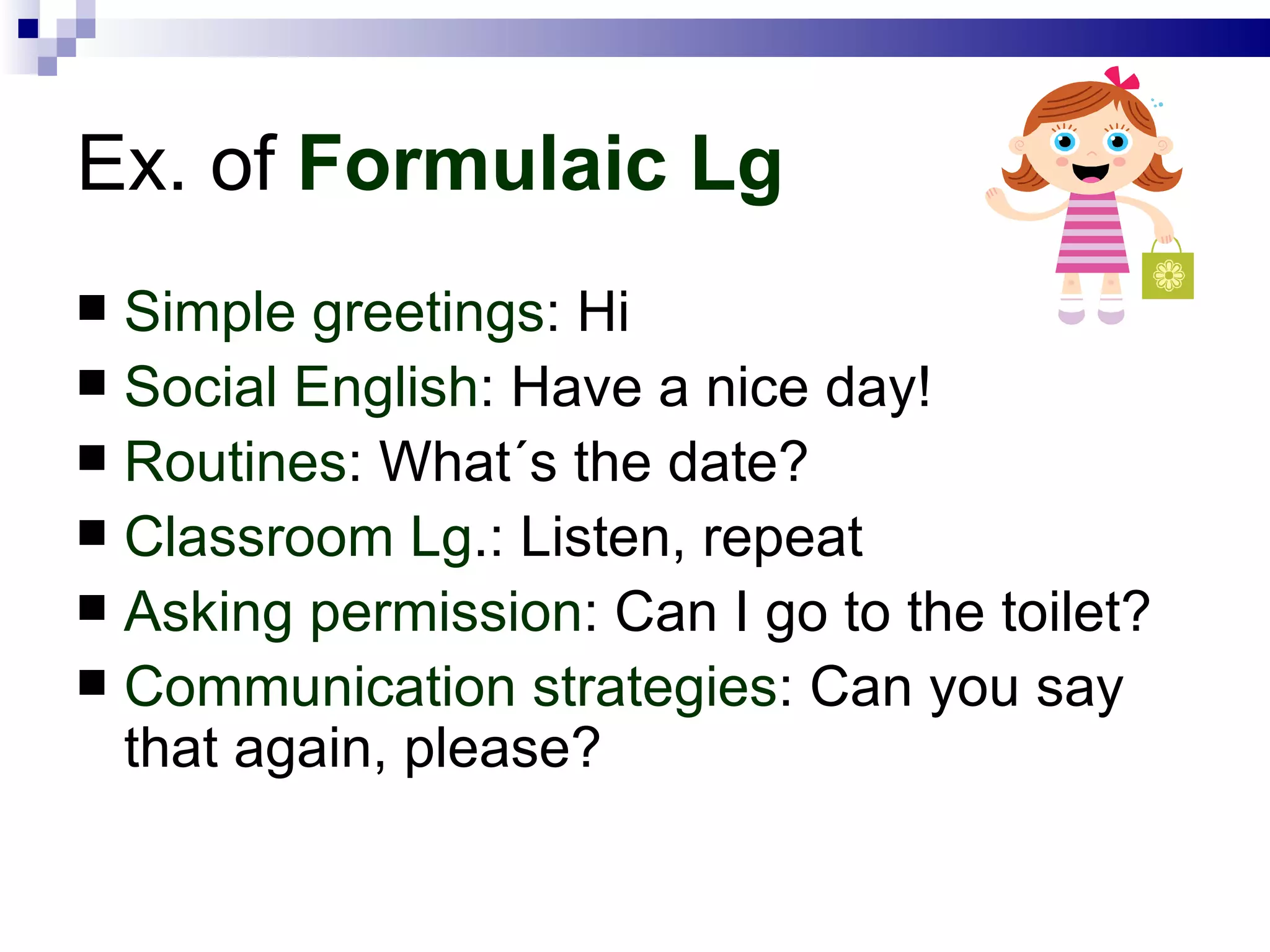
The document discusses expectations and approaches for teaching young learners to speak English. It recommends starting with basic vocabulary, greetings, songs, and rhymes to give students a quick sense of progress. Formulaic language using memorized chunks is important in early stages when spontaneous speech is limited. A variety of speaking activities is needed that involve pairs, groups, and movement, while allowing students to record themselves to focus on pronunciation and building confidence in using English. Teachers should develop different activity types and interaction patterns to maximize talk time and sustain speaking practice.