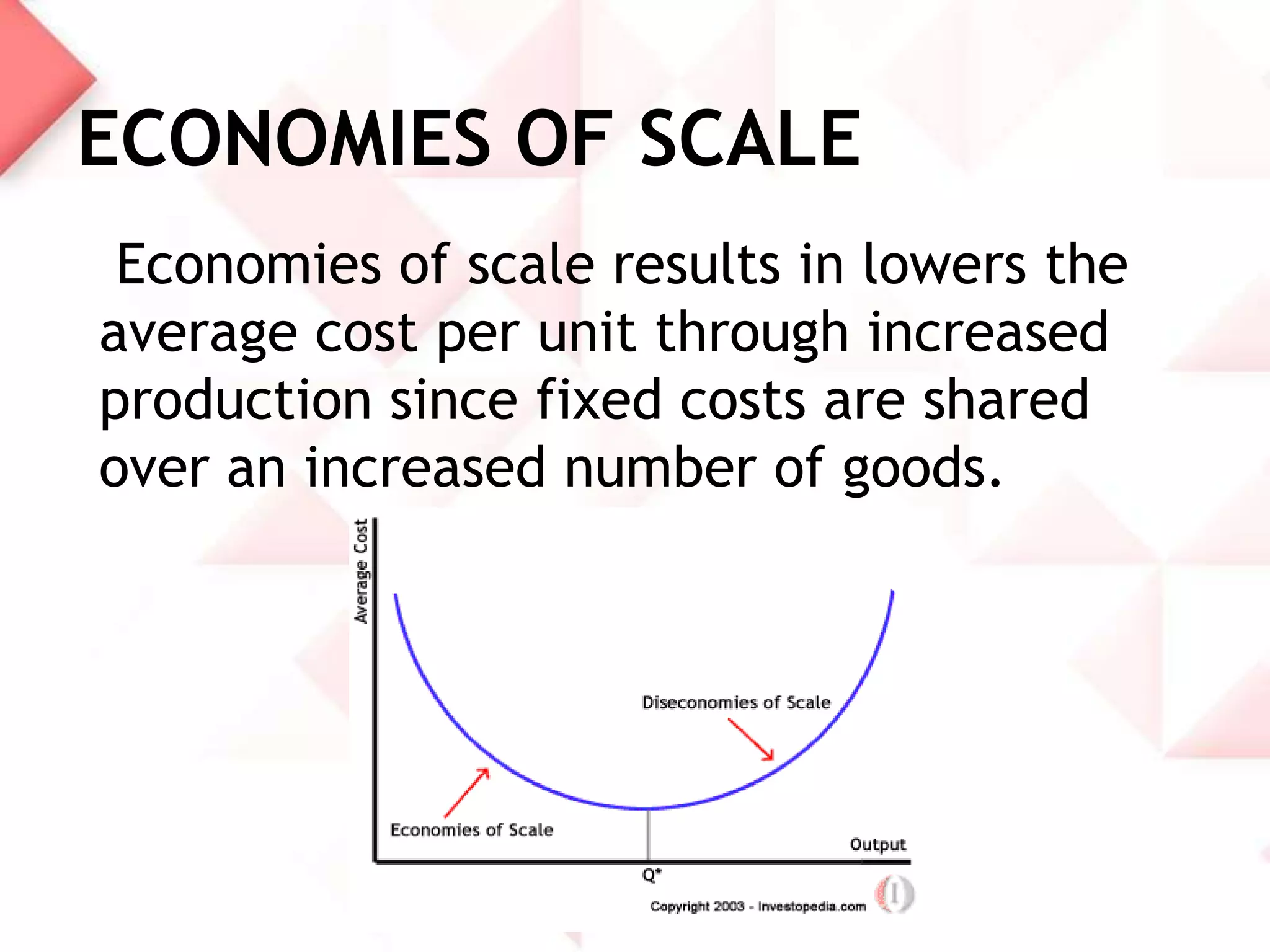
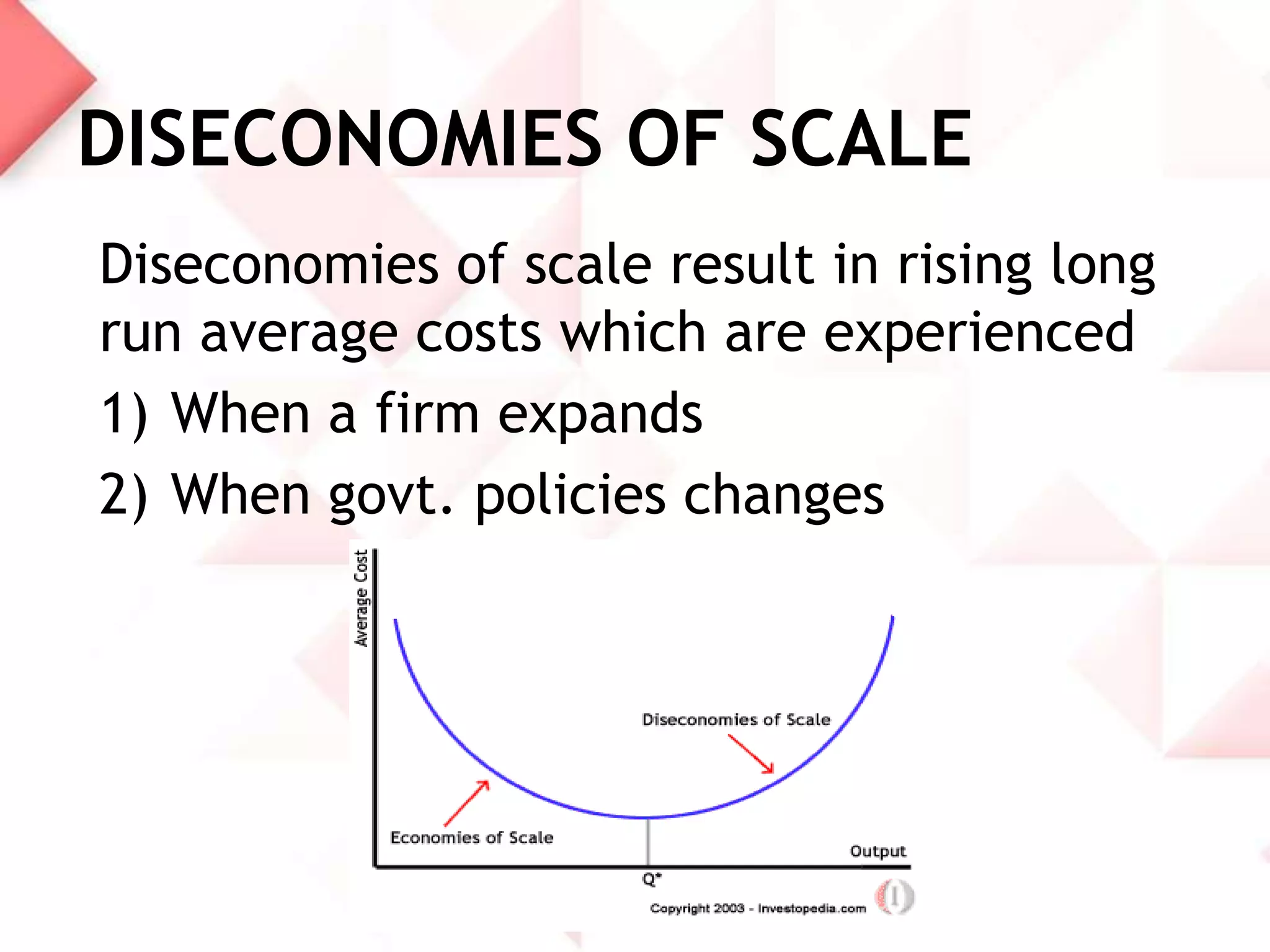
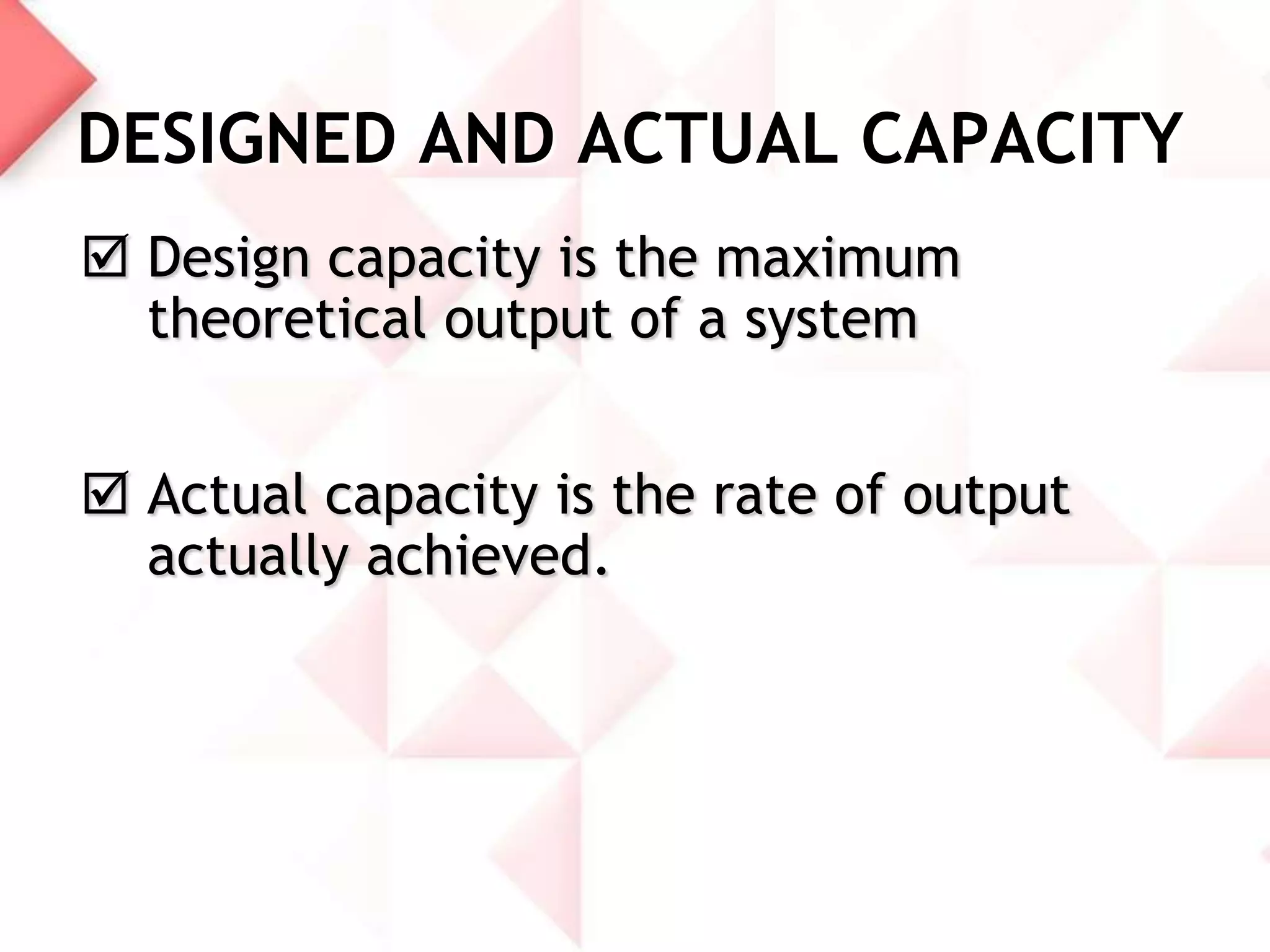
