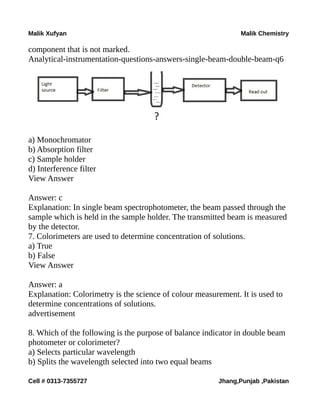
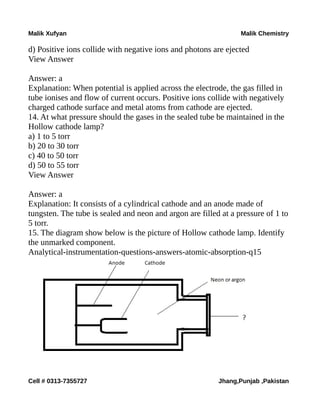
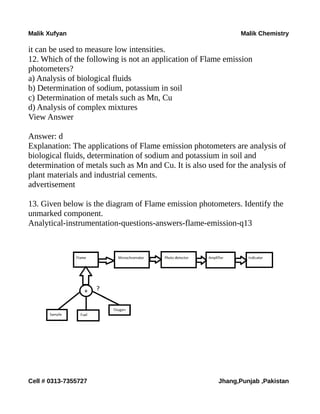
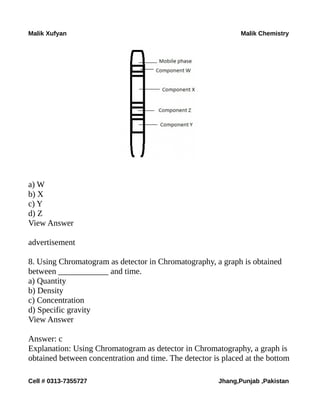
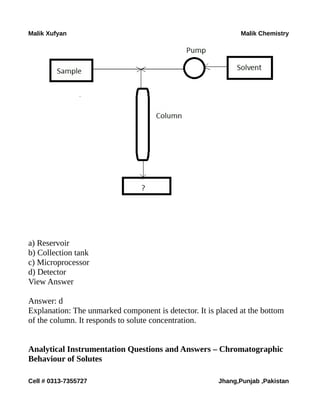
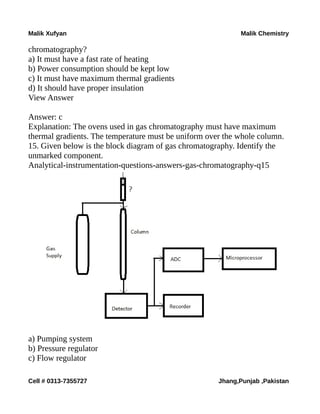
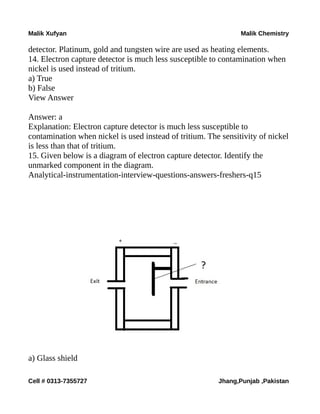
The document is a collection of multiple-choice questions and answers related to analytical chemistry topics, particularly focusing on analytical instrumentation, mass spectrometry, and UV-visible spectroscopy. It includes definitions, key principles like Beer-Lambert's law, and various detectors used in absorption instrumentation. The content is intended for educational purposes to help students prepare for exams in chemistry.