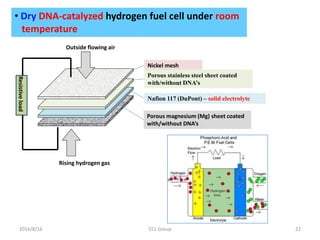
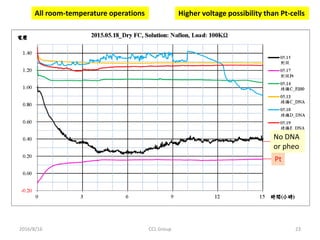
This document discusses the development of a room-temperature hydrogen fuel cell utilizing DNA as a catalyst, highlighting the efficacy of DNA base pairs in hydrogen oxidation. Experimental results indicate that while DNA-catalyzed fuel cells produce significantly lower power density than platinum-catalyzed ones, the costs and sourcing for DNA make it a feasible alternative. The study suggests that these DNA-based systems could mitigate issues related to platinum catalyst poisoning, offering a sustainable and economically viable energy solution.
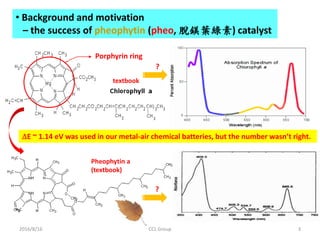



![2016/8/16 CCL Group 13
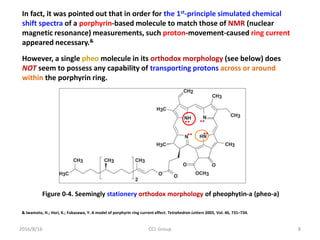
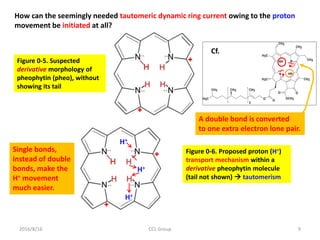
• Similar derivatives within DNA base pairs
Figure 2. DNA double helix [Courtesy of Wikipedia]
Key features for “action zones”:
• Porphyrin ring-like structure
• Presence of N atoms with
2 lone electron pairs
• With N-H away from N atoms
A = adenine (腺嘌呤)
T = thymine (胸腺嘧啶)
G = guanine (鳥嘌呤)
C = cytosine (胞嘧啶)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnafuelcell-160819033639/85/Room-Temperature-DNA-Catalyzed-Hydrogen-Fuel-Cell-13-320.jpg)
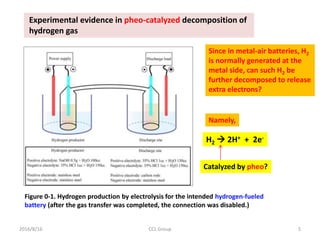
![2016/8/16 CCL Group 14
Figure 3. DNA base pairs A-T and G-C [Courtesy of
Wikipedia], with indication of N atoms associated
with double bonds and subjected to a nearby H
bond, as the action zones for catalytic reactions.
Active zones](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnafuelcell-160819033639/85/Room-Temperature-DNA-Catalyzed-Hydrogen-Fuel-Cell-14-320.jpg)
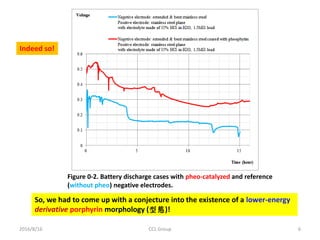
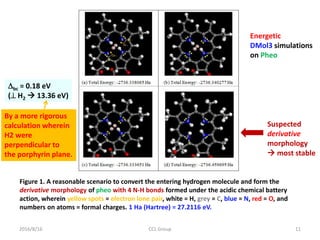
![2016/8/16 CCL Group 16
Figure 4. Proposed simplified
scenario of hydrogen catalytic
decomposition by actions of
derivative morphologies of an A-T
base pair (including deoxyriboses),
with:
(a) one A-T pair approached by a
hydrogen gas molecule
(-1762.678093 Ha).