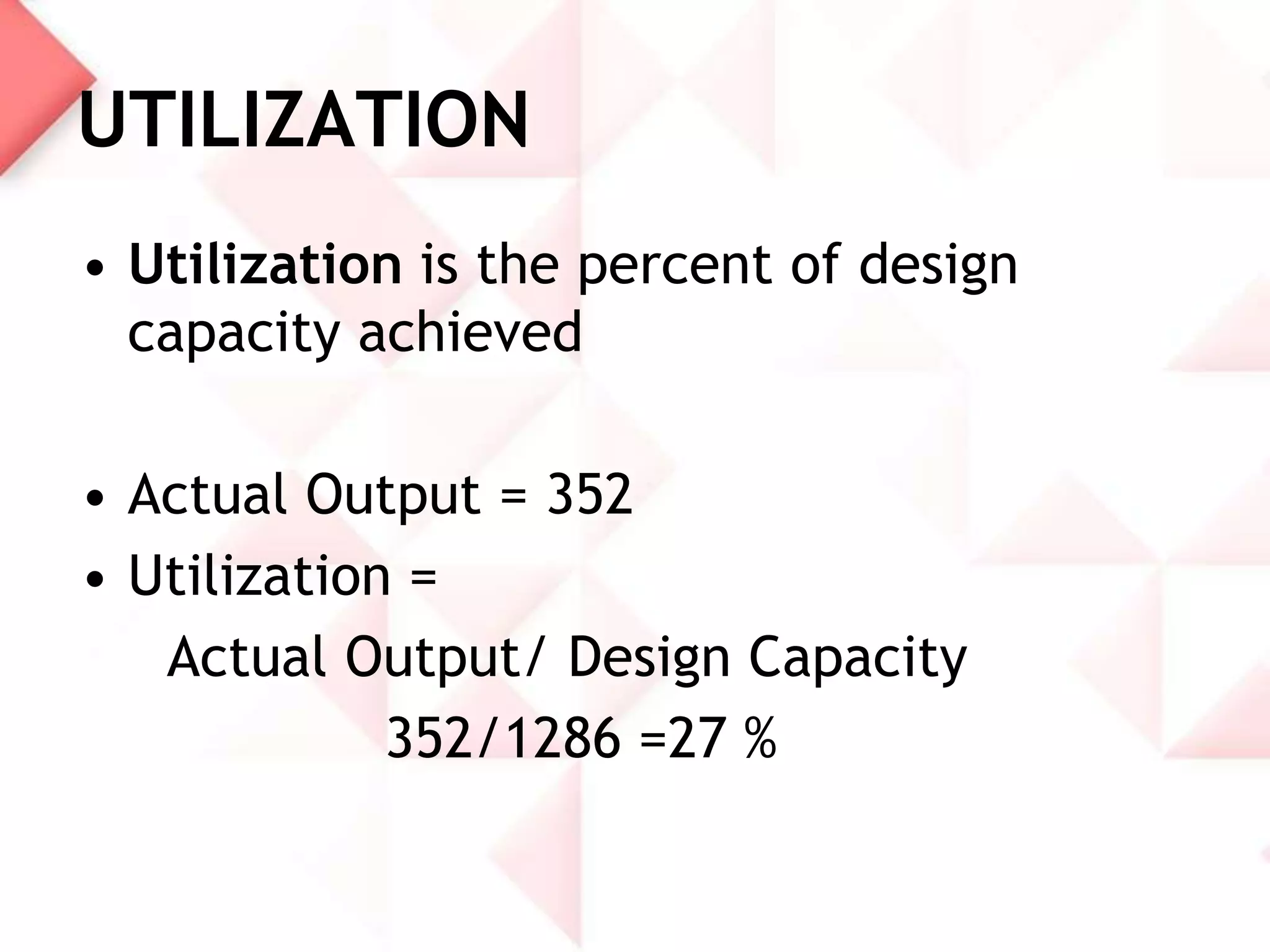
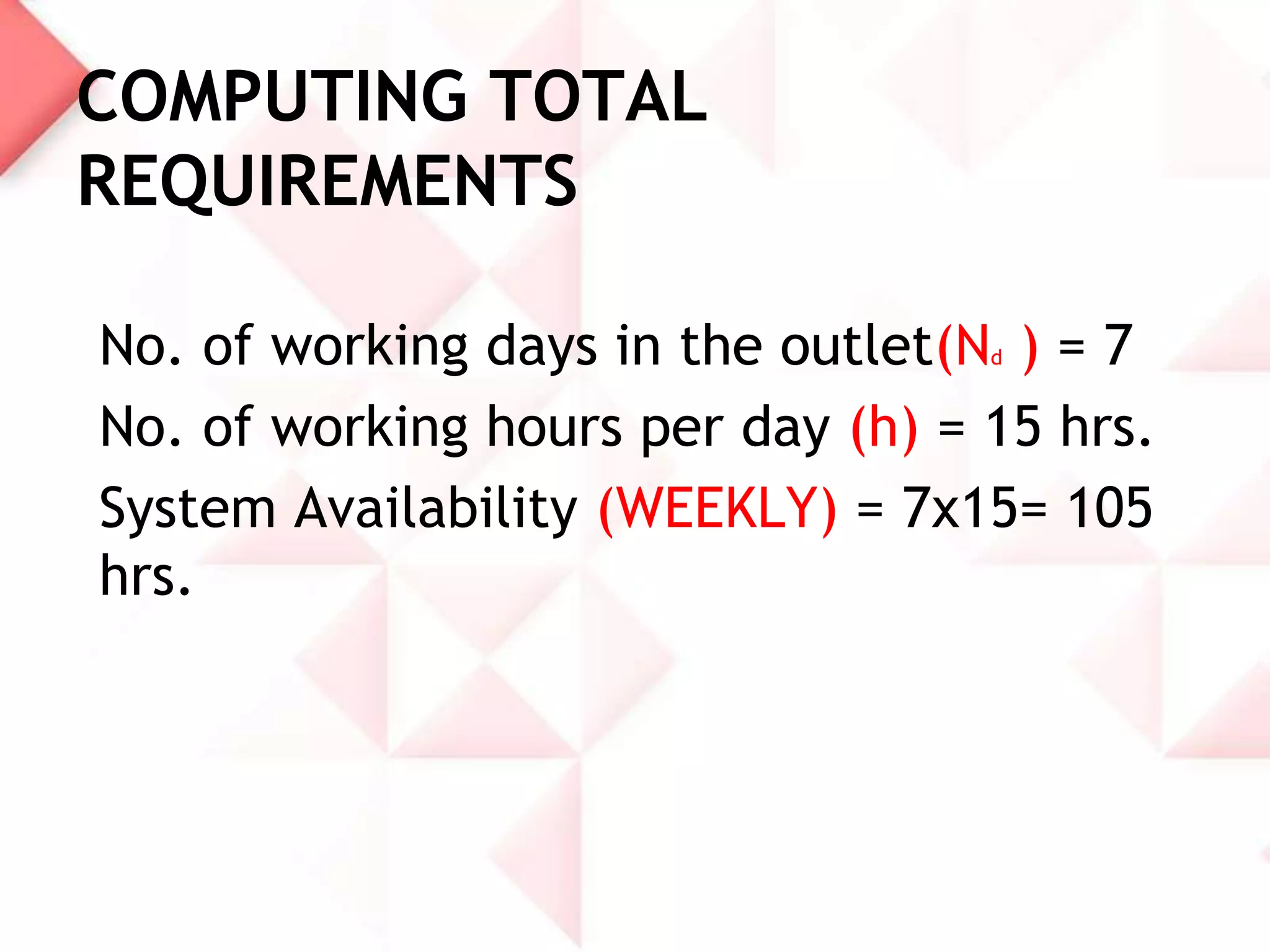
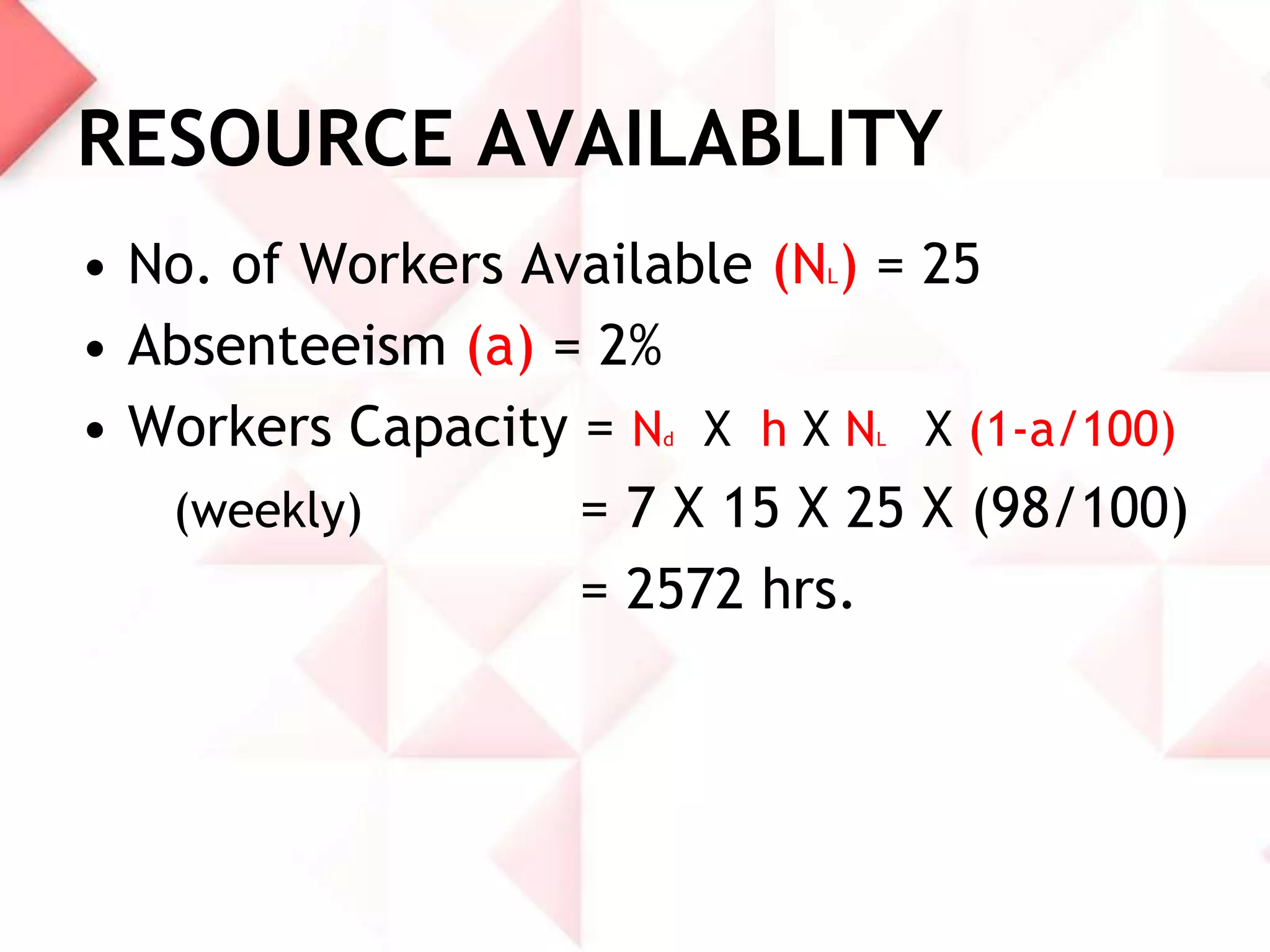
