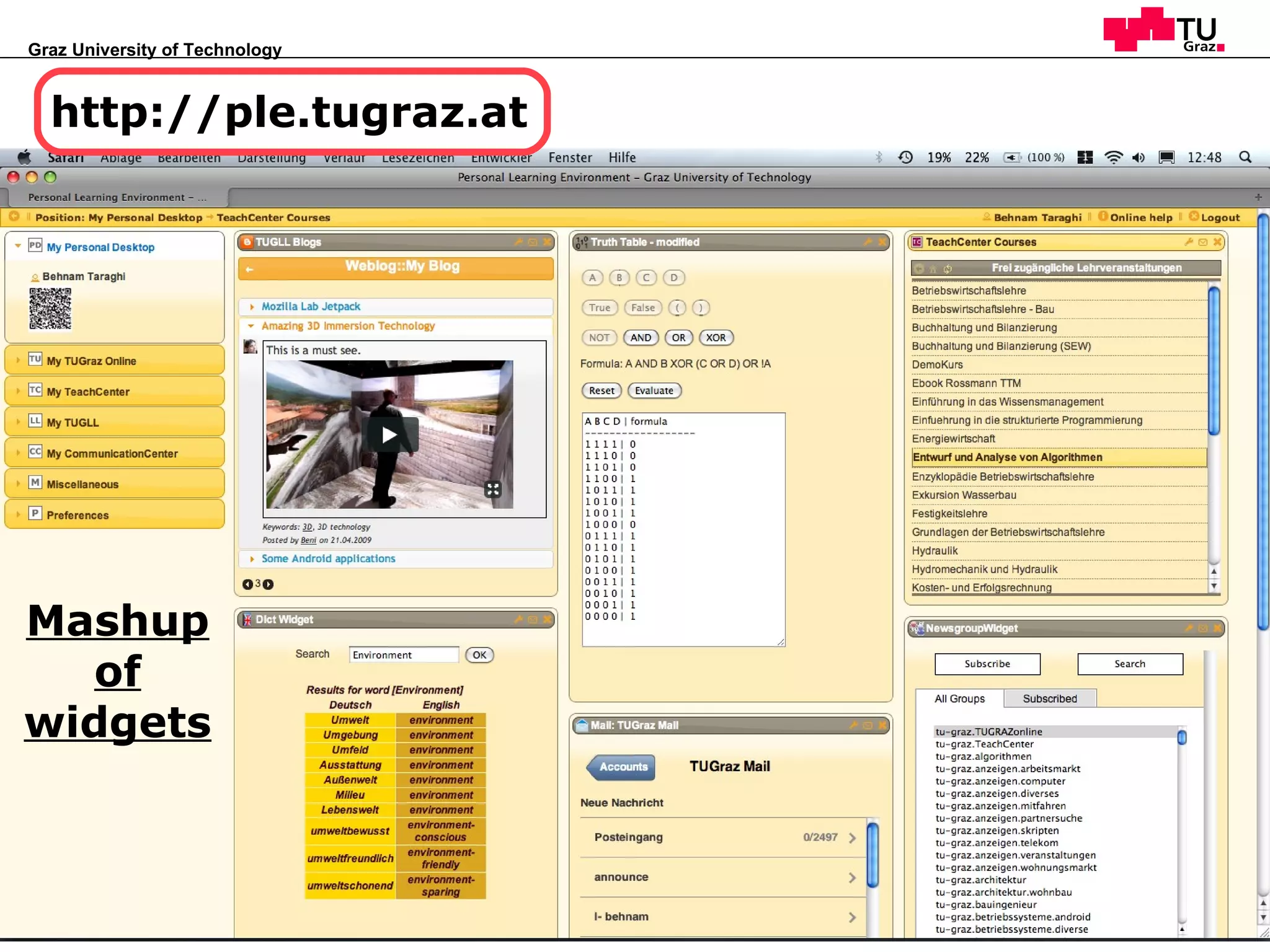
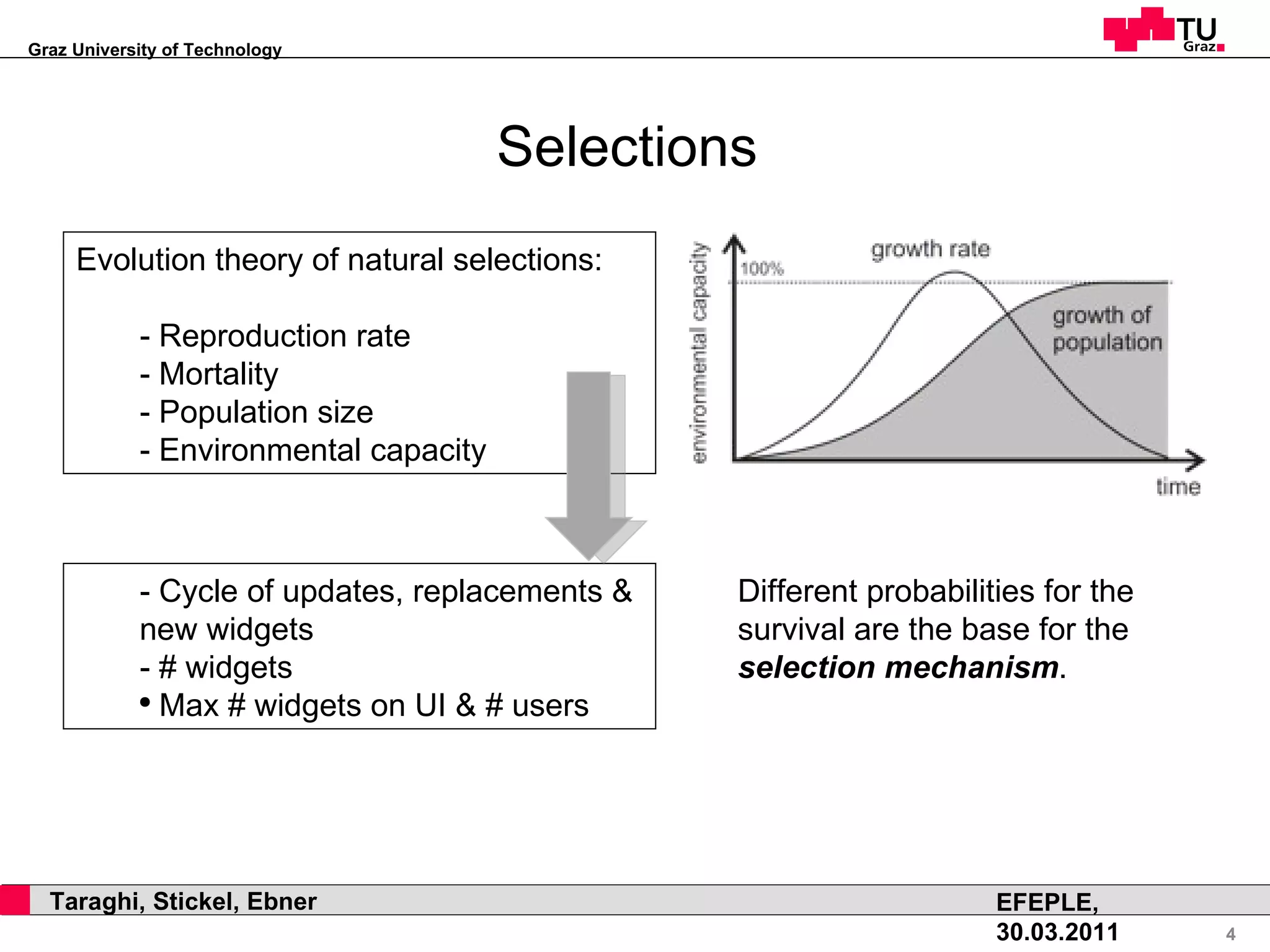
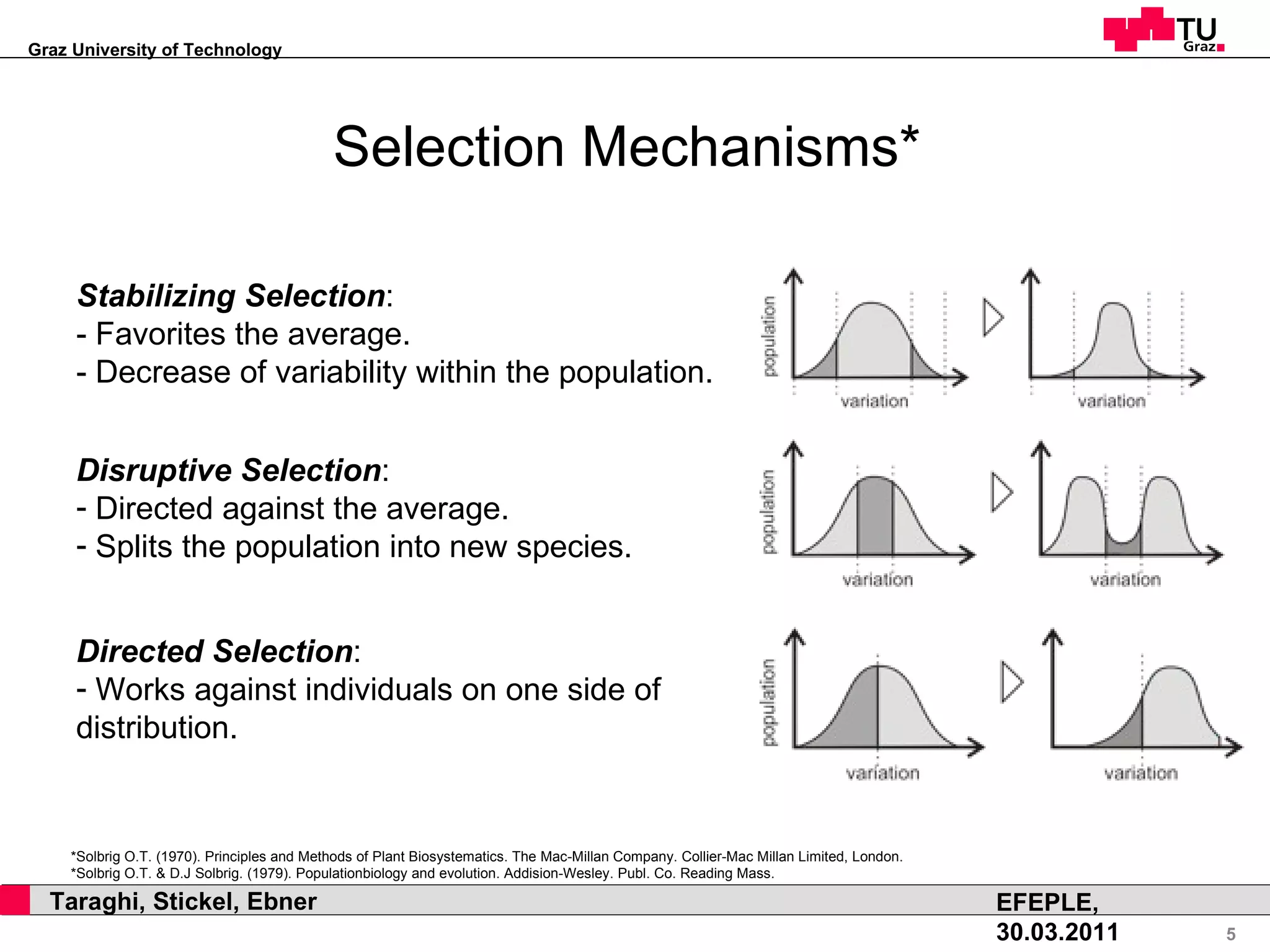
