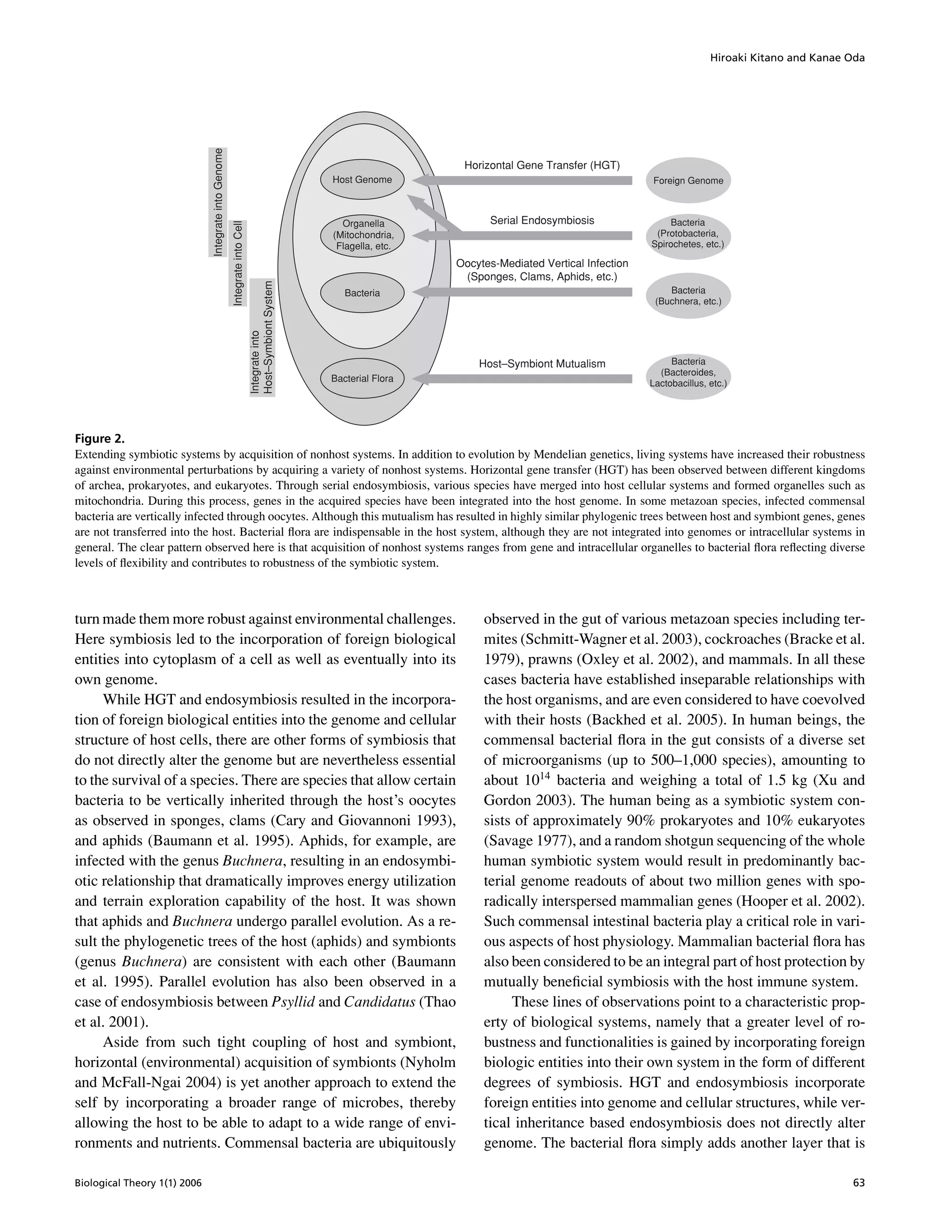
The document discusses the concept of self-extending symbiosis as a mechanism by which biological systems enhance their robustness through evolutionary processes involving incorporation of foreign biological entities. It highlights that symbiotic relationships, particularly with bacteria, contribute to increased adaptability and functionality of organisms against environmental challenges. The paper argues that such symbiotic dynamics are essential for understanding the trade-offs and architectures associated with biological robustness and evolvability.