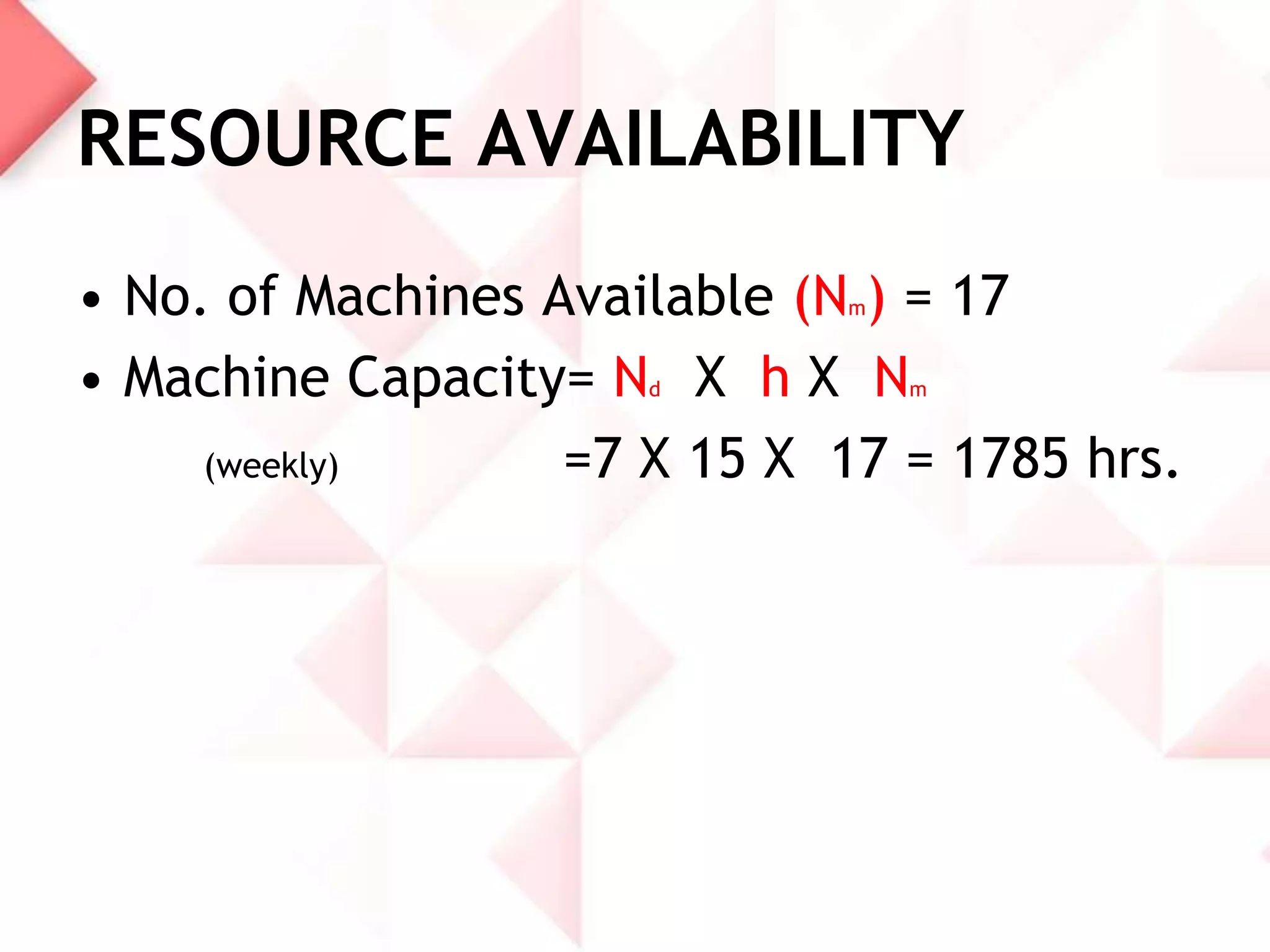
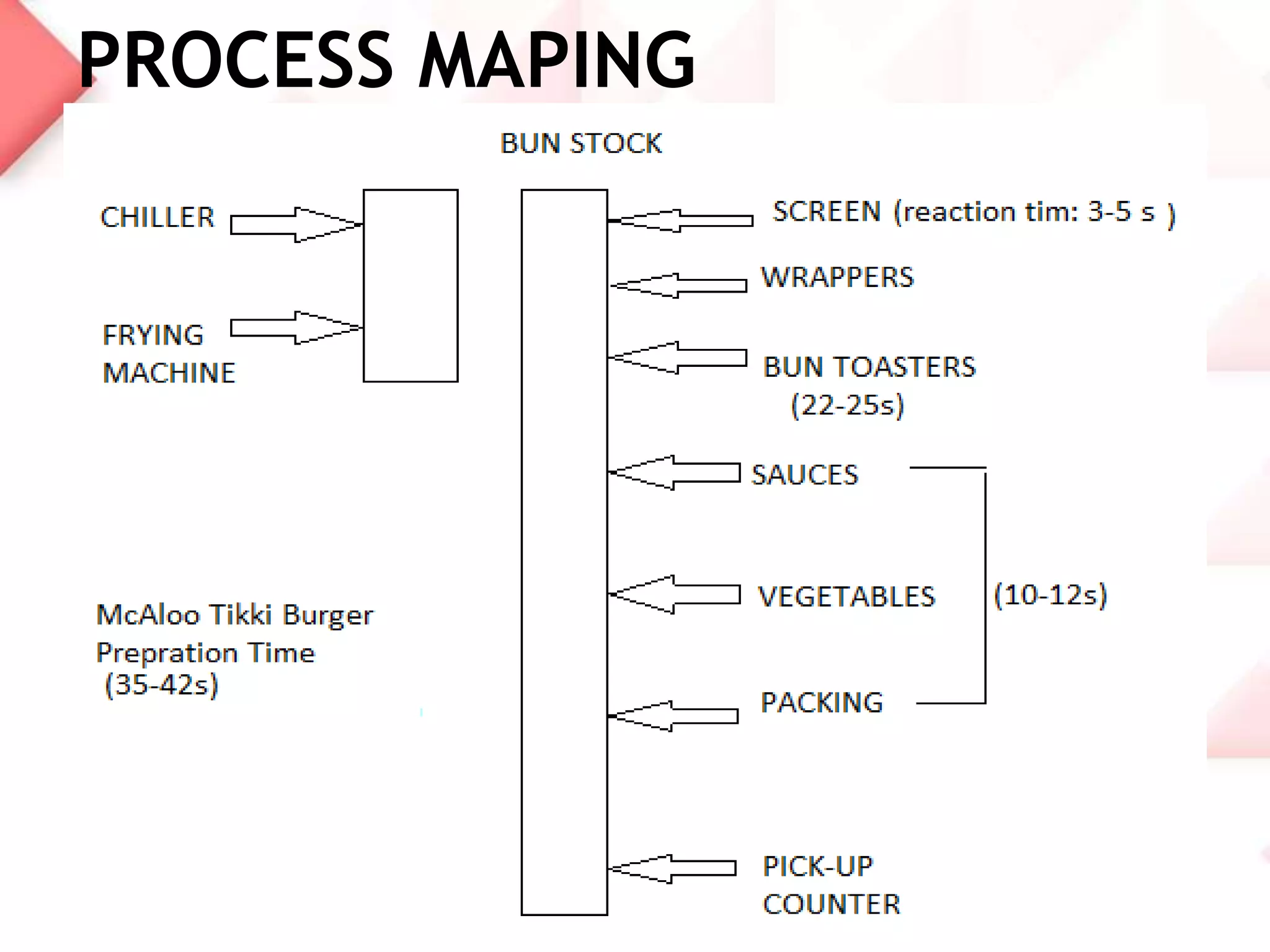
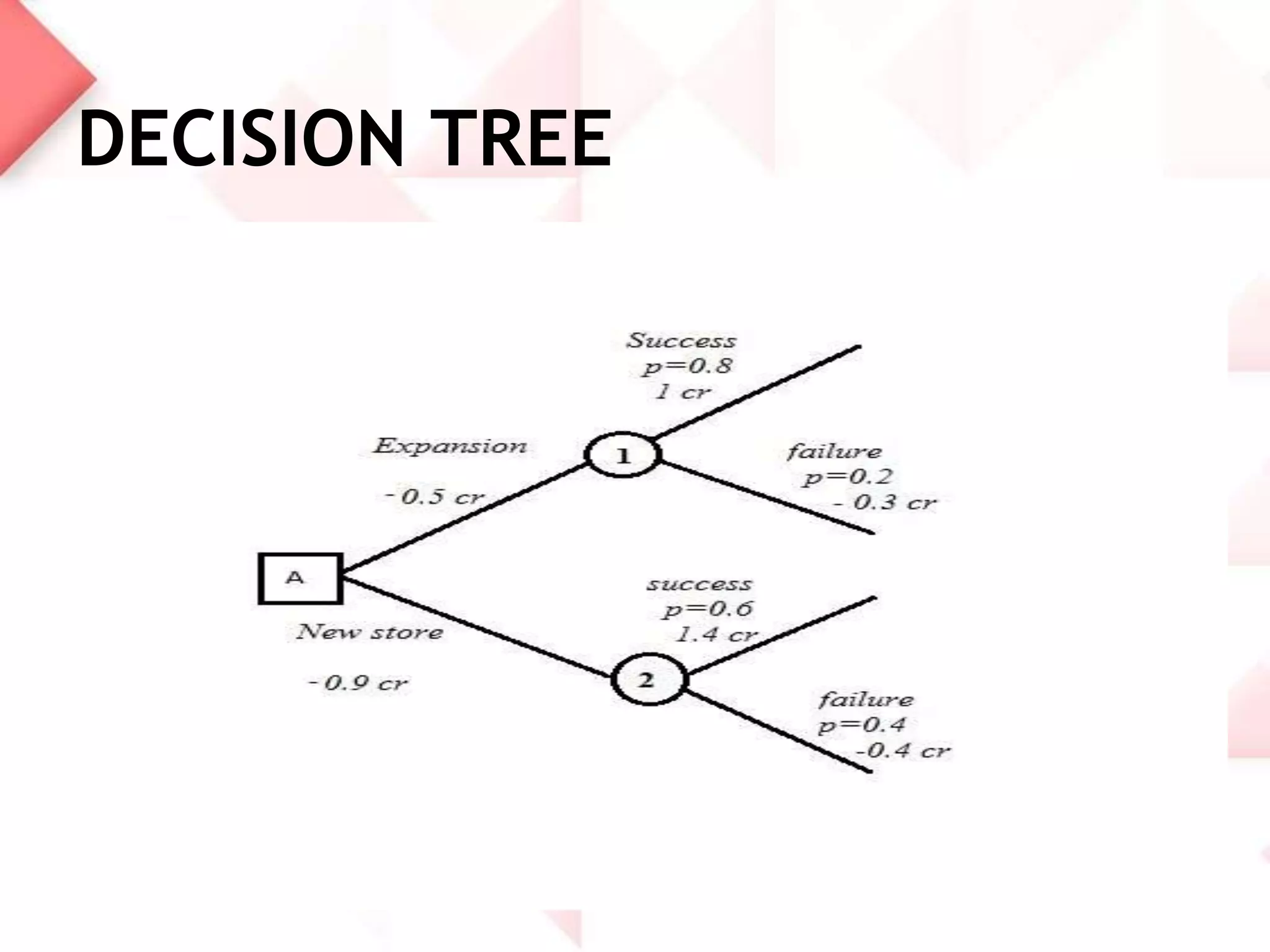