(b) semi-derivative A-T plus H2 in
perpendicular orientation and
elongated from 0.75 Å to 1.781Å
(-1763.0246307 Ha).
(c) the above situation but with two
electrons further stripped away by
an external electromotive force
(-1762.482609 Ha).
[Difference = 0.54202 Ha = 14.75 eV]
[Needed voltage = 7.4 V]
(d) the full derivative morphology (-
1762.7022339 Ha) with one H atom
drifted from A to T, where 1 Ha =
27.2116 eV.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnafuelcell-160819033639/85/Room-Temperature-DNA-Catalyzed-Hydrogen-Fuel-Cell-16-320.jpg)
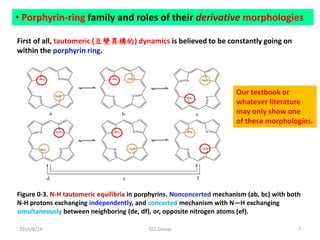
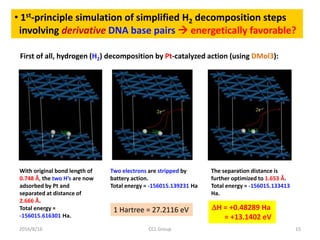
![2016/8/16 CCL Group 17
Figure 5. Proposed simplified
scenario of hydrogen catalytic
decomposition by actions of
derivative morphologies of an G-C
base pair (including deoxyriboses),
with:
(a) one G-C pair approached by a
hydrogen gas molecule
(-1778.740383 Ha).
(b) semi-derivative G-C plus H2 in
perpendicular orientation and
elongated from 0.75 Å to 2.371Å
(-1779.1065312 Ha).
(c) the above situation but with two
electrons further stripped away by
an external electromotive force (of
battery)(-1778.5357000 Ha).
[Difference = 0.57083 Ha = 15.53 eV]
[Needed voltage = 7.8 V]
(d) the full derivative morphology (-
1778.7922571 Ha) with one H atom
drifted from G to C, where 1 Ha =
27.2116 eV.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnafuelcell-160819033639/85/Room-Temperature-DNA-Catalyzed-Hydrogen-Fuel-Cell-17-320.jpg)


![2016/8/16 CCL Group 20
Figure 6. Spectra of
(a) extracted DNA’s from
pork liver- averaged, to
compare with that of
(b) (b) standard reference
[Courtesy of Rittman et
al. (2012)*].
* Rittman M., Hoffmann S. V., Gilroy E.,
Hicks M. R., Finkenstadt B. and Rodger A.,
“Probing the structure of long DNA
molecules in solution using synchrotron
radiation linear dichroism,” Phys. Chem.
Chem. Phys., 14, 353–366 (2012).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnafuelcell-160819033639/85/Room-Temperature-DNA-Catalyzed-Hydrogen-Fuel-Cell-20-320.jpg)
![2016/8/16 CCL Group 21
• Wet DNA-catalyzed chemical battery experiment and result
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0 10 20 30 40
Reference_A
Experimental_A
Reference_B
Experimental_B
Voltage
Time (hr)
Load : 1.5MΩ
Figure 7. Performance of DNA-catalyzed hydrogen fuel cells (with DNA’s from pork liver), as compared with that
of the reference case without DNA’s on the negative electrode. [The constructed chemical battery consisted of a
vase containing an acidic electrolyte (35% HCl : H2O = 1 : 150 in volume), a negative stainless steel (SUS-301)
strip electrode (4 cm wide, 7 cm long, 0.1 mm thick) sealed in a tube filled with hydrogen gas together with 0.2
g of dried DNA’s in the electrolyte, and a graphite positive electrode. The two electrodes were connected
through a resistive load of 1.5 M.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnafuelcell-160819033639/85/Room-Temperature-DNA-Catalyzed-Hydrogen-Fuel-Cell-21-320.jpg)