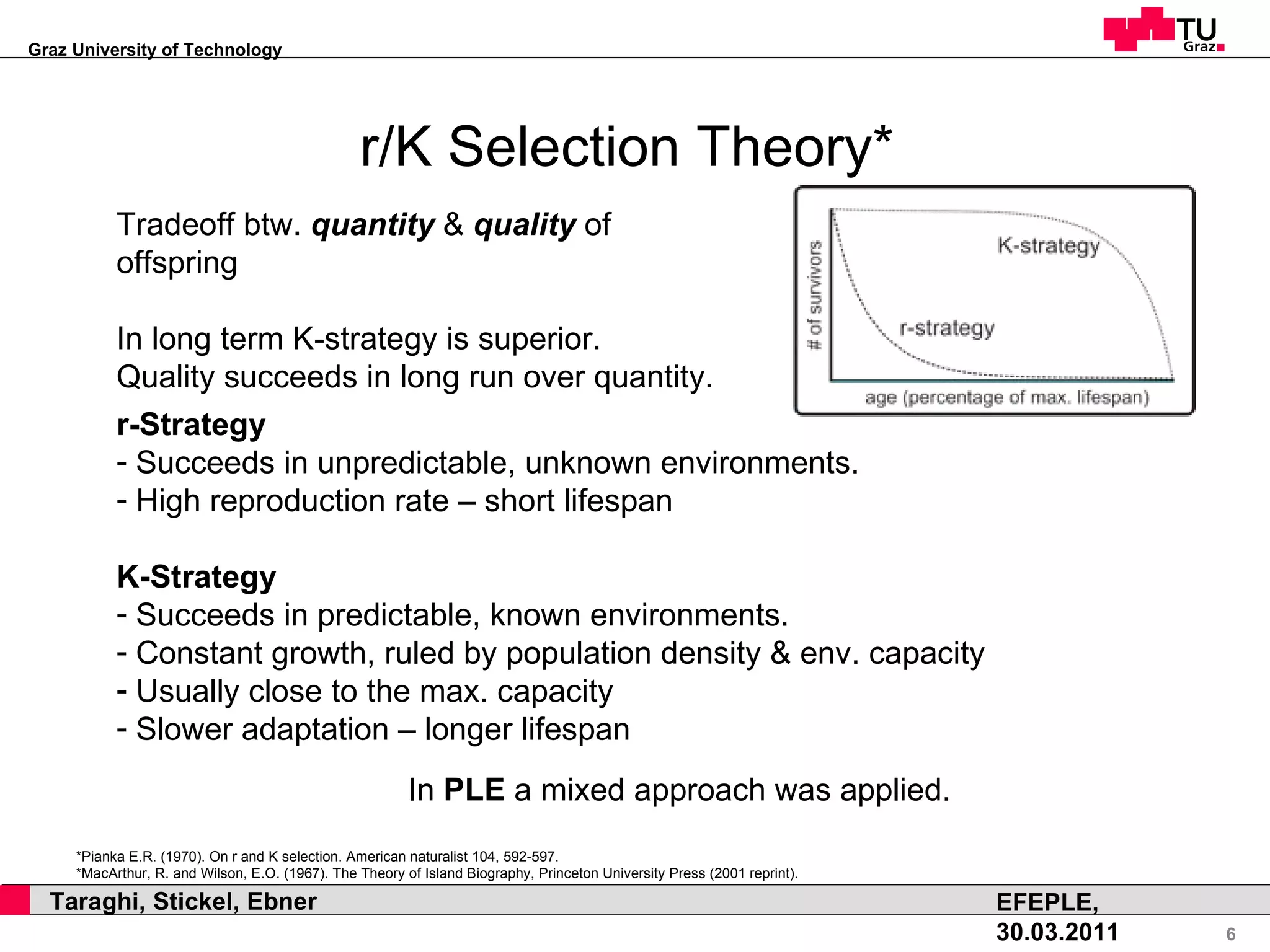
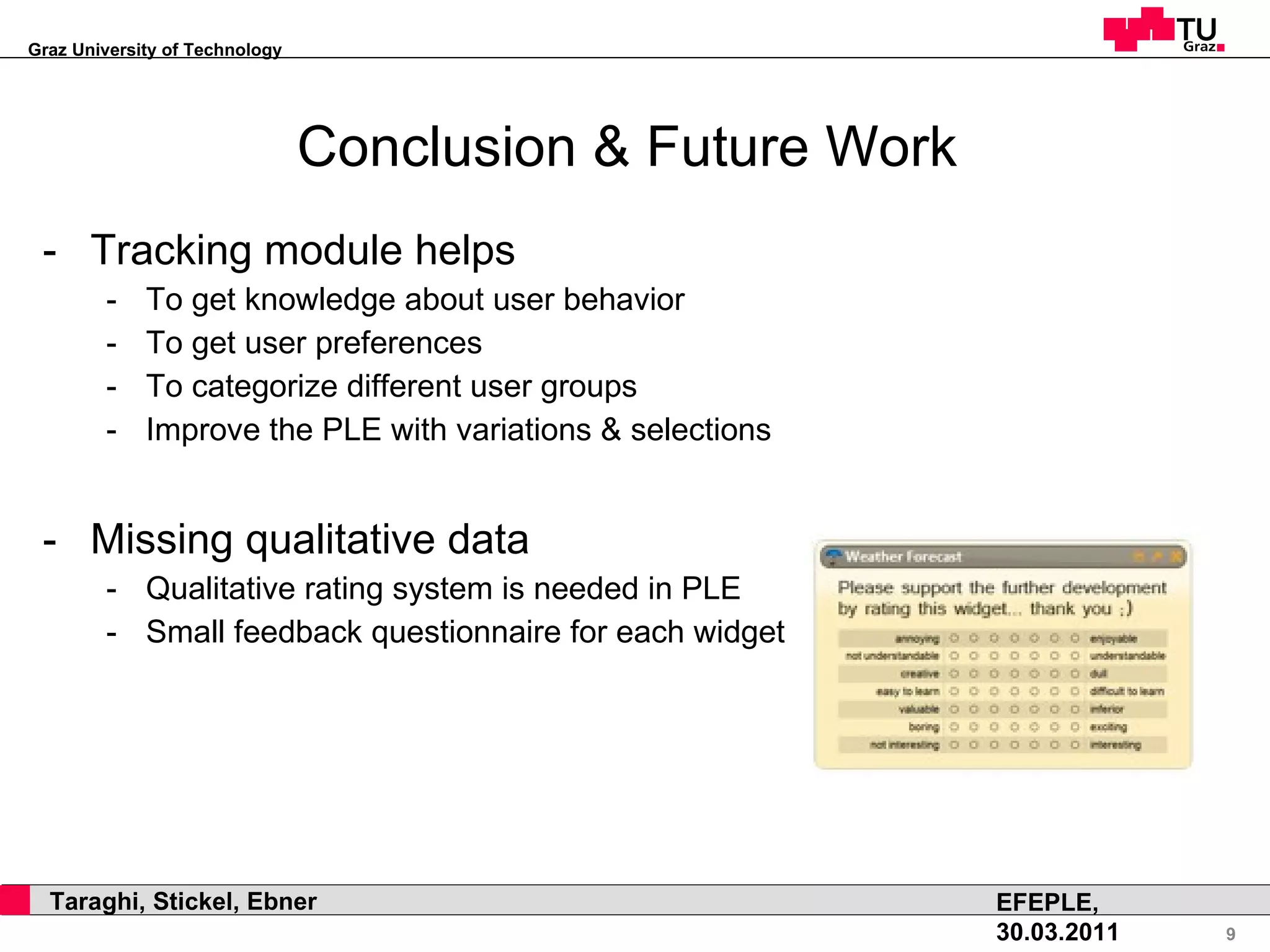
This document discusses how natural selection mechanisms from Darwin's theory of evolution can be applied to improve personal learning environments (PLEs). It describes selection, variation, and tracking user behavior and preferences to evolve widgets through micro and macro evolution. Selection mechanisms like stabilizing, disruptive, and directed selection act on widgets based on factors like usage frequency and activation to improve the most used and activated widgets over time.