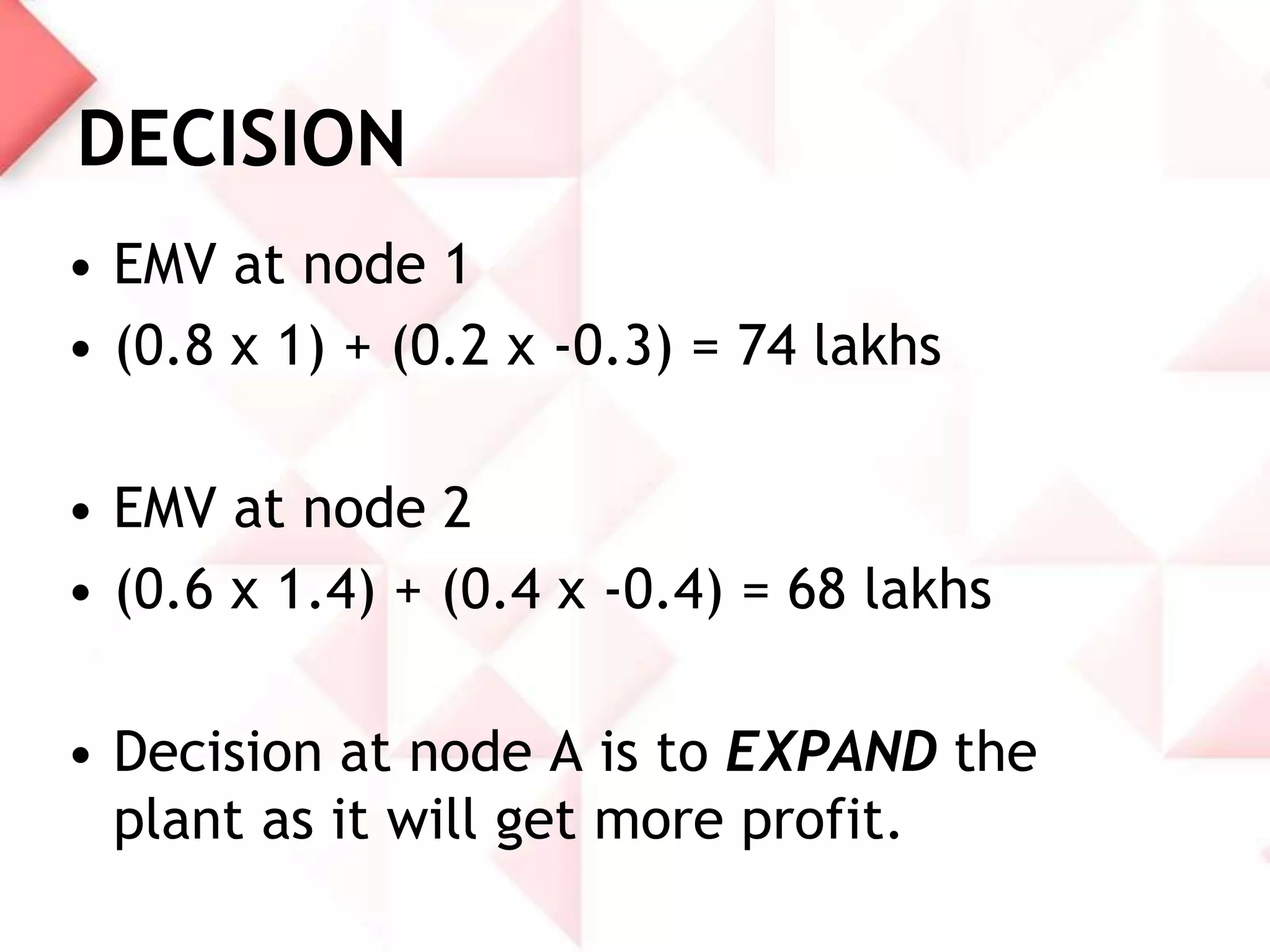
McDonald's capacity planning process involves determining production needs to meet changing demand. Key aspects include estimating total requirements based on factors like product variety and quality, estimating labor and machine needs, and comparing capacity availability to requirements. McDonald's Sonipat location has a capacity strategy of leading demand by keeping a 2-3 day inventory of buns, patties and 15 day inventory of drinks. The document also presents a hypothetical problem comparing expanding the existing location versus opening a new one, with expanding found to have a higher expected monetary value.